1. Aruba Threat Labs. (2020
May 20). Detecting DNS Tunneling with Aruba IntroSpect. Aruba Blogs. This official vendor blog post provides examples of DNS tunneling traffic used for C2
which are visually identical to the traffic in the exhibit
and explains how Aruba security solutions detect this threat.
2. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). (2013). Special Publication 800-81-2: Secure Domain Name System (DNS) Deployment Guide. Section 3.4.2
"DNS Tunneling". This section states
"An attacker can use DNS tunneling to...establish a command and control channel with a compromised host... The data to be tunneled is encoded within the labels of a DNS query for a domain name controlled by the attacker."
3. Dusi
M.
Gringoli
F.
& Salgarelli
L. (2015). A preliminary look at DNS-based covert channels. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS). https://doi.org/10.1109/INFCOMW.2015.7179398. This academic paper analyzes DNS covert channels
noting that encoding information in query names is a common method for C2 and data exfiltration
matching the exhibit's scenario.
 ?
Which security issue is possibly indicated by this traffic capture?
?
Which security issue is possibly indicated by this traffic capture?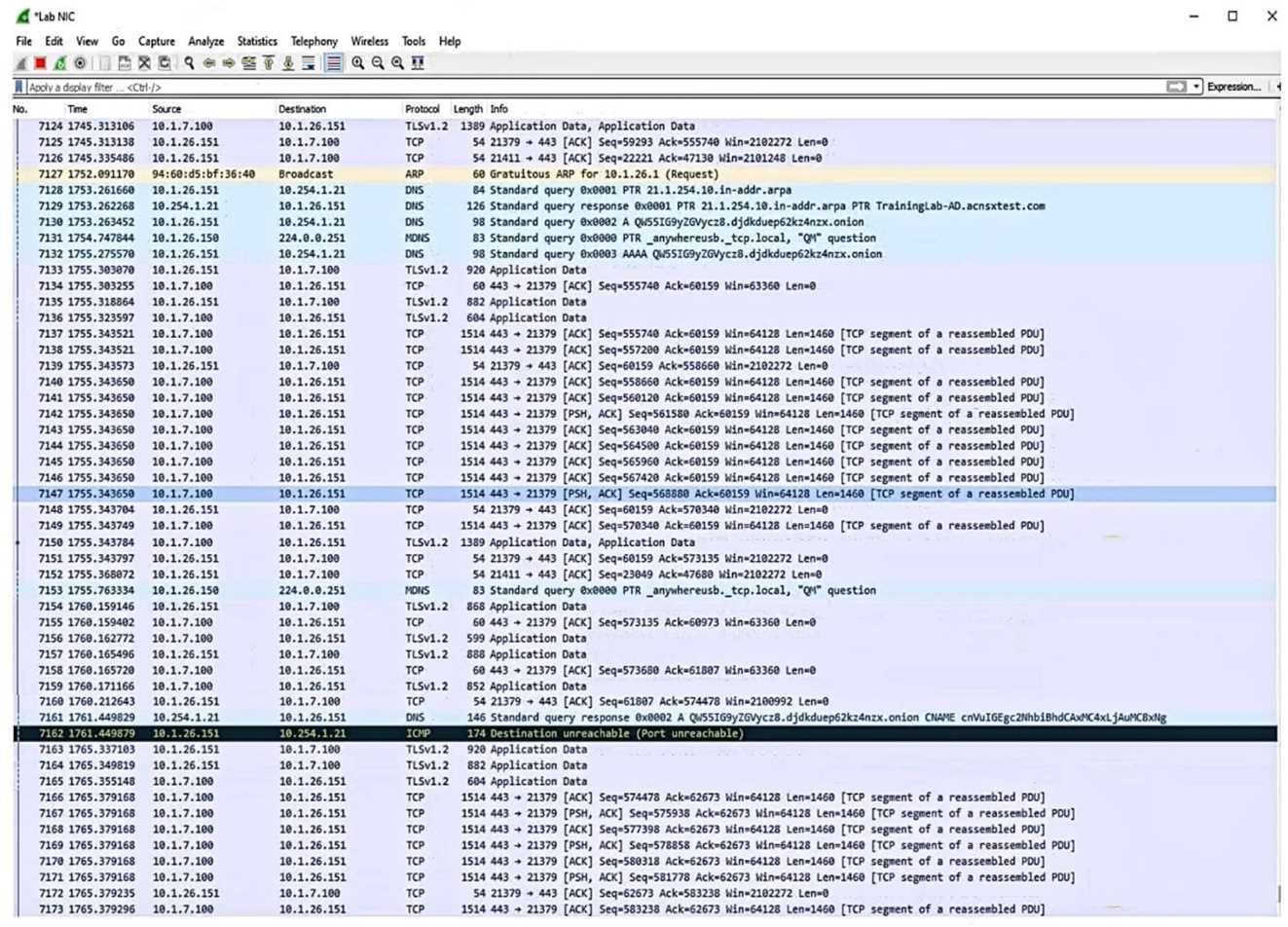 ?
Which security issue is possibly indicated by this traffic capture?
?
Which security issue is possibly indicated by this traffic capture?
