Why Practice Exam Questions Are Essential for Passing Cisco CCNA 200-301 Exam in 2025
Passing the CCNA 200-301 certification isn’t about memorizing terms or rot learning, it’s about developing the aptitude required of a networking professional. Loaded with detailed explanations and extensive references, Cert Empire’s CCNA 200-301 Exam Questions are designed to help you think like an actual network engineer. These practice questions mirror the Cisco exam pattern, guiding you through what’s required to pass the exam on your first attempt.
Prepare Smarter with Exam Familiar Quiz
The CCNA 200-301 exam is challenging and broad, but consistent practice transforms that difficulty into strength. By regularly solving real exam-style questions, you’ll improve your pacing, reduce anxiety, and recognize recurring question logic. Over time, the format will feel second nature, allowing you to focus on accuracy instead of uncertainty on exam day.
Master Every Domain with Real Exam Logic
The CCNA 200-301 practice questions cover all official domains in the correct proportion. This means you’re not just preparing one domain, but all of them, making your exam preparation comprehensive. To further strengthen your Cisco learning path, you can view all Cisco certifications available on our platform for a broader understanding of related credentials.
What’s Included in Our CCNA 200-301 Exam Prep Material
It’s not just a question blob that we offer, but a whole experience that transforms your exam preparation. Here is exactly what you get:
PDF Exam Questions
- Instant Access: Start preparing right after purchase with immediate delivery.
- Study Anywhere: Access the soft form questions from your phone, laptop, or tablet.
- Printable Format: Ideal for offline review and personal note-taking, and especially if you prefer to study from hard-form documents.
Interactive Practice Simulator
- Question Simulation: Our online CCNA 200-301 exam practice simulator is designed to help you interactively review and prepare for the exam with tailored features such as show/hide answers, see correct answers etc.
- Flashcard-like Practice: Save your toughest questions and revisit them until you’ve mastered each domain.
- Progress Tracking: The progress tracking feature of our quiz simulator lets you resume your study journey right from where you left.
3 Months of Unlimited Access
Enjoy full, unrestricted access for three months, long enough to practice, revise, and retake simulations until you are satisfied with your results.
Regular Updates
Networking is an ever-evolving field, so being current is the cornerstone of CCNA 200-301 exam prep. Being mindful of that, CertEmpire’s certified exam coaches keep the content of the practice questions up to date with the latest exam requirements so that you always have the latest exam questions and resources available to you.
Free Practice Tests
To make the decision easy for you, we offer free practice tests for the CCNA 200-301 exam. Look at the right side-bar and you will find the free practice test button that will take you to a sample free CCNA 200-301 practice test. Go through the free CCNA 200-301 exam questions section and discover the richness of our practice questions.
Free Exam Guides
Cert Empire offers free exam preparation guides for CCNA 200-301. You can find a trove of CCNA 200-301 related exam prep resources at our website in our blog section. From tailored study plans for success in CCNA 200-301 to exam day guidelines, we have covered it all. Cherry on the top, you do not have to be our customer to access this material, and it is free for all.
Important Note
Our CCNA 200-301 Exam Questions are updated regularly to match the latest Cisco exam version.
The Cert Empire content team, led by certified CCNA professionals, has taken the newest release and added updated concepts, frameworks, and networking models, security fundamentals, and automation protocols to ensure relevance. To get a deeper look into how our material is structured, you can see what’s inside Cert Empire for a complete overview of our learning approach.
✔ Each question includes detailed reasoning for both correct and incorrect options, helping you understand the full context behind every answer.
✔ Every solution links to official Cisco references, allowing you to expand your knowledge through verified documentation.
✔ Mobile-Compatible – Both the PDF and simulator versions are easy to use across smartphones, tablets, laptops, and even in printed form.
The CCNA 200-301 remains one of the most respected and highest-paying certifications in networking, proving mastery of routing, switching, IP connectivity, network access, and automation.
Is this Exam Dump for Cisco CCNA 200-301?
No, CertEmpire offers exam questions for practice purposes only. We do not endorse using Cisco Exam Dumps. Our product includes expert crafted and verified practice exam questions and quizzes that emulates the real exam. This is why you may find many of the similar questions in your exam, which can help you succeed easily. Nonetheless, unlike exam dumps websites, we do not give any sort of guarantees on how many questions will appear in your exam. Our mission is to help students prepare better for exams, not endorse cheating.

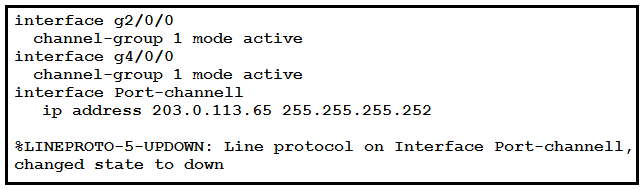 An engineer is configuring a Layer 3 port-channel interface with LACP. The configuration on
the first device is complete, and it is verified that both interfaces have registered the
neighbor device in the CDP table. Which task on the neighbor device enables the new port
channel to come up without negotiating the channel?
A: Change the EtherChannel mode on the neighboring interfaces to auto.
B: Configure the IP address of the neighboring device.
C: Bring up the neighboring interfaces using the no shutdown command.
D: Modify the static EtherChannel configuration of the device to passive mode.
An engineer is configuring a Layer 3 port-channel interface with LACP. The configuration on
the first device is complete, and it is verified that both interfaces have registered the
neighbor device in the CDP table. Which task on the neighbor device enables the new port
channel to come up without negotiating the channel?
A: Change the EtherChannel mode on the neighboring interfaces to auto.
B: Configure the IP address of the neighboring device.
C: Bring up the neighboring interfaces using the no shutdown command.
D: Modify the static EtherChannel configuration of the device to passive mode.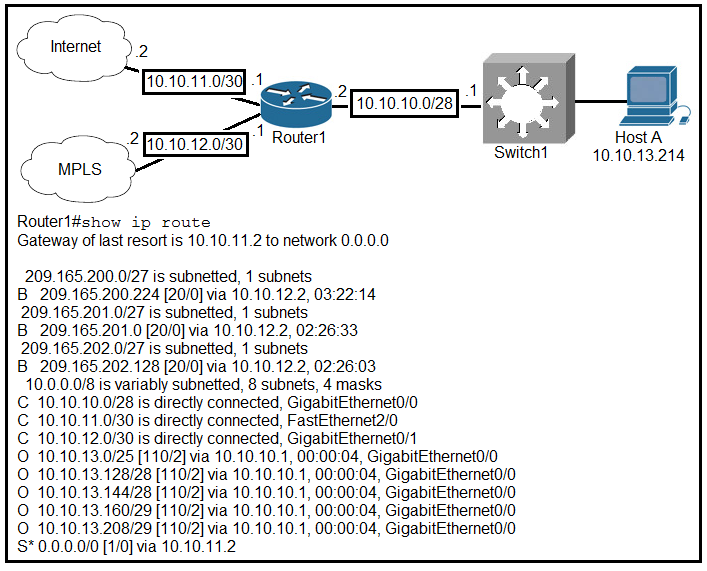 What is the subnet mask of the route to the 10.10.13.160 prefix?
A: 255.255.255.240
B: 255.255.255.128
C: 255.255.248.
D: 255.255.255.248
What is the subnet mask of the route to the 10.10.13.160 prefix?
A: 255.255.255.240
B: 255.255.255.128
C: 255.255.248.
D: 255.255.255.248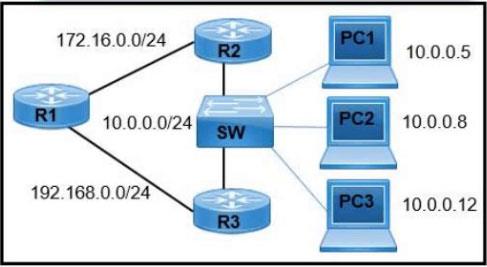 A network engineer must configure R1 so that it sends all packets destined to the
10.0.0.0/24 network to R3, and all packets destined to PC1 to R2. Which configuration must
the engineer implement?
A network engineer must configure R1 so that it sends all packets destined to the
10.0.0.0/24 network to R3, and all packets destined to PC1 to R2. Which configuration must
the engineer implement? An engineer must configure router R2 so it is elected as the DR on the WAN subnet. Which
command sequence must be configured?
A: interface gigabitethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.34 255.255.255.248 ip ospf priority 0
B: interface gigabitethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.34 255.255.255.224 ip ospf priority 100
C: interface gigabitethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip ospf priority 255
D: interface gigabitethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.224 ip ospf priority 98
An engineer must configure router R2 so it is elected as the DR on the WAN subnet. Which
command sequence must be configured?
A: interface gigabitethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.34 255.255.255.248 ip ospf priority 0
B: interface gigabitethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.34 255.255.255.224 ip ospf priority 100
C: interface gigabitethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip ospf priority 255
D: interface gigabitethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.224 ip ospf priority 98


Jacob Dean (verified owner) –
I am not that review-given type of guy but in this scenario, I think Cert Empire deserves a 5-star. Why? Because I just clear my exam all possible to cert empire’s dumps. It was too much effective for preparation for the exam. When I was preparing for the exam, I was just thinking about how it became easy to pass this type of exam. Get dumps and prepares selected question and boom you passed it. BTW, in short, thank you Cert Empire for efficient Dumps. 10/10 recommended.
Henry Cooper (verified owner) –
Prepare Precise content, Attempt the exam and you’ll pass that exam. and that precise content is Dumps. Cert Empire provides one of the best dumps ( whatever the exam code is). Thank you
Bernardo Pachón (verified owner) –
Bom Dia😅 or I should say Good Morning from Brazil. Was thinking about giving my review about CCNA 200-301 dumps when I bought it but then I tell myself ” Wait, Bernardo, first give the exam, after the result post your opinion”. Now, I passed my CCNA 200-301 exam all thanks to the Cert Empire. I don’t know where the owner of this site is living but if he is/was in Brazil, I would give him a party. 10/10 for Cert Empire. love from 🇧🇷
Elijah McClendon (verified owner) –
Perfect Dumps.
Pepo (verified owner) –
Good
Darla Smith (verified owner) –
I cannot thank Cert Empire enough for their help in my passing of the 200-301 exam. Their professionalism, quality resources, and exceptional support were invaluable to my success.
jonathan ava (verified owner) –
thanks to Cert Empire for helping me clear out my 200-3001 exam. I went through the questions list for two days and I cleared the exam.
warner (verified owner) –
Hi everyone, Today I passed the CCNA 200-301 exam with an 854 score – I know, it’s not a high score, but it’s a pass nonetheless, and I’m happy with that. Thanks Cert Empire
smith4murphy.231 (verified owner) –
Cleared my 200-301 exam with Cert Empire’s excellent dumps. Highly recommend their site!
Michael Stevenson (verified owner) –
File….9.5/10
Chat Support….10/10
Price…. Bearable
Manny Sid (verified owner) –
Happy to inform all of you that I’m able to pass my 200-301 exam!!! Thanks Cert Empire.❤︎❤︎❤︎
Wilson Mayer (verified owner) –
Cert Empire has been my go-to for certifications. Their dumps are consistently dependable and up to date.
user-525400 (verified owner) –
awesome
Nathan Ryan (verified owner) –
These 200-301 dumps provided an amazing introduction to CCNA concepts. As a beginner i found them very useful for my exam prep. Recommended!
Wayne Rowland (verified owner) –
The dumps were comprehensive, precise, and provided me with the assurance I required to pass. Without a doubt I would suggest them to others!
Clara Spade (verified owner) –
I passed my CCNA 200-301 exam thanks to the amazing support and materials from Cert Empire. Highly recommended
Stephe Haney (verified owner) –
I was impressed by how detailed and structured the dumps are especially in addressing networking fundamentals and routing protocols. I really appreciate it.
Luna Clay (verified owner) –
Honestly, each question was a new challenge and the explanations made each concept more interesting and easier to understand.
Emilio Pitts (verified owner) –
I appreciated the depth of coverage in these
200-301 dumps ensuring I wasn’t missing out on any critical knowledge areas. I recommend it very much.
Theodore (verified owner) –
The dumps quality of Cert Empire is literally good and the explanation of each question is easy to understand, in short it provide really good quality dumps.
Joshua (verified owner) –
I’m happy to share that I successfully passed my 200-301 exam, and all credit goes to Cert Empire. It helped me a lot in my preparation and in passing my exam.
Leonardo (verified owner) –
The pricing of the dumps is affordable, and the quality is excellent. I think it is one of the sites you can trust.
Olivia Evans (verified owner) –
Firstly i wonder why every one have good words for cert empire on Reddit. But after doing preparation from their dump exams then i understand why it is most highly rated.
alexx (verified owner) –
Great
Bhavin (verified owner) –
Worth every penny! These dumps provided me with incredibly helpful content for my CCNA 200-301 exam preparation. I especially liked that they are available in multiple formats and contain up-to-date content, making studying much easier and more effective.
Clark (verified owner) –
This material was a great help. The questions were very similar to the real exam.
Stephanie (verified owner) –
Trustworthy Site………Trustworthy Dumps
Adhita (verified owner) –
These dumps helped me quickly brush up on all the crucial concepts and topics. An excellent resource overall!
Ahmad (verified owner) –
Cert Empire helped me a lot, I’m able to pass my exam.
Scott (verified owner) –
The best and affordable dumps I have ever seen so far.
Scott (verified owner) –
The content inside the dumps is well-defined and well-structured, which I really liked.
Palmer (verified owner) –
Good and well updated dumps
Dorsey (verified owner) –
Easy and comprehensive. I rate these dumps 4 stars because I think some questions could be worded more simply if Cert Empire chooses to.
Dumpboyneverfailagain (verified owner) –
I took my test on April 20th, 2025 but I made the purchase on March 25th, 2025. I was asked 89 questions on the test, out of the expected 120. Of all the questions on my test, maybe 4-5 werent on the dump, which was no big compared to the other 85 questions that were. The dump contained several pages, of about 600+ questions, so i was confident that i’d be able to find SOMETHING on the pdf. It was well worth the $20 or so i spent. Definitely buy this soon if you plan on taking the ccna test. I am satisfied, and yes, i am a real person
Mia (verified owner) –
Good quality dumps, and it’s a trustworthy site because they deliver the dumps instantly after purchase.
Randle (verified owner) –
I previously used dumps from another provider, but they were outdated. Now I’ve used Cert Empire’s dumps, and they are much better and the content is up to date.
Emily Parker (verified owner) –
I used Cert Empire to prepare for my CCNA 200-301 exam after a friend recommended it. I didn’t know much about the exam before, but their materials were clear and helpful. It made studying easier, and I’d say it’s a good resource to check out.
EKnox (verified owner) –
The 200-301 file was quite affordable and really worth it. The content matched the quality of the more expensive options, without any unnecessary extras. It felt like a fair deal for learners who just want solid, well-organized material for Cisco exam prep.