Blinking green LED just shows port activity on Cisco, so C is right. Solid green would mean link up but no traffic. Pretty sure that's what they want here, let me know if you see different behavior on other series.
B tbh. Had something like this in a mock and only addresses starting with 192.168.200 and /24 fit here. Anything outside .200 in the third octet is out. Let me know if you see it differently.
Guessing B falls in the 192.168.200.0/24 range since the third octet matches that network and /24 means addresses go from .0 up to .255. All the other choices have different third octets so they aren't part of this subnet. I remember seeing a similar subnetting question on a practice test, so pretty sure this is right but correct me if I'm missing something subtle.
I was thinking A and D. Usually I include what the issue is and what I already tried, so support doesn't repeat steps. Maybe C is more about detailed conditions, but to me actions taken (D) feels just as important at first. Not 100 percent on this, anyone else pick D?
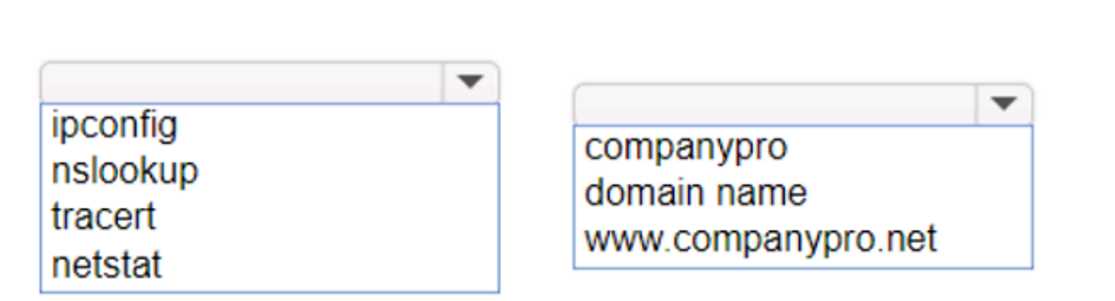
HOTSPOT You want to list the IPv4 addresses associated with the host name www.companypro.net. Complete the command by selecting the correct option from each drop-down list.
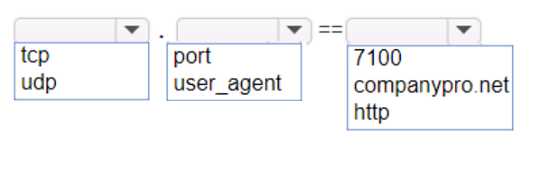
HOTSPOT An app on a user's computer is having problems downloading dat a. The app uses the following URL to download data: https://www.companypro.net:7100/api You need to use Wireshark to capture packets sent to and received from that URL. Which Wireshark filter options would you use to filter the results? Complete the command by selecting the correct option from each drop-down list. Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct selection.
I don't think you'd want "https" as the protocol here, since Wireshark works at the TCP level for ports like 7100. The trap is assuming protocol = https, but it's actually just tcp with port 7100. Anyone disagree?
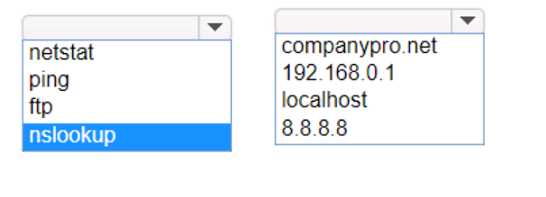
HOTSPOT Computers in a small office are unable to access companypro.net. You run the ipconfig command on one of the computers. The results are shown in the exhibit. You need to determine if you can reach the router. 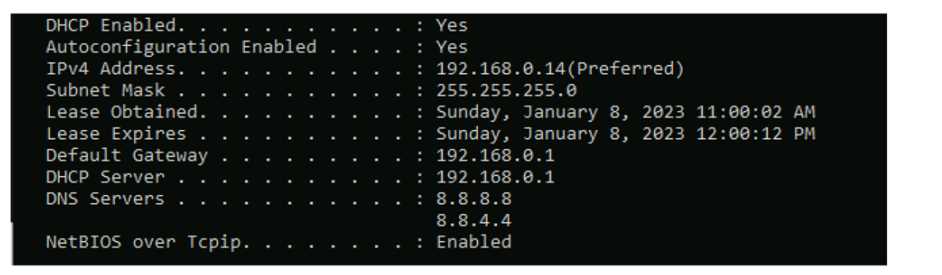
Had something like this in a mock, just need to ping the default gateway to check router reachability.
This checks if you have basic IP connectivity to the gateway router, ignoring any possible DNS issues. Pretty sure that's the intent since reaching the default gateway rules out a local network problem first. Agree with others here but open to other views.
Pretty sure that's it. Sometimes people pick hostname or DNS but for reachability the gateway IP avoids that trap.
The trap is pinging a hostname like companypro.net, which could fail if DNS is broken even if the router's up. Going direct to the default gateway tests L3 connectivity. Pretty sure that's what they're after here, feel free to push back if you think differently.
Not router or hostname, using DNS here would be a trap, safer to go with the gateway IP.
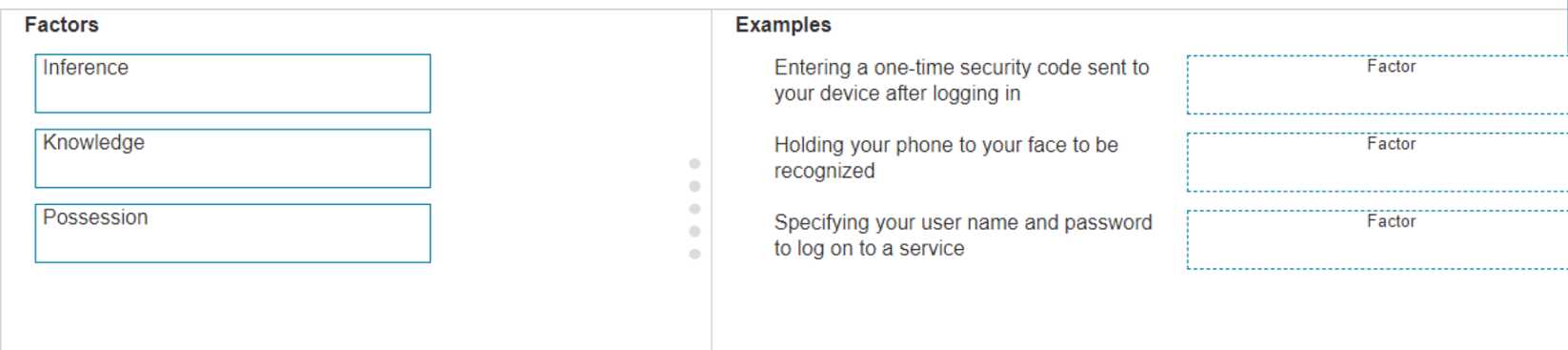
DRAG DROP Move the MFA factors from the list on the left to their correct examples on the right. You may use each factor once, more than once, or not at all. Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct selection.
Seen this style in Cisco practice too. Should be:
Entering a one-time code: Possession
Holding phone to face: Inference (biometrics)
User name + password: Knowledge
This lines up with what the official guide says.
Entering a one-time code: Possession, Holding phone to face: Inference, Username & password: Knowledge. This matches how MFA splits between something you have, are, or know. Pretty sure this is right but open to other opinions.
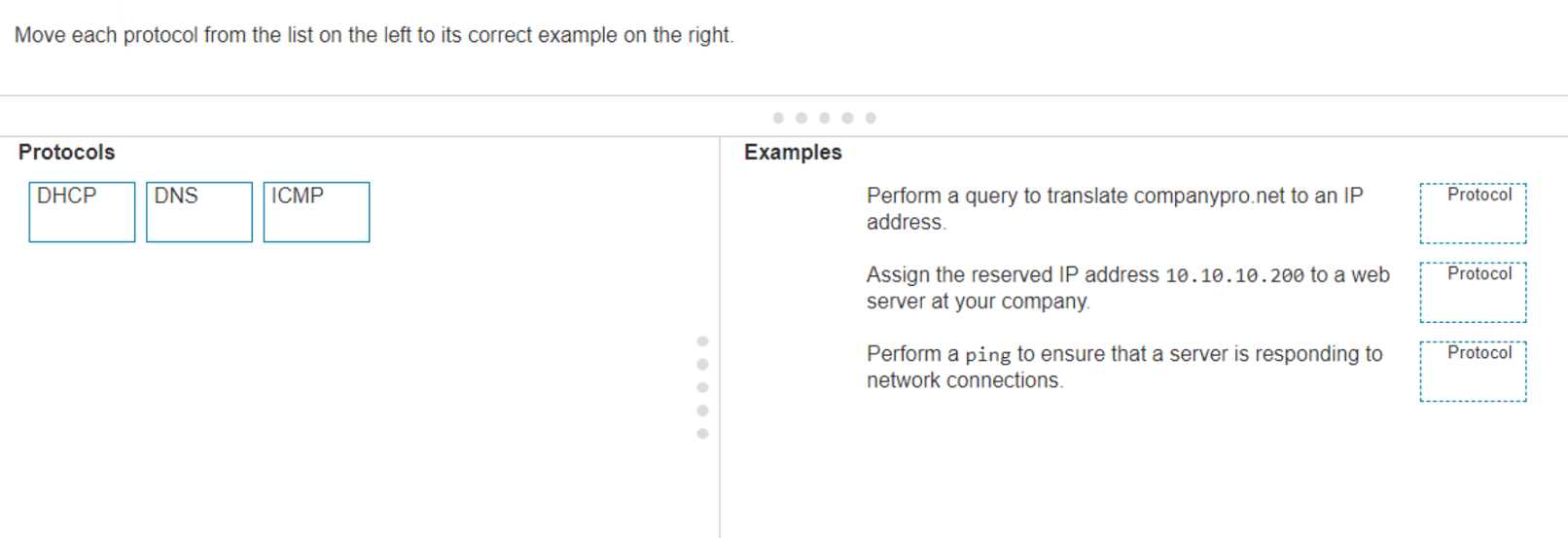
DRAG DROP Move each protocol from the list on the left to its correct example on the right.
Pretty straightforward if you know how each protocol functions. DHCP is for dynamic IP assignment, DNS does name resolution, and ping uses ICMP for reachability tests. I think this matches real-world use and what I've seen on other practice sets, but open to comments if anyone spots a catch.
Had something like this in a mock. The right order should be: DNS matches with "translate companypro.net", DHCP goes to "assign the reserved IP", and ICMP lines up with "ping the server". Pretty sure that's how Cisco wants it for protocol-to-use type questions, but correct me if you see it differently.
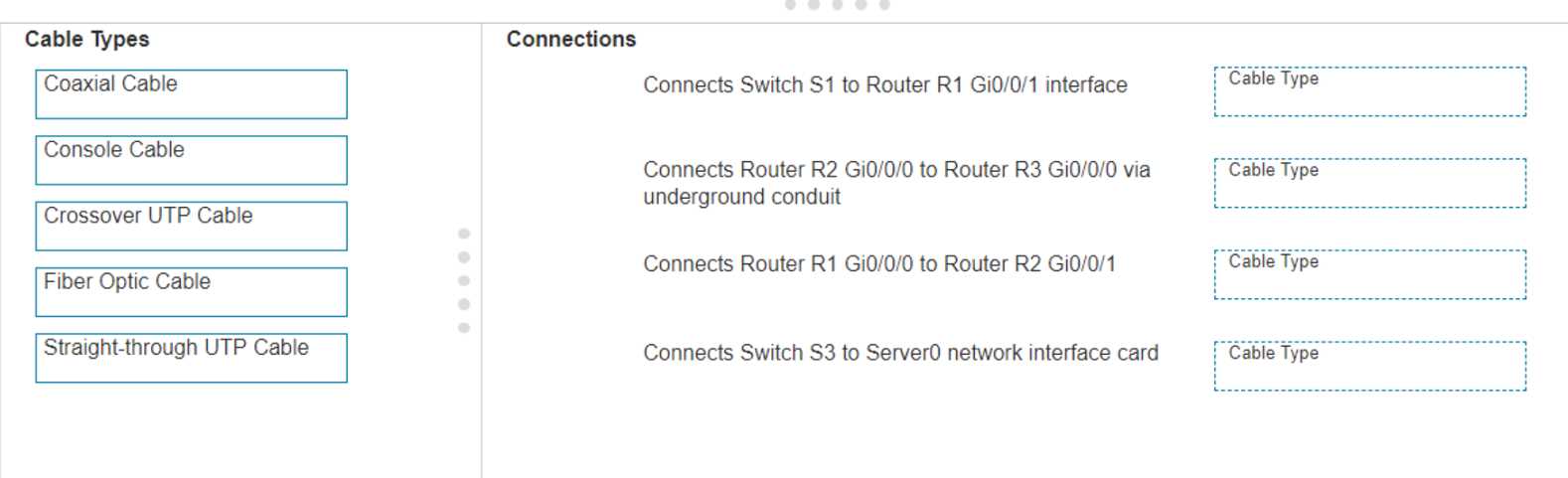
DRAG DROP Examine the connections shown in the following image. Move the cable types on the right to the appropriate connection description on the left. You may use each cable type more than once or not at all. 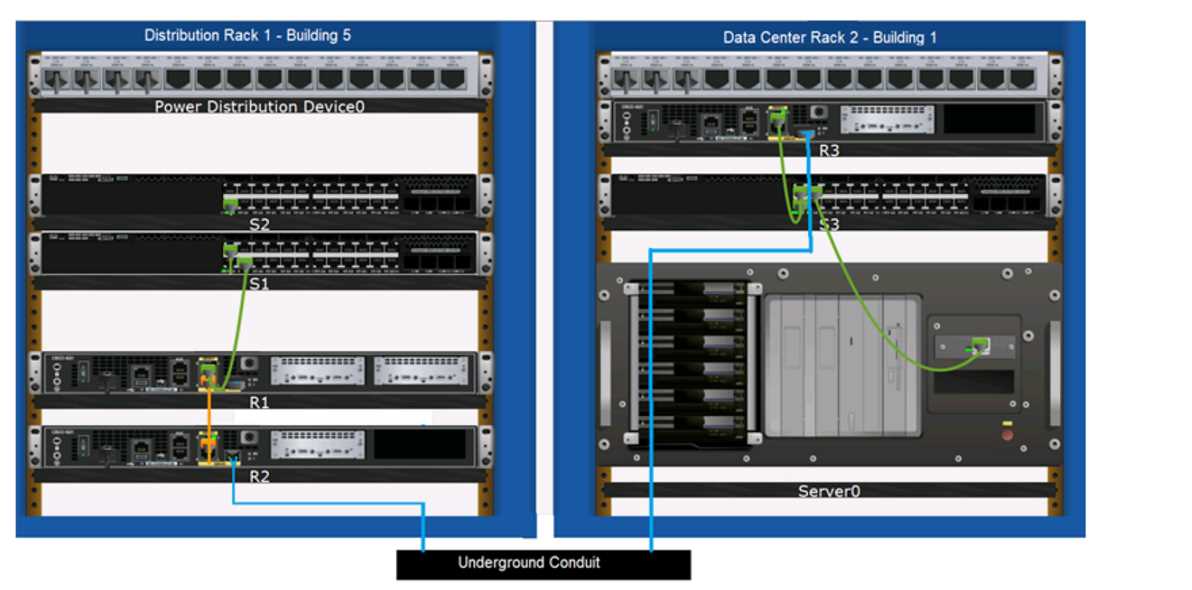
Switch S1 to Router R1: Straight-through UTP, R2 to R3 (underground): Fiber Optic, R1 to R2: Crossover UTP, S3 to Server0: Straight-through UTP. That's standard cabling logic for these setups, I think-unless they're hinting at something tricky. Agree?