Cybersecurity within the U.S. defense ecosystem has changed significantly since the introduction of the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). As federal contractors adapt to CMMC 2.0 requirements, the need for certified cybersecurity professionals has increased dramatically. Two certifications now sit at the center of compliance readiness and consulting demand: CMMC Certified Professional (CCP) and CMMC Certified Assessor (CCA).
These credentials define the skill pathways and responsibilities for those working toward Cyber AB-recognized roles, helping organizations meet contractual requirements and maintain eligibility within the Defense Industrial Base (DIB). In 2025, CCP and CCA certifications are not just technical achievements—they have become strategic career accelerators, enabling practitioners to participate in assessments, guide organizations through compliance, and support the expanding CMMC ecosystem.
This article explores how the two certifications differ, what roles they prepare you for, what skills you need, and how they contribute to long-term cybersecurity career growth.
Understanding the CMMC Landscape in 2025
Before comparing CCP and CCA, it’s important to understand how CMMC functions in its current form. CMMC 2.0 focuses on safeguarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Federal Contract Information (FCI) through three maturity levels.
CMMC 2.0 Maturity Levels (2025)
| Level | Focus | Requirement Type | Who Needs It? |
| Level 1 (Foundational) | Protecting FCI | Annual self-assessment | Small DIB suppliers |
| Level 2 (Advanced) | Protecting CUI | Third-party assessment (triennial) or self-assessment (annually, when permitted) | Most defense contractors |
| Level 3 (Expert) | Critical national security information | Government-led assessments | High-risk contractors |
CMMC assessments are conducted by certified assessors under the Cyber AB ecosystem. Organizations preparing for certification often seek guidance from CCP- and CCA-certified professionals to interpret requirements, perform gap analysis, and prepare necessary evidence.
What Is the CMMC Certified Professional (CCP)?
The CCP certification is the entry-level credential for professionals seeking to support CMMC assessments or provide organizational consulting.
CCP Role Overview
A CCP acts as:
- A knowledgeable advisor for organizations preparing for CMMC compliance
- A support resource for formal assessment teams
- A pathway candidate toward becoming a Certified Assessor
- A cybersecurity practitioner with foundational CMMC knowledge
CCP certification validates that you understand CMMC requirements thoroughly enough to assist contractors, consulting firms, and assessment organizations.
CCP Responsibilities in 2025
Core Responsibilities
- Conduct pre-assessment readiness reviews
- Interpret NIST SP 800-171 controls
- Assist with POA&M development
- Support assessment teams under supervision
- Translate technical requirements into business language
- Prepare documentation and evidence packages
Additional Contributions
- Help organizations prepare for Level 1 or Level 2 compliance
- Identify gaps in cybersecurity practices
- Support third-party assessment organizations (C3PAOs)
- Participate in training workshops or governance initiatives
Skills Required for CCP
Technical Skills
- Strong understanding of NIST 800-171
- Knowledge of cybersecurity fundamentals
- Familiarity with risk assessments
- Ability to evaluate policies and procedures
Soft Skills
- Communication and documentation
- Stakeholder alignment
- Compliance interpretation
- Basic project coordination
What Is the CMMC Certified Assessor (CCA)?
The CCA certification is designed for those who want to lead and conduct official assessments. It requires more advanced knowledge, field experience, and technical depth.
CCA Role Overview
A CCA:
- Leads assessment teams under a C3PAO
- Performs detailed evidence evaluation
- Rates cybersecurity implementations against CMMC practices
- Conducts interviews, system reviews, and verification activities
- Ensures organizations meet Cyber AB and DoD assessment standards
CCA is the highest-impact credential in the CMMC workforce ecosystem.
CCA Responsibilities in 2025
Core Responsibilities
- Lead Level 2 CMMC assessments
- Evaluate NIST SP 800-171 implementation maturity
- Perform in-depth technical control analysis
- Validate artifacts, configurations, and logs
- Communicate results to contractors and the Cyber AB
Assessment Process Duties
- Conduct planning and scoping workshops
- Perform system and process evaluations
- Review documentation and evidence
- Score and report assessment findings
- Guide contractors through remediation period
Skills Required for CCA
Technical Skills
- Deep understanding of NIST SP 800-171 / 800-172
- Expertise in cybersecurity frameworks
- Familiarity with system security plans (SSP)
- Ability to analyze logs, artifacts, and configurations
- Understanding of incident response, access control, encryption, and network security
Soft Skills
- Interviewing and verification
- Assessment leadership
- Advanced report writing
- Decision-making under regulatory constraints
Key Differences Between CCP and CCA
Below is a clear, structured comparison table.
CCP vs CCA (2025)
| Category | CCP (Certified Professional) | CCA (Certified Assessor) |
| Purpose | Entry-level certification for advisory and support roles | Mid- to senior-level credential for conducting formal CMMC assessments |
| Who It’s For | Consultants, analysts, IT staff, compliance professionals | Assessors, auditors, cybersecurity specialists |
| Exam Difficulty | Moderate | High |
| Experience Needed | Basic IT/cybersecurity | Strong technical & assessment experience |
| Role in Assessments | Support | Lead & perform evaluations |
| Required for C3PAOs? | Optional | Mandatory |
| Career Growth Path | Toward assessor or consultant roles | Senior assessor, C3PAO lead, program manager |
| Annual Demand in 2025 | Very high | Extremely high |
| Certification Validity | 3 years | 3 years |
How CMMC CCP and CCA Certifications Fit Into Cyber AB Pathways
Cyber AB (the governing body) defines the certification ecosystem. Both CCP and CCA fit into this architecture.
The Cyber AB Ecosystem Structure
CCP → CCA Level 1 → CCA Level 2 → C3PAO Assessor → Lead Assessor / Program Lead
- CCP acts as the entry point.
- CCA is the credential that qualifies professionals to participate in official assessments.
- Assessors typically work under certified assessment organizations (C3PAOs).
Career Growth Benefits of Holding CCP and CCA in 2025
The CMMC ecosystem is expanding rapidly as compliance becomes mandatory for thousands of contractors. Certified professionals hold a strong competitive advantage.
CCP Career Opportunities
CCP Opens Careers In:
- CMMC readiness consulting
- Cybersecurity governance
- Compliance documentation roles
- Contractor advisory positions
- Risk assessment support
CCP is ideal for someone who wants to enter the compliance sector without becoming a full assessor.
CCA Career Opportunities
CCA Enables Roles Such As:
- Lead assessor within a C3PAO
- Cybersecurity program consultant
- Federal compliance auditor
- Governance, risk, and compliance leader
- Compliance operations specialist
CCA-certified professionals are among the highest-demand cybersecurity specialists in the DIB.
Salary Outlook for CCP and CCA in 2025
The compensation difference between CCP and CCA reflects their responsibilities.
Data Table — Salary Ranges
| Role | Average Salary (2025) | Range |
| CCP | $92,000 | $70,000–$120,000 |
| CCA Level 1 | $126,000 | $110,000–$150,000 |
| CCA Level 2 | $142,000 | $120,000–$170,000 |
| CCA Senior Assessor | $168,000 | $145,000–$190,000 |
CCA salaries trend higher due to the technical depth and regulatory oversight involved.
CCP and CCA Exam Requirements
CCP and CCA follow different exam formats, prerequisites, and core knowledge areas.
CCP Exam Details
Requirements
- Recommended knowledge of cybersecurity fundamentals
- CMMC fundamentals understanding
- Experience with compliance or IT roles (optional but useful)
Exam Structure
- Scenario-based questions
- Multiple choice
- Interpretation of compliance controls
- Understanding of NIST SP 800-171
CCA Exam Details
Requirements
- Must hold valid CCP
- Background in cybersecurity, auditing, or systems engineering
- Experience in assessment activities
Exam Structure
- Deep technical assessment scenarios
- Evidence interpretation
- Artifact analysis
- Cybersecurity threat modeling
- CMMC practice application
The CCA exam is significantly more demanding.
Why Organizations Hire CCPs and CCAs in 2025
Demand for CMMC-certified professionals continues to rise as Cyber AB assessment requirements mature. Contractors preparing for CMMC compliance need guidance long before formal assessments occur. Meanwhile, C3PAOs require assessors with deep technical and auditing expertise.
Why Companies Hire CCPs
Organizations value CCP-certified professionals because they:
Support Early-Stage Compliance
CCPs help contractors perform gap assessments, interpret requirements, and understand how to align their cybersecurity environment to CMMC 2.0.
Reduce Pre-Assessment Costs
Contractors avoid costly rework by resolving foundational issues before a CCA-led assessment.
Improve Documentation Quality
CCPs assist with building strong:
- SSPs
- POA&Ms
- Network diagrams
- Policy frameworks
- Evidence documentation
Enable Faster Assessment Readiness
By handling preliminary compliance work, CCPs shorten the contractor’s timeline to achieve certification.
Why Companies Hire CCAs
CCA-certified professionals play a more specialized role:
Perform Official CMMC Assessments
Only CCAs can execute assessments under a C3PAO for Level 2 organizations.
Provide High-Level Compliance Expertise
They understand the technical depth necessary to evaluate control implementations.
Validate Evidence and Security Practices
CCAs verify that a contractor’s cybersecurity program meets the maturity and technical standards required.
Reduce Compliance Risk
Organizations rely on CCAs to ensure their security practices stand up to federal scrutiny.
Decision Framework — Should You Pursue CCP or CCA?
Choosing between CCP and CCA depends on your background, goals, and preferred career path.
CCP vs CCA Pathway
| Question | Best Answer = CCP | Best Answer = CCA |
| Do you want to support compliance efforts? | ✔ | — |
| Do you want to lead official assessments? | — | ✔ |
| Are you new to cybersecurity or GRC? | ✔ | — |
| Do you prefer advisory or consulting roles? | ✔ | — |
| Do you enjoy deep technical analysis? | — | ✔ |
| Do you want to work for a C3PAO? | Optional | Highly recommended |
| Are you looking for advanced career growth? | ✔ | ✔✔ |
| Do you prefer leadership roles in the assessment ecosystem? | — | ✔ |
Visual Decision Chart: CCP or CCA?
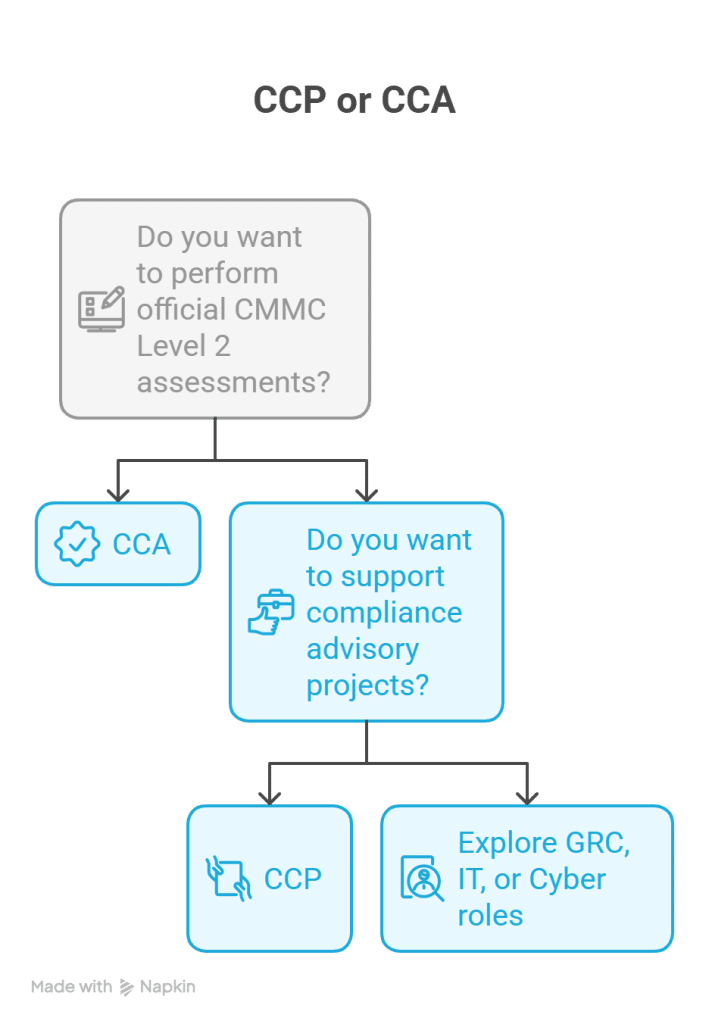
This framework gives beginners and intermediates a clear sense of which certification aligns with their goals.
Industry Demand for CCP and CCA in 2025
CMMC adoption has accelerated throughout 2024 and into 2025. Federal contracts increasingly require proof of compliance, especially for Level 2 contractors.
Demand Drivers
1. Mandatory CMMC 2.0 Requirements
Organizations cannot bid on or maintain certain DoD contracts without CMMC compliance.
2. Increase in Third-Party Assessments
Thousands of contractors require official evaluations—creating massive demand for CCAs.
3. Shortage of Skilled Assessors
The industry faces a talent shortage for:
- Qualified CCA personnel
- Cybersecurity analysts with CMMC knowledge
- GRC professionals who can interpret NIST frameworks
4. Growth in GRC Consulting Firms
Consulting firms rely on CCPs to scale their teams, manage clients, and support readiness assessments.
Demand Comparison Table
| Job Title | Current Demand (2025) | Projected Growth (2026–2028) |
| CCP Consultant | Very High | Steady↑ |
| CCP Analyst | High | Moderate↑ |
| CCA Level 1 Assessor | Extreme | Rapid↑↑ |
| CCA Level 2 Assessor | Critical Shortage | Very Rapid↑↑↑ |
| Senior CCA Lead | Severe Shortage | High↑ |
CCA remains the most in-demand role, especially as more organizations seek Level 2 certification.
Training and Preparation Roadmap for CCP and CCA
CCP and CCA require structured learning paths. Below is a human-friendly roadmap.
CCP Roadmap
Step 1 — Understand CMMC 2.0 Framework
Learn the maturity levels, assessment types, and control structure.
Step 2 — Study NIST SP 800-171
This is the backbone of CMMC Level 2.
Step 3 — Learn Governance and Documentation Practices
Understand SSPs, POA&Ms, and evidence management.
Step 4 — Train With Official CCP Course Material
Follow the Certified Professional curriculum.
Step 5 — Practice Scenario Analysis
CCP exams include scenario-based evaluation.
Step 6 — Join CMMC Community Groups
This builds networking and real-world awareness.
Many professionals supplement their preparation using online CMMC-CCP exam questions and CMMC-CCA exam questions found through platforms like certempire.com.
CCA Roadmap
Step 1 — Become a CCP First
CCA requires CCP completion.
Step 2 — Deep Study of NIST SP 800-171 and 800-172
CCA exam questions go deeper into technical requirements.
Step 3 — Learn Assessment Methodologies
Understand how cybersecurity audits are performed.
Step 4 — Master CMMC Assessment Procedures (CAP)
Learn scoping, sampling, evidence collection, and reporting.
Step 5 — Build Technical Breadth
Cover IAM, encryption, logging, incident response, and network security.
Step 6 — Practice Artifact Evaluation
Review mock artifacts such as:
- Log files
- Configuration outputs
- Policy evidence
- Network architecture diagrams
Step 7 — Join a C3PAO or Consulting Firm
Real-world experience strengthens your assessment judgment.
Why CCP and CCA Certifications Are Critical for the Future of Federal Cybersecurity
As cyber threats evolve and federal systems become more interconnected, the need for skilled cybersecurity professionals grows. CCP and CCA certifications ensure:
- Controlled Unclassified Information is protected
- Contractors maintain strong cyber hygiene
- Federal supply chains remain secure
- Organizations adopt security-by-design practices
In 2025, these roles are essential to supporting national defense infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Do I need CCP before becoming CCA?
Yes. CCP certification is a prerequisite for the CCA pathway.
Is CCP enough to consult organizations on CMMC readiness?
Yes, CCP equips professionals with the knowledge to guide contractors through preparation stages.
How difficult is the CCA exam compared to CCP?
CCA is significantly more technical and scenario-driven, requiring deeper knowledge and experience.
Can I join a C3PAO as a CCP?
Yes, but you can only support assessments—not lead them—until you obtain CCA.
Which certification leads to higher salary potential?
CCA offers higher earning potential due to its role in official assessments.
Conclusion
The path to CMMC certification is complex, but CCP and CCA roles create a structured roadmap for professionals seeking to support or lead Cyber AB assessments. These credentials build foundational and advanced expertise that align cybersecurity practices with federal expectations. As organizations continue to prioritize security and compliance in 2025, CCP- and CCA-certified professionals play a pivotal role in safeguarding national supply chains and enabling trustworthy defense operations. Whether you choose the advisory route or the assessor pathway, both certifications open doors to meaningful and high-demand career opportunities.
Resources
- Cyber AB Official Website — https://cyberab.org
- DoD CMMC Program Site — https://dodcio.defense.gov/CMMC/
- NIST SP 800-171 Framework — https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-171/rev-2/final
- NIST SP 800-172 Enhanced Security Requirements — https://csrc.nist.gov
- CMMC Assessment Process (CAP) Guide — https://cyberab.org/assessment
Last Updated on by Team CE