Q: 18
HOTSPOT A technician is diagnosing several device issues reported by employees. INSTRUCTIONS Click on each device to review the issue. Then select the appropriate issue and solution from the drop-down menu. Each option may be used more than once. 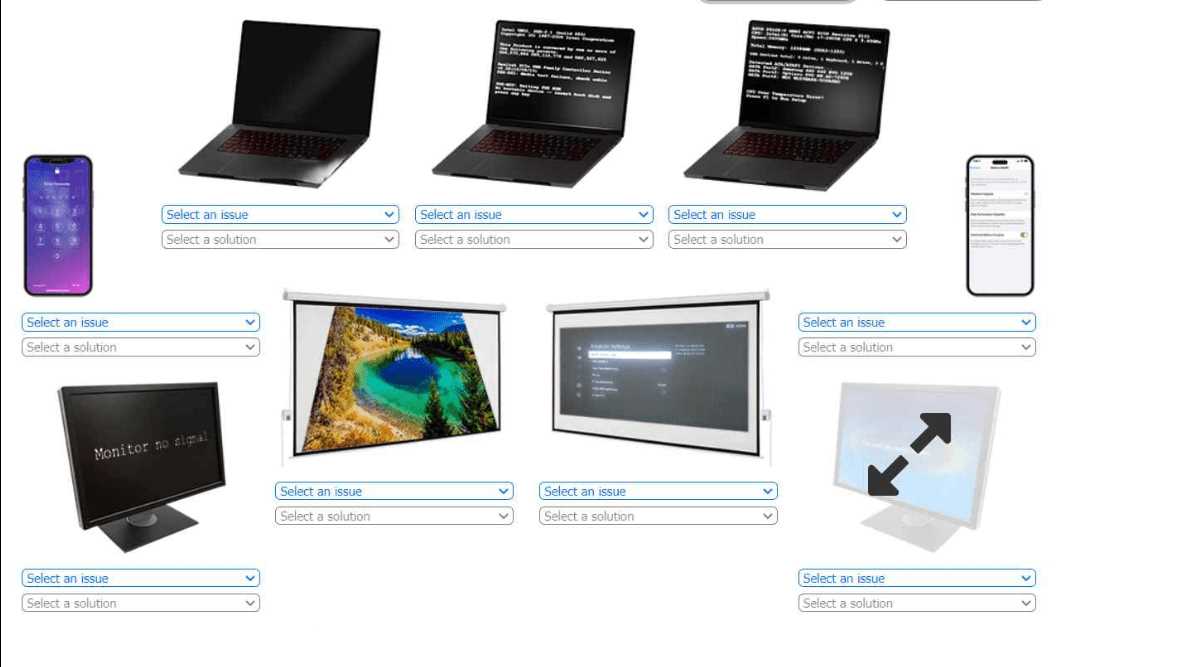
Your Answer
Discussion
Had something like this in a mock, definitely swollen battery for the bulging laptop. Boot partition issue needs BIOS config fix too.
Yeah, swollen battery for the laptop with bulging chassis. Needs replacement, no workaround.
Is the bulging chassis always a battery problem or could it ever be the motherboard?
Swollen battery for the bulging laptop. Pretty common, gotta swap it out, can't fix that. The other ones line up too, like keystoning on projectors and input/source mixup for "no signal" monitors. Seen similar stuff come up on practice. Let me know if anyone got different choices.
Swollen battery is the real issue for the bulging chassis, not a motherboard fault like some practice tests suggest.
If the instructions said "first step" instead of "solution," would that change what you pick for the POST issues or fuzzy display?
Can the official guide or labs help clarify POST freeze issues for laptops? Not sure if it's always a boot partition problem.
Be respectful. No spam.


