The openstack server show command provides detailed information about a specific virtual machine
(VM) instance in OpenStack. The output includes details such as the instance name, network
attachments, power state, and more. Let’s analyze the question and options:
Key Information from the Exhibit:
The addresses field in the output shows
public1=10.0.2.176
This indicates that the VM-A instance is attached to the virtual network named public1 , with an
assigned IP address of 10.0.2.176 .
Option Analysis:
A . m1.tiny
Incorrect: m1.tiny refers to the flavor of the VM, which specifies the resource allocation (e.g., CPU,
memory, disk). It is unrelated to the virtual network.
B . public1
Correct: The addresses field explicitly states that the VM-A instance is attached to the public1 virtual
network.
C . Nova
Incorrect: Nova is the OpenStack compute service that manages VM instances. It is not a virtual
network.
D . kollaopenstack
Incorrect: kollaopenstack appears in the output as the hostname or project name but does not
represent a virtual network.
Why public1?
Network Attachment: The addresses field in the output directly identifies the virtual network
(public1) to which the VM-A instance is attached.
IP Address Assignment: The IP address (10.0.2.176) confirms that the VM is connected to the public1
network.
JNCIA Cloud Reference:
The JNCIA-Cloud certification emphasizes understanding OpenStack commands and outputs,
including the openstack server show command. Recognizing how virtual networks are represented in
OpenStack is essential for managing VM connectivity.
For example, Juniper Contrail integrates with OpenStack Neutron to provide advanced networking
features for virtual networks like public1.
Reference:
OpenStack CLI Documentation: openstack server show Command
Juniper JNCIA-Cloud Study Guide: OpenStack Networking
 You have issued the openstack server show VM-A command and received the output shown in the
exhibit.
To which virtual network is the VM-A instance attached?
You have issued the openstack server show VM-A command and received the output shown in the
exhibit.
To which virtual network is the VM-A instance attached?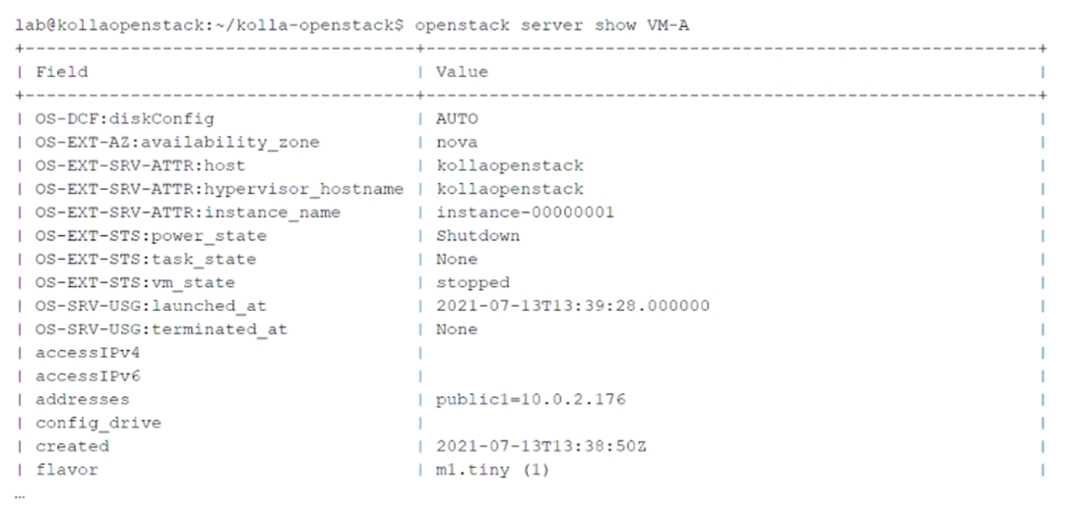 You have issued the openstack server show VM-A command and received the output shown in the
exhibit.
To which virtual network is the VM-A instance attached?
You have issued the openstack server show VM-A command and received the output shown in the
exhibit.
To which virtual network is the VM-A instance attached?
