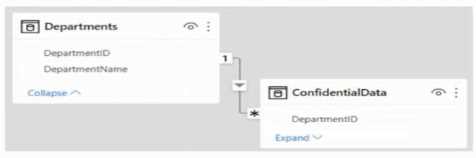
 There are four departments in the Departments table.
You need to ensure that users can see the data of their respective department only.
What should you do?
There are four departments in the Departments table.
You need to ensure that users can see the data of their respective department only.
What should you do?C or A? In practice exams and the official guide, row-level security (RLS) like A comes up when you need to actually restrict data by department, but filtering with DAX or slicers is common for just UI filtering. Not totally sure without seeing how strict the requirement is. Worth checking Microsoft docs or labs for this scenario.
I used to think B could work if you wanted some user-driven filtering, since parameters can limit data in the query. But it doesn't actually secure data per department by user identity, so users could just switch the parameter. Pretty sure real access restriction needs RLS (A), but parameters might confuse some scenarios. Agree?
Yeah, A is the way to go here. Slicers (D) only change what you see, not what you can access. RLS actually restricts the data so users can't even query other departments. Pretty sure that's what the question wants.

