📖 About this Domain
This domain covers the implementation of core network security controls and architectures. It focuses on securing network access, traffic, and devices using fundamental security technologies like Layer 2 controls, NGFW, and VPNs.
🎓 What You Will Learn
- You will learn to implement Layer 2 security controls like 802.1X, port security, and DHCP snooping to mitigate LAN-based attacks.
- You will learn to configure and verify network security solutions including NGFW, NGIPS, and NetFlow for traffic inspection and visibility.
- You will learn the fundamentals of VPN technologies, including the components of IPsec like IKE, ESP, and AH for secure remote access.
- You will learn to implement infrastructure protection mechanisms such as Control Plane Policing (CoPP) and Unicast RPF to secure network devices.
🛠️ Skills You Will Build
- You will build skills to configure network segmentation and zoning to isolate traffic and reduce the attack surface.
- You will build skills to deploy and manage secure remote access solutions using IPsec and SSL VPNs.
- You will build skills to harden network devices and implement secure management access using protocols like SNMPv3 and SSH.
- You will build skills to analyze network traffic using tools like SPAN, RSPAN, and NetFlow for security monitoring.
💡 Top Tips to Prepare
- Focus on hands-on configuration of Layer 2 security features like DAI and IP Source Guard in a lab environment.
- Master the IPsec framework, including the differences between IKEv1 and IKEv2 phases, and the roles of ESP and AH.
- Understand the traffic flow and policy enforcement on Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW) and Next-Generation IPS (NGIPS).
- Practice interpreting syslog and NetFlow data to identify security events and anomalies on the network.
📖 About this Domain
This domain covers security solutions and concepts for public, private, hybrid, and multicloud environments. It focuses on comparing key cloud security technologies like CASB, CWPP, and CSPM, and integrating security into modern development pipelines.
🎓 What You Will Learn
- Compare cloud security solutions like Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP), and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM).
- Describe security concepts for modern cloud environments, including DevSecOps, CI/CD pipelines, and container security for Docker and Kubernetes.
- Explain security considerations for serverless architectures and the use of cloud-native controls such as security groups and network ACLs.
- Understand secure network design principles for the cloud, including segmentation, microsegmentation, and Zero Trust architecture.
🛠️ Skills You Will Build
- Ability to evaluate and select appropriate security solutions (CASB, CWPP, CSPM) for different cloud deployment models.
- Capability to integrate security practices into DevOps and CI/CD pipelines to implement a DevSecOps model.
- Competence in securing cloud-native applications, including containers, Kubernetes clusters, and serverless functions.
- Proficiency in designing secure cloud networks using principles like microsegmentation, Zero Trust, and encryption.
💡 Top Tips to Prepare
- Focus on the distinct functions and use cases of CASB, CWPP, and CSPM, as comparing them is a key objective.
- Understand the security challenges and solutions specific to containers like Docker and orchestrators like Kubernetes.
- Master cloud-native security controls like security groups and network ACLs, and how they differ from traditional on-premises firewalls.
- Grasp the core tenets of Zero Trust and how it applies to cloud environments, particularly with microsegmentation.
📖 About this Domain
This domain covers foundational security principles, threat landscapes, and cryptographic components. It establishes the core knowledge for understanding network security architectures, threat intelligence, and concepts like Zero Trust and defense-in-depth.
🎓 What You Will Learn
- You will learn to identify common threats, vulnerabilities using CVE/CVSS, and exploits including malware types and threat actor profiles.
- You will learn to compare fundamental security concepts such as risk assessment, threat intelligence feeds, and the principle of least privilege.
- You will learn to describe core cryptography components like PKI, hashing, symmetric vs. asymmetric encryption, and cipher suites.
- You will learn to explain network security architecture principles for on-premises and cloud environments, including segmentation and SIEM/SOAR integration.
🛠️ Skills You Will Build
- You will build the skill to differentiate between threat actors and analyze attack vectors using threat intelligence platforms.
- You will build the skill to apply the Zero Trust security model and principles of least privilege to network design.
- You will build the skill to interpret cryptographic elements in secure communications like SSL/TLS handshakes and SSH.
- You will build the skill to differentiate between North-bound and South-bound APIs in an SDN architecture.
💡 Top Tips to Prepare
- Focus on the practical differences between symmetric and asymmetric encryption, including their specific use cases in protocols.
- Master the key tenets of Zero Trust and how it contrasts with traditional perimeter-based security models.
- Practice interpreting CVSS scores and understanding the vulnerability management lifecycle from discovery to patching.
- Understand the data flow and API functions within a Software-Defined Networking (SDN) architecture for security automation.
📖 About this Domain
This domain covers network access control, visibility, and enforcement using core Cisco security solutions. It emphasizes endpoint compliance and identity-based access through Cisco ISE. It also details network telemetry and threat detection with Stealthwatch and micro-segmentation with Cisco Secure Workload.
🎓 What You Will Learn
- You will learn to configure network access device functionality including 802.1X, MAB, and WebAuth for endpoint authentication.
- You will learn to build and verify authentication and authorization policies within Cisco ISE policy sets.
- You will learn the architecture of Cisco Stealthwatch Enterprise and Stealthwatch Cloud for network traffic analysis using NetFlow.
- You will learn the concepts of application workload protection and policy enforcement using Cisco Secure Workload (formerly Tetration).
🛠️ Skills You Will Build
- You will build skills to implement RADIUS-based network access control for wired and wireless endpoints.
- You will build skills to create granular authorization profiles in Cisco ISE that assign dACLs and SGTs for policy enforcement.
- You will build skills to interpret network telemetry from flow collectors and sensors to identify security incidents.
- You will build skills to describe application dependency mapping and micro-segmentation policy for data center security.
💡 Top Tips to Prepare
- Master the complete 802.1X operational flow, including EAP methods and the role of the supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server.
- Practice configuring Cisco ISE policy sets, focusing on the differentiation between authentication and authorization rules.
- Understand the architectural components of Stealthwatch, including the role of the SMC, Flow Collector, and Flow Sensor.
- Differentiate the primary use cases for ISE, Stealthwatch, and Secure Workload in a zero-trust framework.
📖 About this Domain
This domain covers the security of host systems using advanced endpoint solutions. It details the implementation of Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR). The focus is on threat detection, investigation, and response at the endpoint level.
🎓 What You Will Learn
- You will learn to implement endpoint security controls including antimalware, host intrusion prevention, and application control.
- You will learn to compare persistent agent and agentless endpoint posture assessment solutions for network access.
- You will learn the core features of an EDR solution, such as threat hunting, investigation, and response.
- You will learn to configure and verify Cisco AMP for Endpoints policies, groups, exclusions, and custom detections.
🛠️ Skills You Will Build
- You will build the skill to deploy and manage Cisco AMP for Endpoints, including policy and group creation.
- You will build the skill to interpret endpoint event data like file trajectory, network flow, and parent process information.
- You will build the skill to configure outbreak controls and Indicators of Attack (IOA) for proactive threat mitigation.
- You will build the skill to implement custom detections and exclusions to tune endpoint security performance.
💡 Top Tips to Prepare
- Focus on Cisco AMP for Endpoints configuration, specifically policies for outbreak control and IOA rules.
- Understand the functional differences between EPP for prevention and EDR for detection and response.
- Practice analyzing file trajectory and process lineage within the AMP console to trace malware execution.
- Master the role of asset and patch management as a critical component of endpoint security posture.
📖 About this Domain
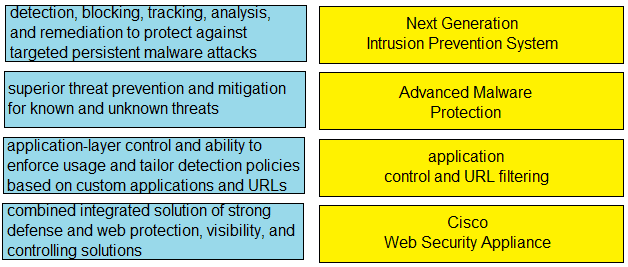
This domain covers the implementation of content security to protect against threats delivered via web and email traffic. It focuses on Cisco's security portfolio, including web proxies, email security gateways, and DNS-layer security. Key technologies include Cisco Secure Web Appliance (WSA), Secure Email Gateway (ESA), and Cisco Umbrella.
🎓 What You Will Learn
- Implement web security using Cisco Secure Web Appliance (WSA) and Secure Web Cloud, including decryption policies and authentication methods.
- Configure Cisco Secure Email Gateway (ESA) and Cloud Email Security (CES) to mitigate threats like spam, malware, and data loss.
- Deploy Cisco Umbrella to provide DNS-layer security and block malicious destinations before a connection is established.
- Utilize application visibility and control (AVC) to enforce granular policies on specific web applications and user activities.
🛠️ Skills You Will Build
- Configuration of traffic redirection methods like Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) and transparent proxy settings.
- Policy creation for SSL/TLS decryption, URL filtering, and application control on a web security appliance.
- Implementation of anti-spam, anti-virus, and outbreak filters on an email security gateway.
- Deployment and policy enforcement within the Cisco Umbrella dashboard for DNS and web security.
💡 Top Tips to Prepare
- Gain hands-on experience with the GUIs of Cisco WSA, ESA, and the Umbrella dashboard to understand policy configuration workflows.
- Master the concepts of traffic redirection, specifically WCCPv2, and explicit proxy forwardings for web security deployments.
- Understand the architectural differences between on-premises solutions versus their cloud-based counterparts like WSA vs. Secure Web Cloud.
- Focus on SSL/TLS decryption policies, as inspecting encrypted traffic is a critical component of modern content security.