According to the Azure Cosmos DB documentation1, Always Encrypted is a feature designed to
protect sensitive data, such as credit card numbers or national identification numbers, stored in
Azure Cosmos DB. Always Encrypted allows clients to encrypt sensitive data inside client applications
and never reveal the encryption keys to the database.
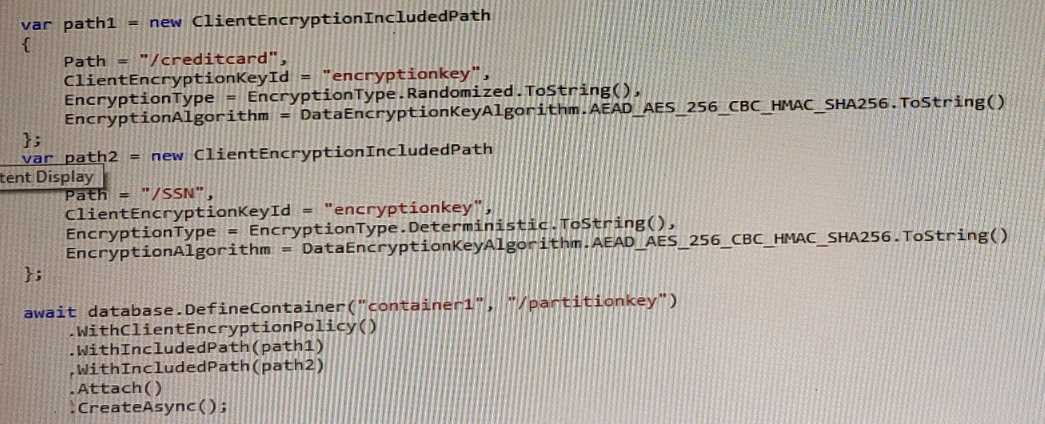
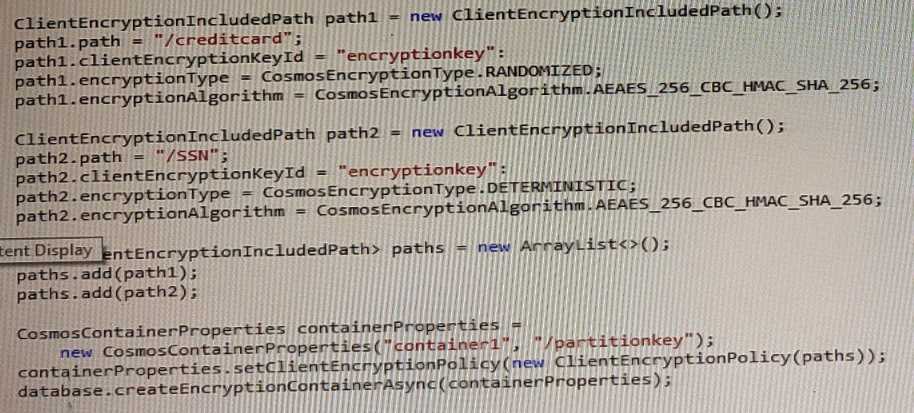
To use Always Encrypted, you need to define an encryption policy for each container that specifies
which properties should be encrypted and which data encryption keys (DEK) should be used. The
DEKs are stored in Azure Cosmos DB and are wrapped by customer-managed keys (CMK) that are
stored in Azure Key Vault.
Based on the encryption policy shown in the exhibits, the creditcard property is encrypted with a DEK
named dek1, and the SSN property is encrypted with a DEK named dek2. Both DEKs are wrapped by
a CMK named cmk1.
To answer your statements:
You can perform a query that filters on the creditcard property = No. This is because the creditcard
property is encrypted and cannot be used for filtering or sorting operations1.
You can perform a query that filters on the SSN property = No. This is also because the SSN property
is encrypted and cannot be used for filtering or sorting operations1.
An application can be allowed to read the creditcard property while being restricted from reading the
SSN property = Yes. This is possible by using different CMKs to wrap different DEKs and applying
access policies on the CMKs in Azure Key Vault. For example, if you use cmk2 to wrap dek2 instead of
cmk1, you can grant an application access to cmk1 but not cmk2, which means it can read the
creditcard property but not the SSN property2.

 For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

 For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


