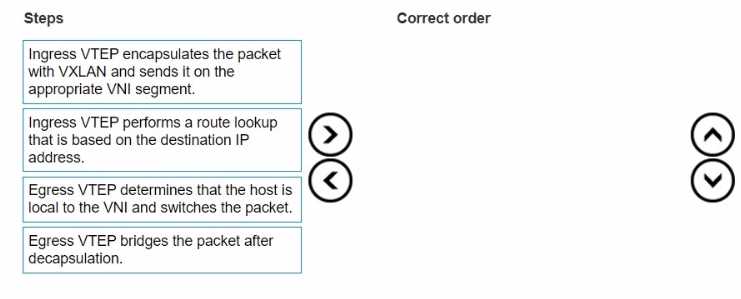
Ingress VTEP performs a route lookup that is based on the destination IP address. Ingress VTEP encapsulates the packet with VXLAN and sends it on the appropriate VNI segment. Egress VTEP determines that the host is local to the VNI and switches the packet. Egress VTEP bridges the packet after decapsulation. Steps and Correct Order: Ingress VTEP performs a route lookup that is based on the destination IP address. The ingress VTEP (Virtual Tunnel Endpoint) first needs to determine the next hop for the packet. This involves performing a route lookup using the destination IP address. Ingress VTEP encapsulates the packet with VXLAN and sends it on the appropriate VNI segment. Once the route lookup is complete, the ingress VTEP encapsulates the packet in a VXLAN header, which includes the appropriate VNI (VXLAN Network Identifier) segment, and forwards it. Egress VTEP determines that the host is local to the VNI and switches the packet. The egress VTEP receives the encapsulated VXLAN packet, decapsulates it, and then checks its local VNI to determine if the destination host is within the same VNI. Egress VTEP bridges the packet after decapsulation. After determining the destination host's locality, the egress VTEP bridges the packet to the appropriate interface to deliver it to the final destination. Reference: Dell Technologies Networking - SONiC Dell Enterprise SONiC Deployment Guide These steps provide a comprehensive guide to understand the correct order of operations in asymmetric IRB (Integrated Routing and Bridging) frame encapsulation within a VXLAN environment.