Cybersecurity is a field that’s been blowing up in recent years. With every company relying on digital systems and online platforms, securing those systems has become a top priority. It’s not just tech companies, either. Banks, healthcare providers, schools, governments; they’re all hunting for skilled pros who can keep them safe from hackers and data thieves.
Cybercrime’s not slowing down anytime soon; in fact, it’s expected to cost businesses trillions in the coming years. That’s why companies are shelling out big bucks to hire cybersecurity experts.
Let’s discuss how you can secure a Cybersecurity career path. We will discuss all the roles, skills, and certifications you might need to make a breakthrough for yourself.
Executive Summary
| Certification | Demand | Education/Prerequisites | Average Salary (USD) | Career Path | Key Roles |
| CompTIA Security+ | High demand for entry-level roles in IT security. | No prerequisites; great for beginners. | $70,000 – $85,000 | Entry-level; transition to roles like Security Analyst or Engineer. | Junior Security Analyst, IT Support, Cybersecurity Analyst. |
| Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) | Growing demand due to increasing focus on ethical hacking. | Basic IT knowledge; suitable for those with some experience in IT. | $90,000 – $110,000 | Ethical Hacker, Penetration Tester, Vulnerability Assessor. | Penetration Tester, Ethical Hacker, Cybersecurity Consultant. |
| CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) | Widely recognized for senior-level and management roles. | Requires 5+ years of experience in two or more security domains. | $120,000 – $150,000 | Security Architect, Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). | Security Architect, Information Systems Manager, CISO. |
| CISM (Certified Information Security Manager) | Valued for managing and assessing information risks. | Management-level experience in information security recommended. | $115,000 – $140,000 | Information Security Manager, Risk Manager, Consultant. | Risk Assessor, Information Security Manager, Consultant. |
| GIAC (Global Information Assurance Certification) | Demand for specialized skills in forensics, penetration testing, and more. | Varies by specialization; often requires prior experience. | $100,000 – $130,000 | Specialist roles like Malware Analyst, Incident Responder. | Forensics Analyst, Pen Tester, Security Operations Specialist. |
| CCSP (Certified Cloud Security Professional) | Highly sought after for securing cloud environments. | Prior experience with cloud platforms is helpful. | $110,000 – $140,000 | Cloud Security Architect, Cloud Engineer. | Cloud Security Architect, Cloud Compliance Analyst. |
| GIAC IoT Security Essentials | Emerging demand as IoT devices increase security risks. | General knowledge of IoT systems is useful. | $95,000 – $120,000 | IoT Security Specialist, Network Security Engineer. | IoT Security Engineer, Risk Analyst, Device Security Specialist. |
What Does a Cybersecurity Career Look Like?
Getting into cybersecurity isn’t like walking a straight line. It’s more of a winding path with plenty of options depending on your interests and skills. It’s a field that’s full of roles for problem-solvers, tech enthusiasts, and creative thinkers who want to make systems safer.
Whether you’re just starting out or you’re aiming to climb the ladder to a top-tier role, there’s something for everyone.
If you’re curious about the toughest exams in this field, check out our detailed guide on the hardest cybersecurity certifications that demand rigorous preparation and in-depth expertise.
Mapping the Cybersecurity Career Path: From Entry-Level to Expert
Your journey in cybersecurity might start small, but the opportunities grow fast. Entry-level gigs like IT Support or Junior Security Analyst are a great way to get your feet wet. These jobs teach you how networks work, how to spot weak spots, and what kinds of threats are out there. Learn more about certifications that are best to kickstart your Cybersecurity journey here
As you gain experience, you can move into more specialized roles like Penetration Tester, Security Engineer, or Malware Analyst. These positions demand more technical know-how, but they also come with bigger paychecks and cooler projects.
For those who stick with it, senior-level roles like Security Architect or CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) are the ultimate goals. Certifications act as milestones along your career journey, guiding you from entry-level roles to senior positions. Our breakdown of the cybersecurity certifications worth pursuing in 2026 highlights which ones to prioritize at each stage.
These jobs are about strategy, leadership, and making decisions that can protect entire organizations.
Popular Job Roles in Cybersecurity and What They Involve
The beauty of a cybersecurity career is the variety. You’re not locked into one role, and there’s plenty of room to explore. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most in-demand positions:
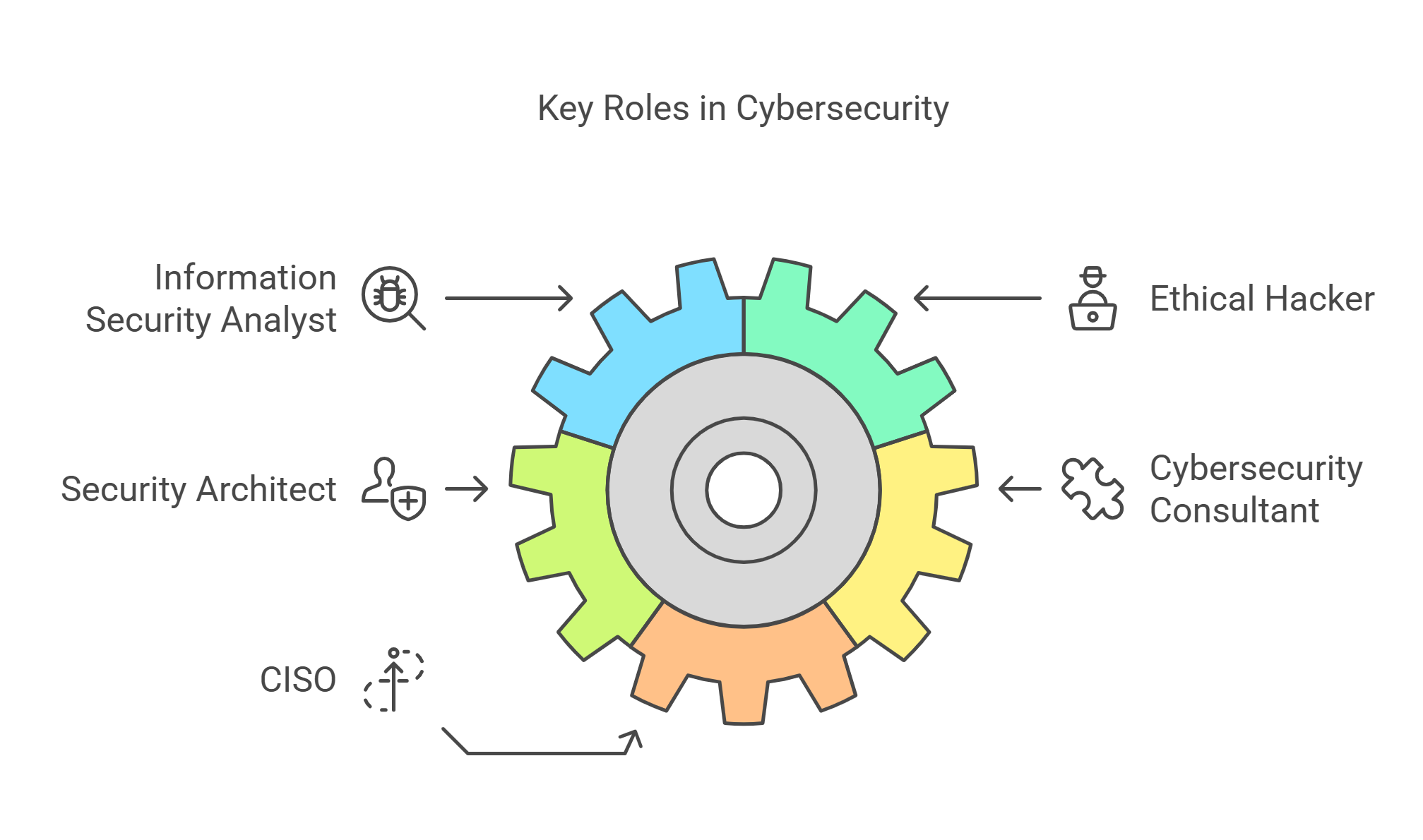
Information Security Analyst: The Backbone of Cyber Defense
This is often where people start in cybersecurity, and for a good reason. InfoSec analysts are the first line of defense. They monitor systems for breaches, install security measures, and create reports on threats. It’s a job that requires a keen eye and a sense of responsibility.
You’ll spend a lot of time scanning for vulnerabilities, patching software, and responding to incidents. It’s not flashy work, but it’s crucial. Companies rely on analysts to keep their systems running smoothly and their data safe.
Ethical Hacker: Breaking Systems to Strengthen Them
If you’ve ever dreamed of being a hacker but don’t want to end up in jail, this is the job for you. Ethical hackers, or penetration testers, get paid to think like the bad guys. Their goal? Find holes in a system before the actual hackers do.
This job involves running simulated attacks, testing firewalls, and digging deep into networks to uncover flaws. It’s hands-on, exciting, and perfect for people who love solving puzzles. Plus, it’s one of the most satisfying roles because you’re directly preventing disasters.
Security Architect: Building Strong Digital Fortresses
Think of a Security Architect as the person who designs the blueprint for a company’s defenses. They don’t just fix problems; they create systems that make attacks nearly impossible. This role is about building layers of protection, from firewalls to encryption protocols, and making sure everything works together.
This is a job for experienced pros who understand both tech and business. Architects work closely with leadership teams to design security plans that align with company goals. It’s challenging, but it’s a role that makes a massive impact.
To step into advanced cybersecurity roles like Security Architect, a solid understanding of threat analysis and incident response is essential. Certifications that focus on these areas, such as the Comprehensive Guide to the Analyst+ CS0-003 Certification, can be a valuable stepping stone in building the expertise required for designing robust security frameworks.
Cybersecurity Consultant: Solving Security Puzzles for Businesses
Consultants are like cybersecurity freelancers. They work with multiple companies, analyzing their systems, identifying risks, and offering solutions. It’s a flexible role that lets you tackle a variety of projects, from small businesses to large corporations. Understanding the key aspects of cybersecurity certifications can be crucial for consultants, especially when aiming to build a strong foundation in the field.
The job requires a mix of technical expertise and people skills. You need to communicate complex ideas in simple terms and build trust with clients. If you like variety and don’t mind traveling, consulting might be your thing.
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): The Strategic Leader
This is the top of the ladder in cybersecurity careers. CISOs don’t just oversee security teams, they shape an organization’s entire security strategy. They decide where to invest, how to respond to threats, and how to stay ahead of attackers.
This role demands years of experience and a deep understanding of both tech and leadership. You’ll need to manage teams, present plans to executives, and stay updated on the latest threats. It’s a high-pressure job, but the financial and professional rewards are worth it.
Skills You will Need to Succeed in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity isn’t just about fancy tools and tech jargon; it’s about skills, real, hands-on abilities that help you protect systems, solve problems, and outsmart hackers. From technical know-how to critical thinking, having the right skills can make or break your career.
Let’s dig into what you’ll actually need to thrive in this field.
Mastering Network Security and System Vulnerabilities
At its core, cybersecurity is about understanding how networks operate and where they’re weakest. You need to know how data flows, what keeps systems running, and where things can go wrong. That means learning about firewalls, VPNs, and encryption methods.
It’s also about spotting vulnerabilities, those little cracks hackers love to exploit. Tools like Wireshark or Nessus can help, but you also need the instincts to see what others miss. Think like an attacker: if you wanted to break into a system, how would you do it? Knowing the answer makes you better at stopping them.
Gaining Proficiency in Penetration Testing and Incident Response
Pen testing, or ethical hacking, is where things get exciting. It’s like being a digital detective, finding weak points in a system before the bad guys do. Tools like Metasploit, Burp Suite, and Kali Linux are your best friends here. But pen testing isn’t just about running tools—it’s about creativity and persistence.
Then there’s incident response, which is all about staying calm when things go wrong. A breach can feel like chaos, but your job is to figure out what happened, how it happened, and how to fix it. This is where experience and a cool head come into play.
Coding and Scripting: How Much Is Necessary?
Let’s clear something up—no, you don’t have to be a coding wizard to work in cybersecurity. But knowing a bit of Python, Bash, or PowerShell can make your life easier. Scripting helps automate repetitive tasks and can be a lifesaver when you’re analyzing logs or setting up defenses.
Think of coding as a tool in your kit. You don’t have to master it, but being comfortable enough to write a quick script or tweak existing code can save time and give you an edge.
Beginners often wonder where to start, and our list of the easiest cybersecurity certifications can help you identify the most accessible options to kickstart your journey.
Certifications That Open Doors in Cybersecurity
Getting a foot in the door of cybersecurity can be tough, especially when companies are looking for people who know their stuff. That’s where certs come in. They’re like a badge that shows you’ve got the skills and knowledge to handle real-world problems. Whether you’re just starting or aiming for the top, earning the right certs can give your career a serious boost.
Cybersecurity is one of those fields where things change fast, and certs help you keep up.
Different certs fit different stages of your career. Some are perfect for beginners trying to break in, while others are built for seasoned pros looking to level up.
Entry-Level Certifications: CompTIA Security+, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
If you’re just starting, the CompTIA Security+ is often your best bet. It’s like the gateway cert for cybersecurity. It covers the basics—network security, threats, vulnerabilities, and risk management. What’s great is that it’s vendor-neutral, so the knowledge applies to any system or company.
Then there’s the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH). This one’s for people who want to learn how hackers think. It teaches you how to break into systems ethically, find vulnerabilities, and fix them before the bad guys show up. It’s hands-on and a lot of fun for those who like to tinker.
For those looking to break into cybersecurity and establish a strong foundation, earning relevant certifications can be a game-changer. The SY0-701 certification Guide is an excellent starting point for aspiring security professionals, providing the essential knowledge and skills needed for roles like Information Security Analyst
Advanced Certifications: CISSP, CISM, and GIAC
When you’ve got some experience under your belt, it’s time to aim higher. The CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) is the gold standard for cybersecurity pros. It’s for people who want to move into leadership roles, as it focuses on designing and managing security programs. But heads up, it’s not an easy cert to earn. The exam is tough, and you need years of experience just to qualify. Learn more about CISSP Exam here: https://certempire.com/cissp-exam-guide/
The CISM (Certified Information Security Manager) is another heavy hitter, but it’s more focused on managing and assessing risks than technical know-how. If you’re aiming to become a manager or consultant, this one’s for you.
For those who love diving deep into specific areas, there’s GIAC (Global Information Assurance Certification). GIAC offers a range of certs, from penetration testing to forensic analysis, so you can pick one that fits your career goals.
Niche Certifications for Specialized Roles: Cloud Security, IoT Security
Cybersecurity isn’t a one-size-fits-all field. As technology evolves, new certs are popping up to match. If you’re into cloud computing, check out CCSP (Certified Cloud Security Professional). It’s all about securing cloud environments, which is a huge deal as more companies move their data to platforms like AWS and Azure.
For those into IoT (Internet of Things), there are certs like GIAC IoT Security Essentials. With smart devices everywhere, knowing how to secure them is a skill that’s in high demand.
To align your career goals with financial growth, take a look at the highest-paying cybersecurity jobs in 2026 that are reshaping industry demand.
The Cybersecurity Landscape in 2026 and Beyond
The cybersecurity field in 2026 doesn’t look anything like it did a decade ago. It’s faster, smarter, and more dangerous on both sides. Hackers are upping their game with cutting-edge tools, and defenders are being pushed to stay ahead. If you’re thinking about working in cybersecurity or already in the field, understanding the trends and shifts shaping the industry is key to staying relevant.
Adapting to AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) aren’t just buzzwords anymore—they’re the engines behind the future of cybersecurity. AI is being used to analyze threats in real time, predict vulnerabilities, and even automate responses to attacks. But here’s the kicker: hackers are using AI too.
Imagine an attack that evolves as you defend. Hackers are training their malware to bypass security systems, mimic legitimate traffic, and target weak points faster than humans can react. On the flip side, AI tools like security information and event management (SIEM) systems are scanning massive amounts of data to detect threats humans might miss.
For cybersecurity pros, knowing how to work with AI-driven tools will be essential. It’s not about replacing humans; it’s about teaming up with machines to cover more ground. Learning about AI frameworks and how they’re applied in cybersecurity—tools like TensorFlow, or systems built for anomaly detection—can give you an edge.
Cybersecurity Trends That Will Shape Job Roles and Skills
The job market for cybersecurity is exploding, but the roles are changing. In 2026, it’s not enough to be a jack-of-all-trades. Employers are looking for specialists—people who can secure cloud environments, analyze threats with AI, or manage risk in IoT networks.
- Cloud Security Is Huge
As businesses move to the cloud, protecting data in these environments has become a top priority. Roles like cloud security architects and engineers are in high demand. Knowing platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud inside out can be a game-changer for your career. - IoT and OT Security Are Taking Off
IoT (Internet of Things) and OT (Operational Technology) devices—think smart home gadgets, industrial control systems—are everywhere. But they’re also poorly secured, making them prime targets for hackers. Cyber pros with expertise in securing IoT and OT devices will have a ton of opportunities in the coming years. - Cyber Resilience Over Cybersecurity
It’s not just about preventing attacks anymore; it’s about bouncing back fast when something goes wrong. Companies want pros who can manage incidents, recover systems, and minimize downtime. Think disaster recovery plans, business continuity, and strong backup systems.
How Remote Work and BYOD Policies Are Shaping the Future of Security
The shift to remote work changed everything. With employees working from coffee shops, home offices, or halfway around the world, the traditional idea of a secure network doesn’t cut it anymore.
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies have added another layer of risk. When employees use personal devices to access company data, it creates a huge attack surface. These devices might not have the latest patches, could be running outdated software, or lack basic security measures like endpoint protection.
To tackle this, businesses are adopting zero-trust models. In a zero-trust setup, every device, user, and connection is treated as a potential threat until verified. Tools like multifactor authentication (MFA), secure access service edge (SASE) systems, and advanced endpoint detection are becoming the new norm.
For cybersecurity pros, this means learning how to secure distributed workforces. It’s not just about securing an office anymore; it’s about securing thousands of mini-offices wherever employees are working from.
If you’re debating between different cloud-focused certs, our comparison of CLF-C02 vs AZ-900 breaks down which certification is the better fit for your career path.
Preparation Tips for Cybersecurity Certifications
Let’s be real, preparing for cybersecurity certs isn’t just about reading a textbook and hoping for the best. These exams are tough for a reason: they’re designed to filter out those who know their stuff from those who don’t. But that doesn’t mean they’re impossible. With the right strategy, tools, and mindset, you can ace them and make a solid impression on recruiters and employers.
Start with the Exam Blueprint
Every cert comes with a detailed blueprint or syllabus, and trust me, it’s your best friend. These outlines tell you exactly what’s on the exam, so you don’t waste time studying things you’ll never be tested on. Focus your energy on the listed domains and break them into manageable chunks.
For example, if you’re going for the Security+, you’ll want to dig into network security, cryptography, and risk management. If it’s the CISSP, get ready for domains like asset security, identity management, and security operations. Knowing where to focus is half the battle.
Mix Study Materials
One mistake people make is sticking to a single source. Don’t do that. Use a mix of resources—official guides, practice tests, video tutorials, and forums. Videos on platforms like YouTube or Udemy can simplify tricky concepts, while books often go deeper into the technical side.
Interactive labs are a game-changer, too. Websites like TryHackMe or Hack The Box let you practice real-world scenarios, which makes it easier to remember concepts. Plus, they’re way more fun than staring at a book for hours.
Practice Tests Are Gold
Practice exams aren’t just about testing your knowledge—they help you get comfortable with the format and timing. A lot of cybersecurity certs use tricky phrasing to test how well you understand the material, so the more practice you get, the better.
Platforms like Cert Mage, Cert Empire, or ExamTopics are great for finding realistic practice questions. Take as many as you can, review your mistakes, and make sure you understand why the correct answers are right.
Importance of Exam Dumps by Cert Empire
Cert Empire offers updated and reliable dumps that give you a clear idea of what the actual exam might look like.
But here’s the thing: don’t rely on dumps as your only resource. Think of them as a supplement, not the main course. Dumps help you understand the question patterns and focus on high-priority topics, but they won’t teach you the reasoning behind the answers.
Dumps can save you time and help you target your weak areas when used responsibly. The key is balance. Pair them with practice exams, study guides, and hands-on labs to get a well-rounded prep experience.
Plan Your Study Schedule
Cramming might have worked in school, but it’s a terrible strategy for cybersecurity certs. Break your prep into weeks or months, depending on how much time you have. Set specific goals for each day—maybe one domain per week—and stick to them.
Make time for review, too. It’s easy to forget things if you don’t revisit them. Spaced repetition is a proven technique that helps you retain information better, so spread out your study sessions instead of cramming all at once.
Stay Hands-On
Cybersecurity isn’t just theory; it’s a hands-on field. Tools like Wireshark, Kali Linux, or even basic PowerShell commands can make all the difference. The more you practice using these tools, the easier it’ll be to connect the dots during your exam. Plus, hands-on experience gives you stories to share during job interviews, which is a bonus.
Final Thoughts!
Cybersecurity exams are tough, but they’re worth it. With a solid plan, the right mix of resources, and maybe a little help from exam dumps, you’ll be walking into that test center ready to crush it. Just remember—it’s not about passing the exam; it’s about building the skills and confidence that’ll take your career to the next level.
Common Questions About Cybersecurity Careers
Can You Start a Cybersecurity Career Without a Technical Background?
Yes, many people transition from non-technical roles by focusing on foundational skills, earning beginner certs like Security+, and gaining hands-on experience through labs and bootcamps.
What Are the Most In-Demand Cybersecurity Skills in 2026?
Cloud security, penetration testing, incident response, and proficiency in tools like Splunk and Wireshark are top skills as businesses prioritize securing digital environments.
How Long Does It Take to Become a Cybersecurity Expert?
It depends on your goals, but reaching a senior level like a Security Architect or CISO can take 5-10 years of experience, with focused learning and certifications along the way.
Are Cybersecurity Certifications Worth the Investment?
Absolutely! Certs validate your skills, open up better job opportunities, and often lead to higher salaries, making them a worthwhile career move.