Q: 1
Refer to the exhibit.
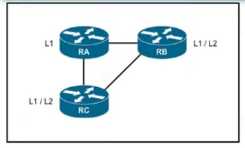
 Routers RA and RB are IS-IS peers configured for NSF but router RC is an IS-IS peer without NSF
capability If RA undergoes processor switchover what is the effect on the network environment?
Routers RA and RB are IS-IS peers configured for NSF but router RC is an IS-IS peer without NSF
capability If RA undergoes processor switchover what is the effect on the network environment?
 Routers RA and RB are IS-IS peers configured for NSF but router RC is an IS-IS peer without NSF
capability If RA undergoes processor switchover what is the effect on the network environment?
Routers RA and RB are IS-IS peers configured for NSF but router RC is an IS-IS peer without NSF
capability If RA undergoes processor switchover what is the effect on the network environment?Options
Discussion
No comments yet. Be the first to comment.
Be respectful. No spam.

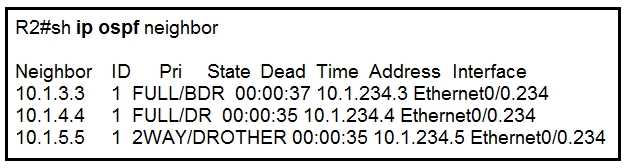 Why is neighbor 10.1.5.5 stuck in “2WAY” state?
Why is neighbor 10.1.5.5 stuck in “2WAY” state?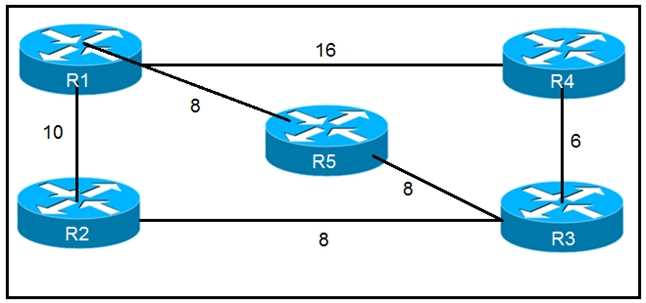 Which router does R1 install as an alternate next hop when trying to reach R3 if LFA is
enabled?
Which router does R1 install as an alternate next hop when trying to reach R3 if LFA is
enabled?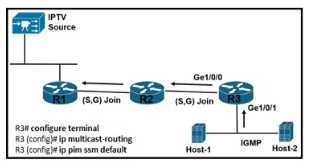 Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is configuring router R3 to handle multicast streams, but
Host-2 cannot send subscriptions messages to the IPTV source. Which configuration must the
engineer apply to router R3 so it passes the IPTV stream to Host-2?
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is configuring router R3 to handle multicast streams, but
Host-2 cannot send subscriptions messages to the IPTV source. Which configuration must the
engineer apply to router R3 so it passes the IPTV stream to Host-2?


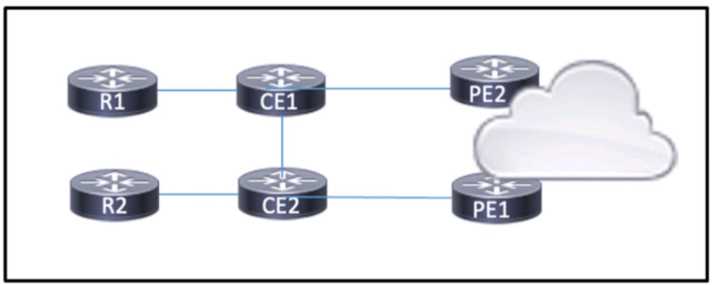 BGP is running on the network, and CE1 currently prefers routes to the internet via PE 1 A network
engineer must manipulate the BGP routes that CE1 receives from PE2 to be more desirable The
engineer configured a route map using MED and applied it on CE1 outbound from PE2. However,
after a BGP soft reset. PE1 is still preferred. Which action must the engineer take so that PE2 is
chosen as the next hop?
BGP is running on the network, and CE1 currently prefers routes to the internet via PE 1 A network
engineer must manipulate the BGP routes that CE1 receives from PE2 to be more desirable The
engineer configured a route map using MED and applied it on CE1 outbound from PE2. However,
after a BGP soft reset. PE1 is still preferred. Which action must the engineer take so that PE2 is
chosen as the next hop?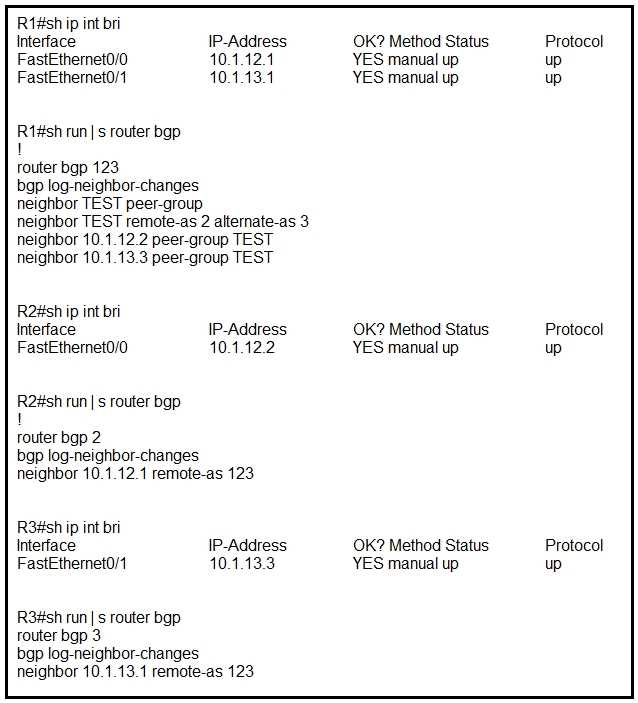 R1 is directly connected to R2 and R3. R1 is in BGP AS 123, R2 is in BGP AS 2, and R3
is in BGP AS 3. Assume that there is no connectivity issue between R1, R2 and R1, R3. Which result
between
BGP peers R1, R2 and R1, R3 is true?
R1 is directly connected to R2 and R3. R1 is in BGP AS 123, R2 is in BGP AS 2, and R3
is in BGP AS 3. Assume that there is no connectivity issue between R1, R2 and R1, R3. Which result
between
BGP peers R1, R2 and R1, R3 is true?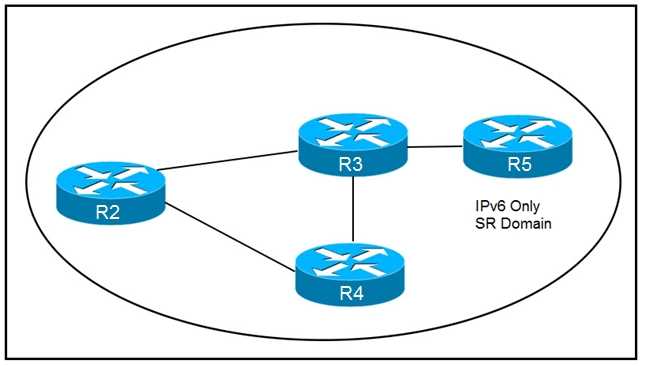 How are packets directed through the data plane when SRv6 is implemented?
How are packets directed through the data plane when SRv6 is implemented?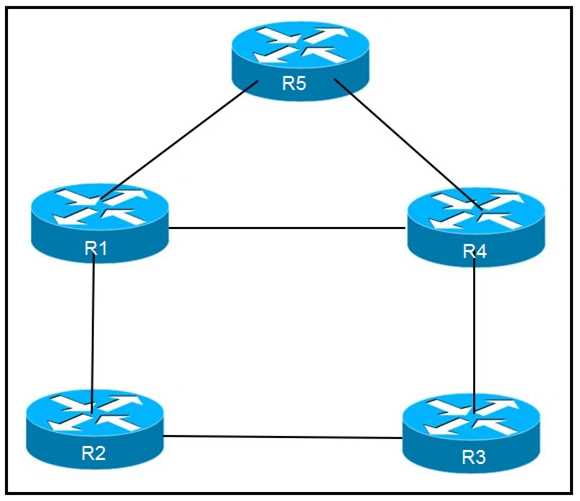 An engineer is addressing an IS-IS design issue which is running within the topology. All
links are running on FastEthernet, except the link between R5 and R4, which is Gigabit Ethernet.
Which statement about the design is true?
An engineer is addressing an IS-IS design issue which is running within the topology. All
links are running on FastEthernet, except the link between R5 and R4, which is Gigabit Ethernet.
Which statement about the design is true?