Kurose, J. F., & Ross, K. W. (2021). Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (8th ed.). Pearson.
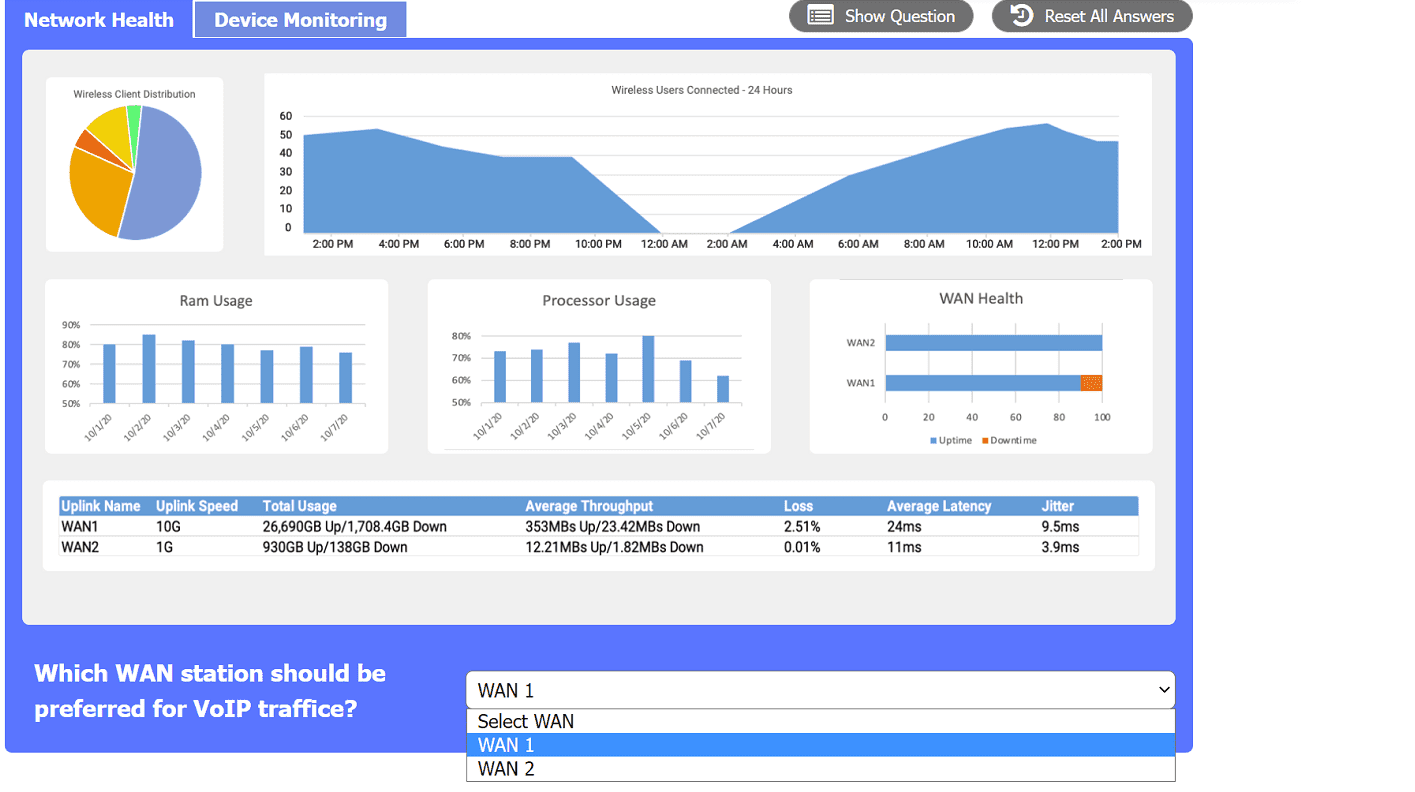
In Chapter 5, Section 5.1 ("Multimedia Networking Applications"), the text details the network requirements for real-time conversational voice/video, emphasizing sensitivity to delays greater than 400ms and the impact of packet loss and jitter on user-perceived quality. This supports the reasoning for selecting WAN 2 based on its lower latency, jitter, and loss metrics for VoIP.
Cisco. (2008). Enterprise QoS Solution Reference Network Design Guide Version 4.0.
In Chapter 2, "QoS Functional and Design Requirements," the document outlines the generally accepted performance targets for voice traffic: one-way latency of 150 ms or less, average jitter of 30 ms or less, and packet loss of 1% or less (pp. 2-5 to 2-6). This official vendor documentation validates the criteria used to evaluate WAN 1 and WAN 2, confirming that WAN 2's metrics (11ms latency, 3.9ms jitter, 0.01% loss) are well within the high-quality thresholds for VoIP.
Stallings, W. (2014). SNMP, SNMPv2, SNMPv3, and RMON 1 and 2 (3rd ed.). Addison-Wesley Professional.
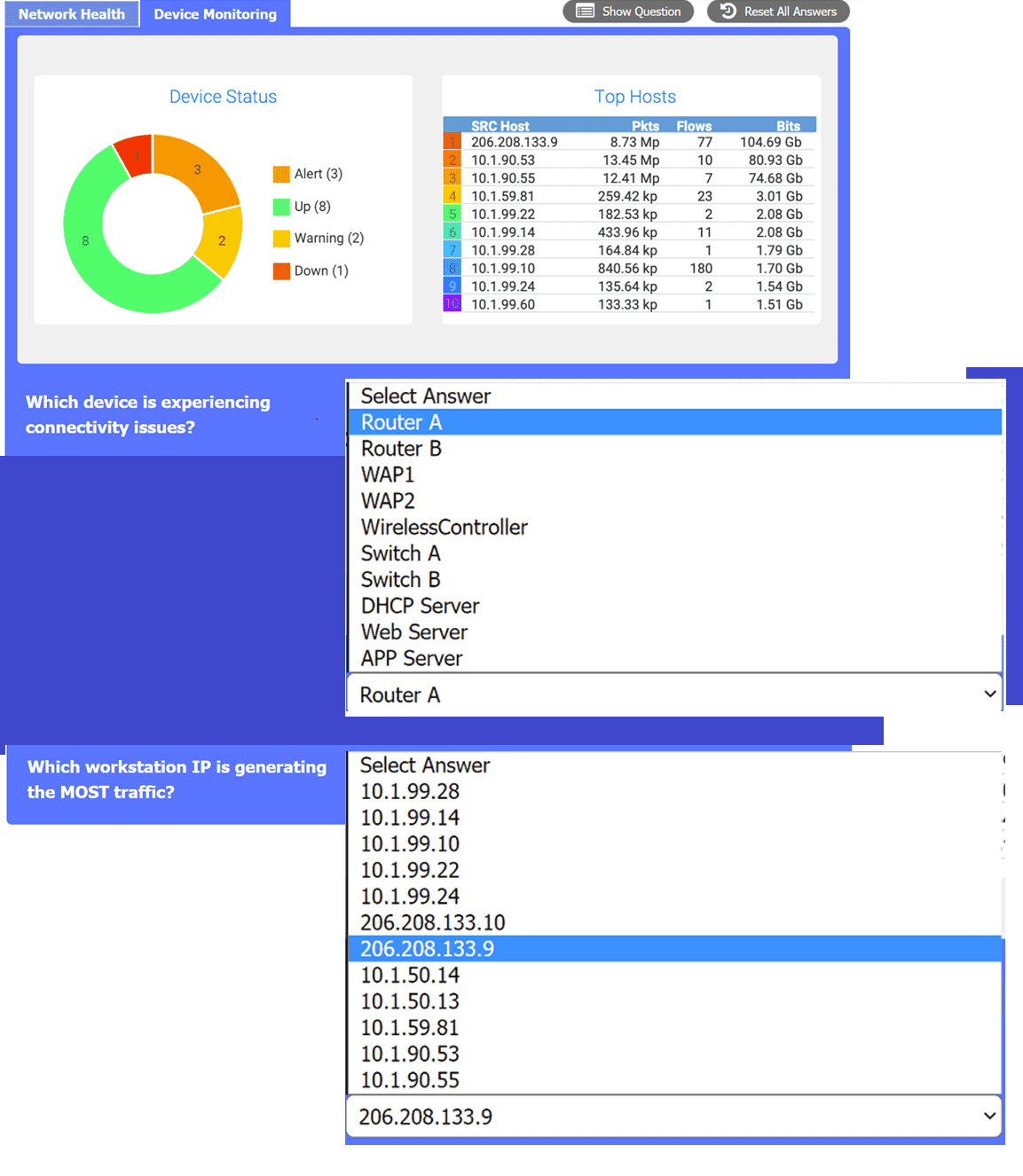
Chapter 6 discusses the IF-MIB (Interface Management Information Base) for SNMP. Specifically, the ifOperStatus object (OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8) defines the operational states of a network interface, including "up" (1), "down" (2), and "testing" (3). The "down" state in the simulation's "Device Status" widget directly corresponds to this standardized management object, indicating a non-functional interface or device.