The customer wants to deploy a solution to authenticate the clients connected to a hardware switch
interface of a FortiGate 400E device. A hardware switch interface is an interface that combines
multiple physical interfaces into one logical interface, allowing them to act as a single switch with
one IP address and one set of security policies. The customer wants to use 802.1X authentication for
this solution, which is a standard protocol for port-based network access control (PNAC) that
authenticates clients based on their credentials before granting them access to network resources.
One condition that allows authentication to the client devices before assigning an IP address is that
devices connected directly to ports 3 and 4 can perform 802.1X authentication. This is because ports
3 and 4 are part of the hardware switch interface named “lan”, which has an IP address of
10.10.10.254/24 and an inbound SSL inspection profile named “ssl-inspection”. The inbound SSL
inspection profile enables the FortiGate device to intercept and inspect SSL/TLS traffic from clients
before forwarding it to servers, which allows it to apply security policies and features such as
antivirus, web filtering, application control, etc. However, before performing SSL inspection, the
FortiGate device needs to authenticate the clients using 802.1X authentication, which requires the
clients to send their credentials (such as username and password) to the FortiGate device over a
secure EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) channel. The FortiGate device then verifies the
credentials with an authentication server (such as RADIUS or LDAP) and grants or denies access to
the clients based on the authentication result. Therefore, devices connected directly to ports 3 and 4
can perform 802.1X authentication before assigning an IP address. Another condition that allows
authentication to the client devices before assigning an IP address is that client devices must have
802.1X authentication enabled. This is because 802.1X authentication is a mutual process that
requires both the client devices and the FortiGate device to support and enable it. The client devices
must have 802.1X authentication enabled in their network settings, which allows them to initiate the
authentication process when they connect to the hardware switch interface of the FortiGate device.
The client devices must also have an 802.1X supplicant software installed, which is a program that
runs on the client devices and handles the communication with the FortiGate device using EAP
messages. The client devices must also have a trusted certificate installed, which is used to verify the
identity of the FortiGate device and establish a secure EAP channel. Therefore, client devices must
have 802.1X authentication enabled before assigning an IP address. Reference:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.0.0/administration-guide/19662/hardware-switchinterfaces https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.0.0/administration-guide/19662/802-1x-
authentication
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.2.0/new-features/959502/support-802-1x-onvirtual-switch-for-certain-np6-platforms
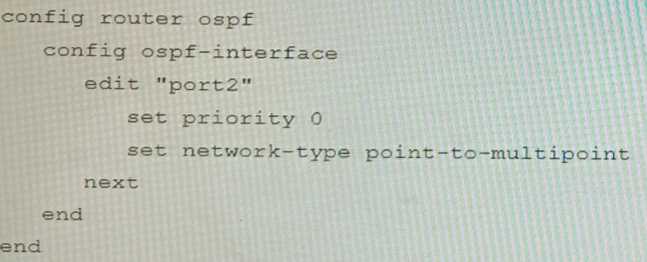
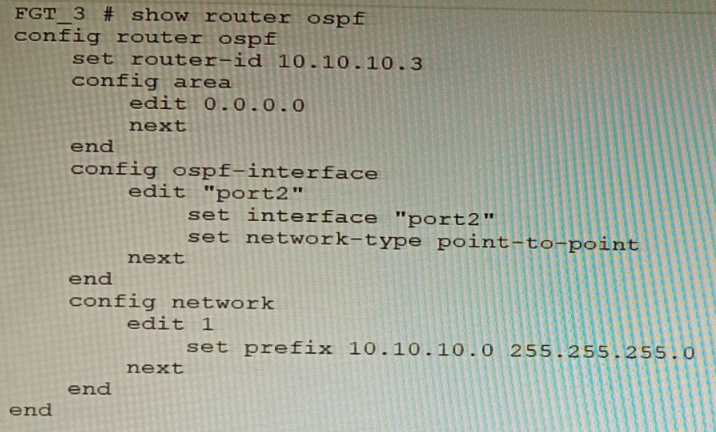 You are operating an internal network with multiple OSPF routers on the same LAN segment. FGT_3
needs to be added to the OSPF network and has the configuration shown in the exhibit. FGT_3 is not
establishing any OSPF connection.
What needs to be changed to the configuration to make sure FGT_3 will establish OSPF neighbors
without affecting the DR/BDR election?
A)
You are operating an internal network with multiple OSPF routers on the same LAN segment. FGT_3
needs to be added to the OSPF network and has the configuration shown in the exhibit. FGT_3 is not
establishing any OSPF connection.
What needs to be changed to the configuration to make sure FGT_3 will establish OSPF neighbors
without affecting the DR/BDR election?
A)
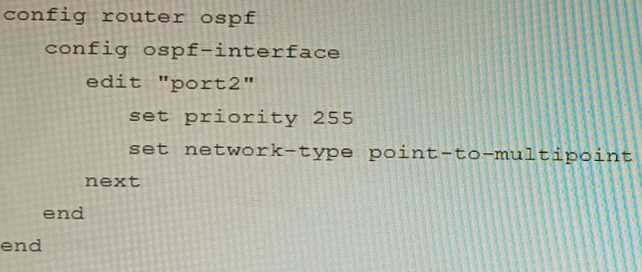 B)
B)
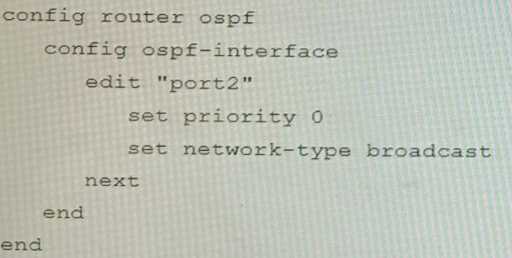 C)
C)
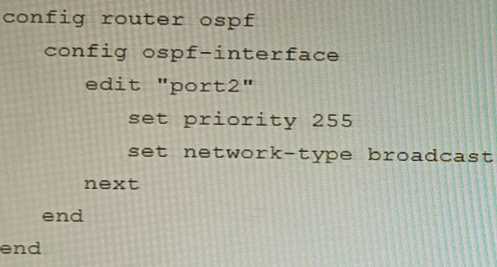 D)
D)

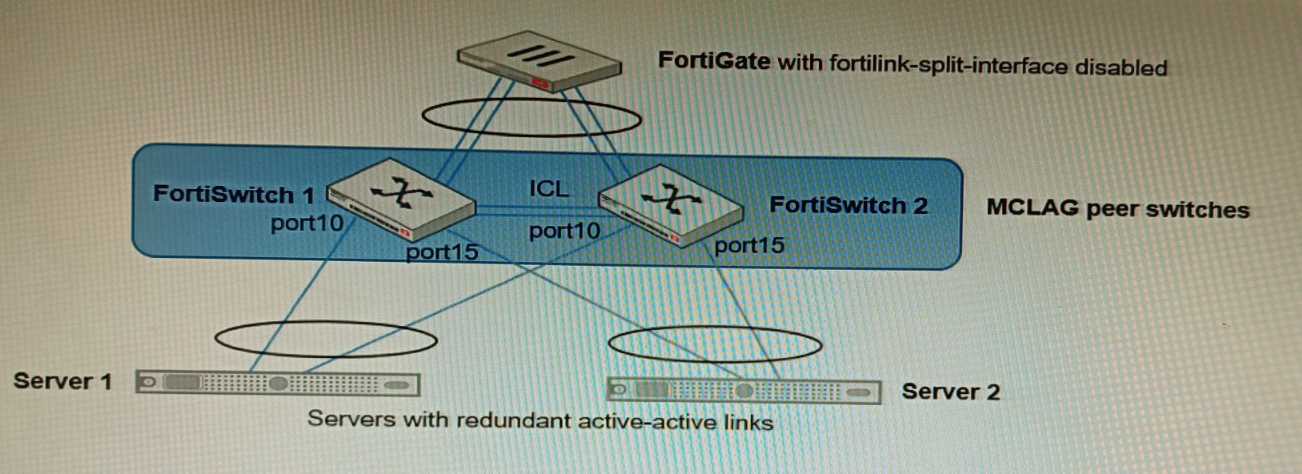 You have been tasked with replacing the managed switch Forti Switch 2 shown in the topology.
Which two actions are correct regarding the replacement process? (Choose two.)
You have been tasked with replacing the managed switch Forti Switch 2 shown in the topology.
Which two actions are correct regarding the replacement process? (Choose two.)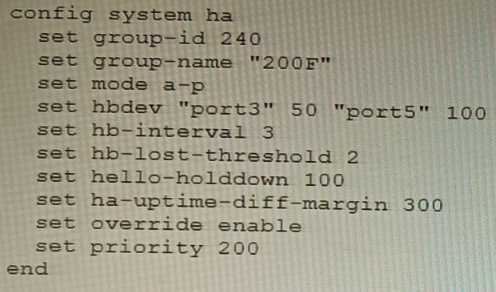 Based on this configuration, how long will it take for a failover to be detected by the secondary
cluster member?
Based on this configuration, how long will it take for a failover to be detected by the secondary
cluster member? You are deploying a FortiGate 6000F. The device should be directly connected to a switch. In the
future, a new hardware module providing higher speed will be installed in the switch, and the
connection to the FortiGate must be moved to this higher-speed port.
You must ensure that the initial FortiGate interface connected to the switch does not affect any other
port when the new module is installed and the new port speed is defined.
How should the initial connection be made?
You are deploying a FortiGate 6000F. The device should be directly connected to a switch. In the
future, a new hardware module providing higher speed will be installed in the switch, and the
connection to the FortiGate must be moved to this higher-speed port.
You must ensure that the initial FortiGate interface connected to the switch does not affect any other
port when the new module is installed and the new port speed is defined.
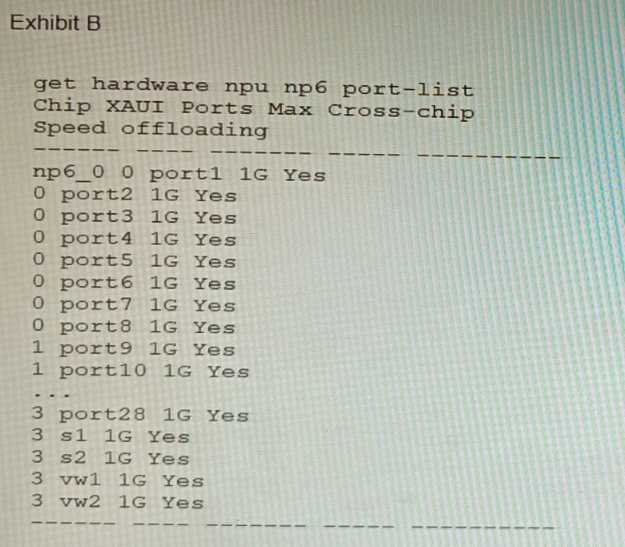
How should the initial connection be made? Given the information shown in the output, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
Given the information shown in the output, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)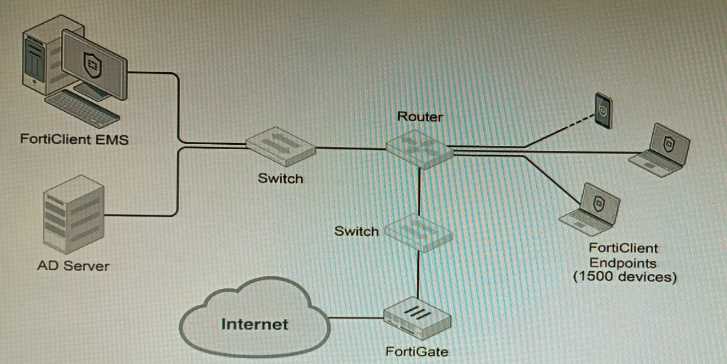 A customer wants FortiClient EMS configured to deploy to 1500 endpoints. The deployment will be
integrated with FortiOS and there is an Active Directory server.
Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, which two statements about the installation are
correct? (Choose two.)
A customer wants FortiClient EMS configured to deploy to 1500 endpoints. The deployment will be
integrated with FortiOS and there is an Active Directory server.
Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, which two statements about the installation are
correct? (Choose two.)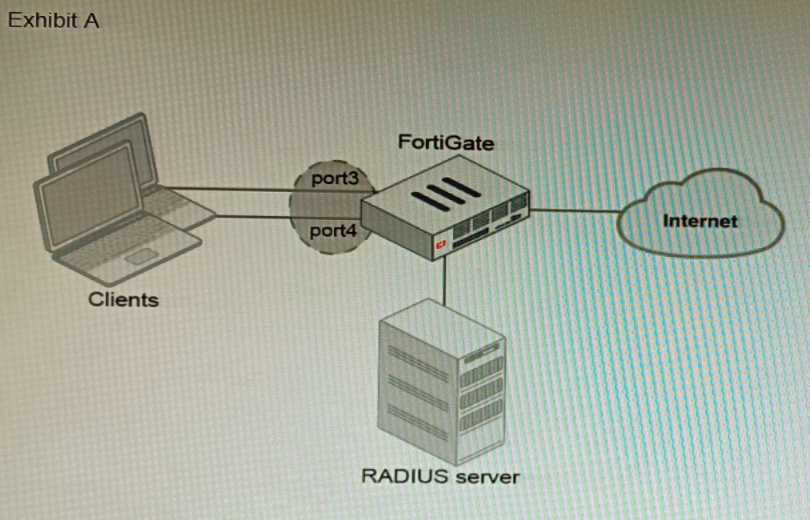
 A customer is looking for a solution to authenticate the clients connected to a hardware switch
interface of a FortiGate 400E.
Referring to the exhibits, which two conditions allow authentication to the client devices before
assigning an IP address? (Choose two.)
A customer is looking for a solution to authenticate the clients connected to a hardware switch
interface of a FortiGate 400E.
Referring to the exhibits, which two conditions allow authentication to the client devices before
assigning an IP address? (Choose two.)