Understanding the Exhibit Setup:
The network diagram shows an EVPN-VXLAN setup, a common design for modern data centers
enabling Layer 2 and Layer 3 services over an IP fabric.
Leaf1 and Leaf2 are the leaf switches connected to Server1 and Server2, respectively, with each
server in a different subnet (172.16.1.0/24 and 172.16.2.0/24).
Spine1 and Spine2 are part of the IP fabric, interconnecting the leaf switches.
EVPN-VXLAN Basics:
EVPN (Ethernet VPN) provides Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPN services using MP-BGP.
VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) encapsulates Layer 2 frames into Layer 3 packets for transmission
across an IP network.
VTEP (VXLAN Tunnel Endpoint) interfaces on leaf devices handle VXLAN encapsulation and
decapsulation.
Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB):
IRB interfaces are required on leaf1 and leaf2 (where the endpoints are directly connected) to route
between different subnets (in this case, between 172.16.1.0/24 and 172.16.2.0/24).
The IRB interfaces provide the necessary L3 gateway functions for inter-subnet communication.
Traffic Flow Analysis:
Traffic from Server1 (172.16.1.1) destined for Server2 (172.16.2.1) must traverse from leaf1 to leaf2.
The traffic will be VXLAN encapsulated on leaf1, sent over the IP fabric, and decapsulated on leaf2.
Since the communication is between different subnets, the IRB interfaces on leaf1 and leaf2 are
crucial for routing the traffic correctly.
Correct Statements:
C . An IRB Interface must be configured on leaf1 and leaf2: This is necessary to perform the inter-
subnet routing for traffic between Server1 and Server2.
D . Traffic from server1 to server2 will transit the VXLAN tunnel between leaf1 and leaf2: This
describes the correct VXLAN operation where the traffic is encapsulated by leaf1 and decapsulated
by leaf2.
Data Center Reference:
In EVPN-VXLAN architectures, the leaf switches often handle both Layer 2 switching and Layer 3
routing via IRB interfaces. This allows for efficient routing within the data center fabric without the
need to involve the spine switches for every routing decision.
The described traffic flow aligns with standard EVPN-VXLAN designs, where direct VXLAN tunnels
between leaf switches enable seamless and scalable communication across a data center network.
 You have implemented an EVPN-VXLAN data center. Device served must be able to communicate
with device server2.
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
You have implemented an EVPN-VXLAN data center. Device served must be able to communicate
with device server2.
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)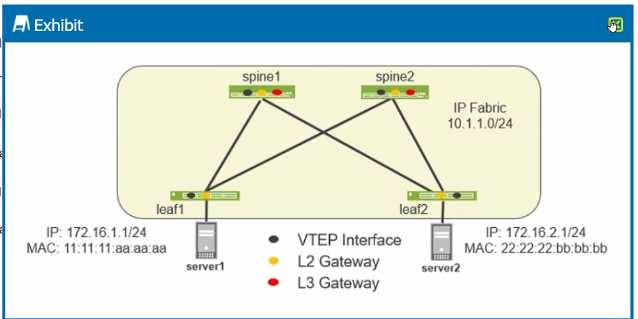 You have implemented an EVPN-VXLAN data center. Device served must be able to communicate
with device server2.
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
You have implemented an EVPN-VXLAN data center. Device served must be able to communicate
with device server2.
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
