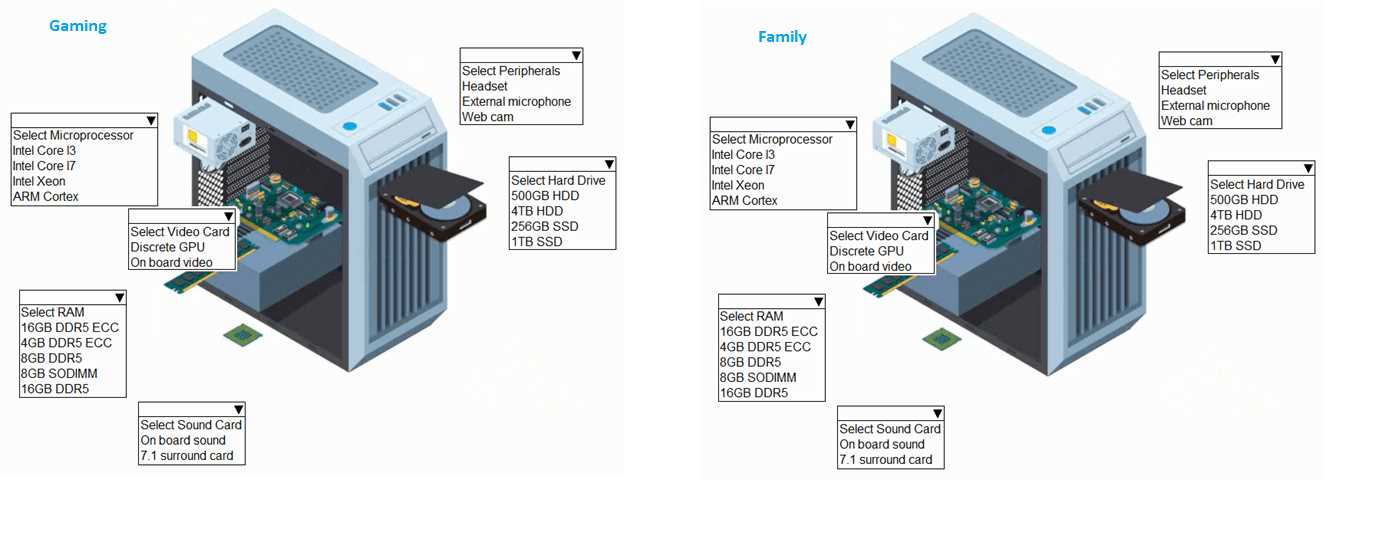
CPU Selection: Intel's product specifications differentiate the Core i7 as a performance-tier processor suitable for demanding tasks like gaming, while the Core i3 is positioned for essential, everyday computing.
Intel Corporation. "Intel® Core™ i7 Processors Product Specifications." Intel ARK. Accessed October 10, 2025.
Intel Corporation. "Intel® Core™ i3 Processors Product Specifications." Intel ARK. Accessed October 10, 2025.
Storage (SSD vs. HDD): Academic studies and foundational computer architecture texts confirm the significant performance advantage of Solid-State Drives (SSDs) over Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) for tasks requiring rapid data access, such as application and game loading. HDDs remain a cost-effective solution for bulk storage where speed is not the primary concern.
Patterson, D. A., & Hennessy, J. L. (2017). Computer Organization and Design RISC-V Edition: The Hardware Software Interface. Morgan Kaufmann. (Section 5.2, "Dependability, Reliability, and Availability" discusses the performance characteristics of different storage media).
Agarwal, S., & Garg, D. (2016). "A review on solid state drives (SSDs): The successor of hard disk drives." In 2016 International Conference on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA). IEEE. (DOI: 10.1109/CCAA.2016.7813735).
Graphics (Discrete vs. Integrated): A discrete GPU is a specialized processor designed for massively parallel computations, making it essential for rendering complex 3D graphics in real-time (i.e., gaming). Integrated graphics, which share resources with the CPU, are designed for basic display output and are sufficient for standard desktop applications but not for performance-intensive gaming.
Kirk, D. B., & Hwu, W. W. (2016). Programming Massively Parallel Processors: A Hands-on Approach. Morgan Kaufmann. (Chapter 1 provides an overview of the evolution from CPU-centric to GPU-centric computing for graphics).