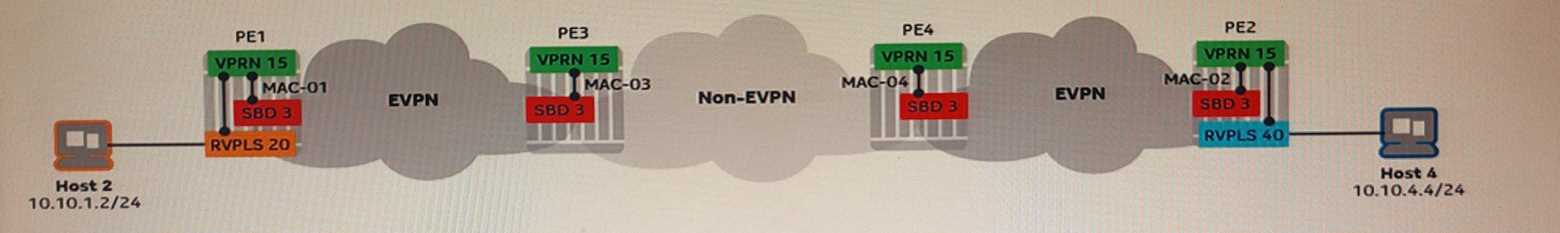
1. Nokia 7x50 SR OS Services Guide, Release 21.10.R1, "EVPN for VXLAN in a VPRN service" section. This section details the interaction between EVPN-IRB and standard VPRN services. It clarifies that routes advertised from the EVPN domain are standard VPN-IPv4 routes to remote PEs. The remote PEs resolve these routes to the BGP next-hop via the transport network, without knowledge of EVPN-specific constructs like overlay indexes.
2. Nokia 7x50 SR OS Services Guide, Release 21.10.R1, "VPRN service overview" section. This section describes the fundamental operation of VPRN services, stating that "When BGP is used to exchange routing information, the PE routers exchange information on a private basis. They use the BGP MPLS VPN extensions (RFC 4364) and the extended BGP community attribute to provide a separate routing information base for each VPN." This confirms that PE3 resolves routes via transport tunnels to the advertising PE.
3. Nokia 4A0-115 Courseware, "Module 4: EVPN and Data Center Interconnect", Section on EVPN Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB). The course material explains that in an EVPN-IRB architecture, the IRB PEs advertise their local subnets into the VPN-IPv4 address family. Remote VPRN PEs receive these advertisements and perform standard L3VPN route resolution to the BGP next-hop. The concept of MAC-OI is presented as a data plane optimization within the IRB PE for forwarding packets to hosts in the EVPN domain.