TL;DR – Quick Summary
Cybersecurity certifications in 2025 aren’t just resume boosters; they’re career accelerators. If you’re new to the field, start with CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) to cover the fundamentals of risk, identity, cloud, and compliance. If you already work in IT, consider advancing your skills with CEH or CySA+, depending on whether you prefer an offensive or defensive approach. For leadership roles, CISSP and CISM remain the gold standards. Specialized tracks like CCSP or GCIH are worth pursuing once you’ve built a foundation.
👉 Bottom line: The right certification depends on your background, career goals, and timeline. Choose strategically, not by hype.
Introduction – Why Certifications Matter More in 2025
Cybersecurity is no longer an optional skill; it’s the backbone of modern business. By 2025, global cybercrime costs are projected to hit $10.5 trillion annually, making trained professionals some of the most sought-after experts worldwide.
But here’s the catch: most employers don’t just want “IT people with some security experience.” They want credentials that prove you understand frameworks, compliance, and technical depth. That’s where certifications step in.
Whether you’re just starting in IT, pivoting from another career, or aiming for a leadership role, certifications are your fastest way to:
- Validate your skills against global standards.
- Stand out in job applications where HR filters for “Security+, CISSP, or CEH required.”
- Unlock higher salary bands (many certs add $10K–$30K annually).
- Stay current in a field that evolves faster than most degrees.
In this guide from Cert Empire, we’ll walk through the best cybersecurity certifications in 2025, break down their difficulty, cost, and ROI, and help you decide which one fits your career journey.
Career Stage vs Certifications
| Career Stage | Recommended Certifications | Purpose |
| Beginner (0–2 yrs) | Security+ (SY0-701), Network+ | Build fundamentals, meet DoD requirements |
| Intermediate (2–5 yrs) | CEH, CySA+, CISA, CCNP Security | Gain specialized skills, prove expertise |
| Advanced (5+ yrs) | CISSP, CISM, CISA | Leadership, governance, enterprise credibility |
| Specialization | CCSP, OSCP, AWS/Azure Security, GCIH | Deep niche expertise (cloud, pen test, IR) |
You don’t have to navigate this journey alone, our comprehensive cybersecurity career path guide helps you align certifications with the roles you want to land.
The Cybersecurity Job Market in 2025
Before we talk about certs, let’s set the stage.
- Job Growth: Cybersecurity roles are expected to grow 33% between 2023 and 2033, much faster than the average for all occupations.
- Talent Gap: There are still over 3.5 million unfilled jobs worldwide, a number that hasn’t budged much in recent years.
- Salary Boosts: Entry-level analysts average around $80K–$95K in the U.S., while experienced consultants and architects often clear $150K–$180K.
- AI & Cloud Pressure: Employers are hungry for professionals who can handle zero trust, automation, cloud-native security, and AI-driven threats.
This means the certification you choose today isn’t just about passing an exam, it’s about proving to employers that you can protect their business against tomorrow’s risks.
Beginner-Friendly Certifications
If you’re brand new to cybersecurity or coming from another IT role, the best strategy is to start with an entry-level certification. These certs don’t require years of work experience, but they prove you have the fundamentals.
CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701)
This is the certification most people start with and for good reason.
- Why it matters: Security+ is DoD 8570 compliant, globally recognized, and covers core areas like risk management, IAM (Identity & Access Management), incident response, and cloud/IoT security.
- What’s new in SY0-701: More emphasis on cloud, zero trust, automation, and performance-based questions (PBQs) compared to older versions.
- Who it’s for: Beginners, career changers, and IT pros looking to step into cybersecurity roles.
- Time to prepare: 2–3 months with steady study (60–100 hours).
- Job roles it supports: SOC Analyst, Security Administrator, Help Desk Manager, IT Auditor.
📌 Pro tip: Don’t treat Security+ as a “check-the-box” exam. The PBQs test real-world scenarios, so focus on CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 exam preparation with hands-on labs, not just flashcards. Also, many learners still compare exam versions and ask Is Security+ 701 easier than 601? A detailed breakdown helps clarify why the newer version is more challenging yet far more relevant for today’s roles.
(ISC)² SSCP (Systems Security Certified Practitioner)
The SSCP is sometimes called the “mini-CISSP.”
- Why it matters: It’s a step above Security+, designed for IT professionals with at least one year of experience.
- Focus areas: Access controls, incident response, cryptography, and secure infrastructure.
- Who it’s for: Junior admins, system engineers, or IT staff moving into security roles.
- Job roles it supports: Security Analyst, Systems Engineer, Database Admin, Junior Consultant.
SSCP is particularly useful if you want a credential from (ISC)²’s SSCP certification program (the same body that offers CISSP) but aren’t ready for the full CISSP commitment.
GIAC Security Essentials (GSEC)
GIAC certifications have a reputation for being rigorous and respected.
- Why it matters: Validates practical security knowledge across active defense, network security, cryptography, and cloud.
- Who it’s for: IT professionals with some background in networking or system administration.
- Job roles it supports: Security Engineer, Forensics Analyst, Security Administrator.
- Downside: At around $999, it’s pricier than Security+, making it better if your employer is footing the bill.
If you’re looking for low-barrier entries to cybersecurity, check out our overview of the easiest cybersecurity certifications that give you fast foundational wins.
Intermediate-Level Certifications
Once you’ve covered the basics (typically after Security+ or equivalent), you’ll want to specialize slightly either in defense, offense, or auditing.
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
Think like a hacker, legally.
- Why it matters: CEH is the most recognized “ethical hacking” credential. It shows you can probe systems, find vulnerabilities, and advise on fixes.
- Who it’s for: Aspiring penetration testers, red team members, or anyone moving into offensive security.
- Requirements: 2 years of IT security experience (or EC-Council’s official training).
- Cost: $950–$1199 depending on the testing center.
- Job roles it supports: Pen Tester, Threat Analyst, Cybersecurity Engineer.
💡 Reality check: Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) exam preparation is a strong entry point into offensive security, but employers may prefer OSCP for hardcore pen-testing roles. Still, CEH opens many doors.
CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst (CySA+)
If CEH is an offense, CySA+ is a defense.
- Why it matters: Focuses on threat detection, analytics, and proactive defense. You’ll learn SIEM tools, vulnerability management, and how to hunt threats.
- Who it’s for: Analysts working in a SOC, or IT pros pivoting into monitoring/response roles.
- Time to prepare: 2–3 months, especially if you’ve done Security+.
- Job roles it supports: SOC Analyst, Threat Hunter, Security Operations Specialist.
CompTIA CySA+ certification training is often underrated, but it’s a great way to show employers you can work hands-on with logs, alerts, and SIEM dashboards.
Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
Security isn’t just about tools, it’s also about compliance and controls. That’s where CISA shines.
- Why it matters: One of the most recognized certs for auditing, governance, and compliance.
- Who it’s for: IT professionals pivoting into audit/GRC work.
- Requirements: 5 years of IS audit/control/security experience (waivers available for degrees or other certs).
- Cost: $575–$760.
- Job roles it supports: IT Auditor, Compliance Manager, Risk Analyst.
CISA certification details are especially powerful if you’re targeting finance, healthcare, or government sectors, where regulatory frameworks dominate.
Advanced Certifications
These are the certifications that separate practitioners from strategists. They usually require 5+ years of experience and prove you can handle enterprise-level security programs.
CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional)
The gold standard.
- Why it matters: CISSP proves you can design, implement, and manage large-scale security programs. Many senior roles require it by default.
- Requirements: 5 years of cumulative paid experience in at least two domains (waivers available).
- Cost: $749.
- Job roles it supports: Security Architect, Senior Consultant, CISO, Security Director.
- Average salary bump: Often puts professionals into the $130K–$160K+ range.
CISSP certification requirements aren’t just an exam—it’s a career milestone. If you want to lead teams, work with executives, or become a consultant, this cert is essential.
CISM (Certified Information Security Manager)
If CISSP is about breadth, CISM is about leadership.
- Why it matters: Focuses on governance, risk management, and security program leadership.
- Who it’s for: IT managers, consultants, and professionals aiming for management-heavy roles.
- Requirements: 5 years of IS management experience (with some waivers available).
- Cost: $575–$760.
- Job roles it supports: IT Manager, Risk Consultant, Director of Information Security.
CISM is highly valued when you want to shift from being the “doer” to the “decision-maker.”
Not all certifications are created equal. If you’re up for a real challenge, learn which are considered the hardest cybersecurity certifications, and whether they’re worth the effort.
Specialized Certifications in 2025
Not every cybersecurity career follows the same path. Once you’ve covered the basics and maybe earned an intermediate cert, it’s time to specialize. Specialized certifications signal deep expertise in a niche area and they often come with premium salaries.
CCSP (Certified Cloud Security Professional)
Cloud is no longer optional, it’s the backbone of enterprise IT.
- Why it matters: CCSP is the gold standard for cloud security, offered by (ISC)². It covers cloud architecture, governance, risk, and compliance.
- Who it’s for: Professionals securing AWS, Azure, or GCP environments.
- Requirements: 5 years of IT experience, including 3 in security, and 1 in cloud. (Waivers exist if you already hold CISSP.)
- Cost: $599.
- Job roles supported: Cloud Security Architect, Cloud Engineer, Security Consultant.
📌 Pro tip: CCSP certification guide pairs best with CISSP. Many employers see the duo as the perfect blend of enterprise + cloud expertise.
GCIH (GIAC Certified Incident Handler)
The frontline defender’s certification.
- Why it matters: Validates skills in detecting, responding to, and containing attacks. Covers hacker exploits, forensics, and incident management.
- Who it’s for: Incident responders, SOC leads, red teamers transitioning into IR.
- Requirements: None formally, but you’ll need strong networking/security basics.
- Cost: $999.
- Job roles supported: Incident Handler, Security Engineer, Threat Hunter.
This cert is especially valuable as AI-driven threats and ransomware continue to dominate. Employers want proof you can respond effectively.
Other High-Value Specializations
- OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional): Hardcore pen testing cert. Known for its 24-hour practical exam. Employers respect it because it proves hands-on skill, not just theory.
- AWS Certified Security – Specialty / Azure Security Engineer Associate: Vendor-specific cloud certs. Strong ROI if your company relies heavily on a single cloud provider.
- DFIR (Digital Forensics & Incident Response) certs: Growing demand as breaches become more complex. Useful for consultants and forensic analysts.
- CISA + CISM combo: For GRC and audit-heavy careers, this pairing builds strong credibility with executives.
Average Study Hours per Certification
| Certification | Estimated Study Hours | Timeframe (Typical) |
| Security+ | 60–100 hours | 8–12 weeks |
| CySA+ / CEH | 80–120 hours | 10–14 weeks |
| CISSP | 200–300 hours | 3–6 months |
| CISM / CISA | 150–200 hours | 3–5 months |
| CCSP | 120–150 hours | 2–4 months |
| OSCP | 300+ hours | 4–6 months (lab-heavy) |
How to Choose the Right Certification (Decision Framework)
Here’s the mistake many professionals make: they collect certifications without a strategy. You don’t need 10 certs, you need the right 2–4 that align with your career goals.
Think of it like this: What role do you want in 2–3 years? Then build backward.
If You’re a Beginner (No IT Experience)
- Start with Security+ (SY0-701).
- Learn the fundamentals of networking and Linux.
- After 6–12 months, aim for CySA+ or SSCP.
This path sets you up for SOC Analyst, Security Administrator, or Help Desk Manager with security focus.
If You’re Pivoting from IT (SysAdmin, Help Desk, Networking)
- Start with Security+ to validate your security knowledge.
- Move into CySA+ (defense) or CEH (offense).
- After 3–5 years, pursue CISSP or CISM.
This path moves you from technician → analyst → consultant/manager.
If You’re Aiming for Penetration Testing / Red Teaming
- Start with Security+ (always).
- Move into CEH for a recognized entry point.
- Add OSCP to prove hardcore hands-on ability.
This is the fastest way into ethical hacking roles, with OSCP being the differentiator.
If You’re Targeting Audit, Governance, or Compliance (GRC)
- Start with Security+.
- Earn CISA (audit) → CISM (management).
- Add CISSP if you want enterprise credibility.
This is the path to compliance consulting, risk analyst, or governance manager roles.
If You Want Cloud Security Specialization
- Start with Security+ (for fundamentals).
- Earn CCSP or a vendor-specific cert (AWS, Azure, GCP).
- Layer it with CISSP later for maximum ROI.
This is one of the highest-paying specialties in 2025.
Time, Cost, and ROI of Certifications
One of the top questions readers have is: “How long will this take, and is it worth it?” Let’s break it down honestly.
Time Investment (Average Study Hours)
- Security+: 60–100 hours (8–12 weeks).
- CEH / CySA+: 80–120 hours (10–14 weeks).
- CISSP: 200–300 hours (3–6 months).
- CISM / CISA: 150–200 hours each.
- CCSP: 120–150 hours.
- OSCP: 300+ hours (lab-heavy, hands-on).
Cost (Exam Fees Only)
- Security+: $425
- CEH: $950–$1199
- CySA+: $392
- CISSP: $749
- CISM / CISA: $575–$760 each
- CCSP: $599
- OSCP: $1599+ (includes lab access)
📌 Keep in mind: most employers reimburse exam fees, always ask.
ROI (Return on Investment)
Certifications don’t guarantee jobs, but they do:
- Unlock higher salary brackets.
- Security+ can take you from $60K → $80K–$95K.
- CISSP often boosts mid-career pros from $100K → $140K+.
- Security+ can take you from $60K → $80K–$95K.
- Clear HR filters.
- Many job postings require Security+ or CISSP just to apply.
- Many job postings require Security+ or CISSP just to apply.
- Accelerate promotions.
- Adding CISM can fast-track you into management roles.
- Adding CISM can fast-track you into management roles.
- Support consulting/freelance income.
- With CISSP + CCSP, consultants often bill $100–$200/hour.
👉 Smart sequencing (Security+ → CySA+ → CISSP) can yield a 3–5x ROI in salary within 3–6 years.
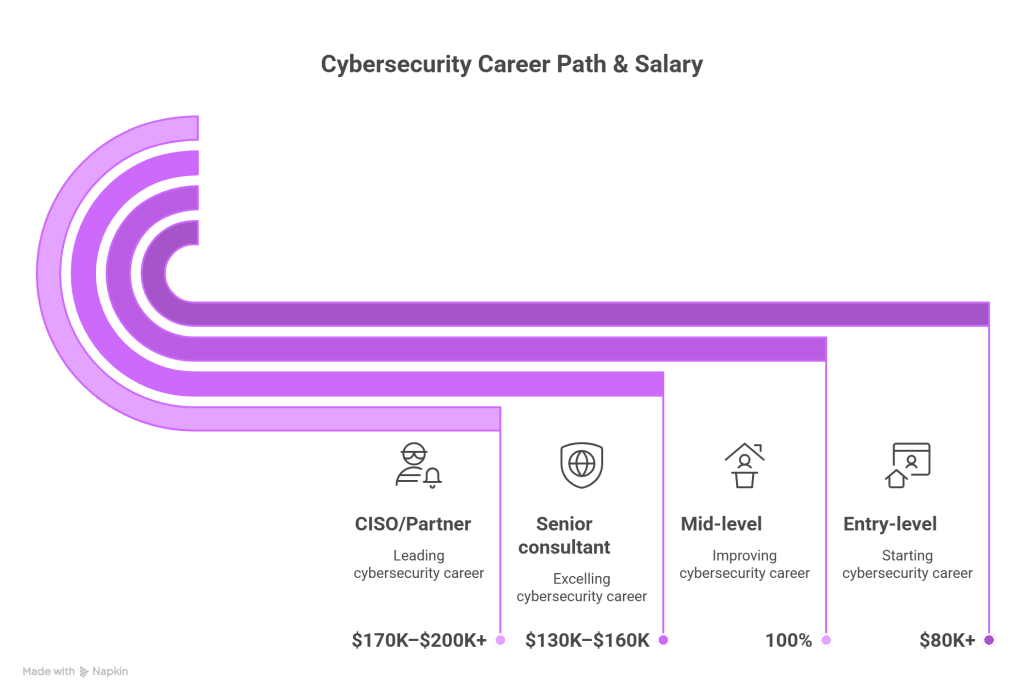
Salary Expectations by Role (2025)
| Role / Level | Average Salary (US) |
| Entry-Level Analyst (Security+) | $80K–$100K |
| Pen Tester / Risk Specialist (CEH, CySA+) | $100K–$120K |
| Senior Consultant / Architect (CISSP, CISM) | $130K–$160K |
| Principal / CISO / Partner | $170K–$200K+ |
Cybersecurity consultants often bill a premium, many command $100K–$200K+ as freelancers or permanent hires. Explore real-world roles and earning potentials in our deep dive on the highest-paying cybersecurity jobs.
A 90-Day Starter Roadmap (For New Learners)
If you’re reading this thinking “where do I start?” – here’s a practical plan.
- Weeks 1–2: Learn basics of networking (TCP/IP, subnets), Linux commands, IAM concepts.
- Weeks 3–6: Study Security+ content. Break it into domains: risk, IAM, cloud, network security.
- Weeks 7–8: Do practice tests and performance-based questions (PBQs). Identify weak spots.
- Weeks 9–10: Book the exam. Keep reviewing labs and scenarios.
- Weeks 11–12: While waiting for results, research your next step (CySA+ if defense, CEH if offense).
This keeps you from stalling and ensures momentum into your next certification.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Do I really need a degree to work in cybersecurity?
No. While a degree can help waive some certification requirements (like CISSP or CISM), many professionals enter the field with certifications + experience only. Employers increasingly prioritize skills and credentials over formal degrees.
2. Which certification should I start with if I have no IT background?
CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) is the best entry point. It covers essential concepts like risk, IAM, and cloud security. From there, you can move into CySA+ (defense) or CEH (offense).
3. Is CISSP still worth it in 2025?
Absolutely. CISSP remains the gold standard for senior-level roles. Employers use it as a benchmark when hiring for consultants, architects, and CISOs. If you want to lead teams or manage enterprise security, CISSP is almost mandatory.
4. How long does it take to become a cybersecurity consultant?
On average, 4–6 years. That includes:
- 1–2 years building IT foundations.
- 1–2 years in entry-level security roles.
- 2–3 years earning advanced certs like CISSP or CISM.
With dedication (and the right certs), some professionals shorten this timeline to 3–4 years.
5. Can I work remotely as a cybersecurity consultant?
Yes. Many consulting roles are fully remote, especially in compliance, auditing, and incident response. Pen testing and cloud security consulting are also highly remote-friendly.
6. What’s the hardest certification to pass?
OSCP (for pen testing) is widely considered the toughest because it’s a 24-hour hands-on exam. CISSP is also challenging due to its breadth, requiring mastery across 8 domains.
Career Paths and Salaries (Explained in Text)
Cybersecurity salaries vary widely based on role, certification level, and region. Here’s a breakdown:
- Entry-Level Roles (Security+ level): Security Analysts, SOC Analysts, or SysAdmins with a security focus typically earn $80K–$100K. This is the first big step after breaking into the field.
- Mid-Level Roles (CySA+, CEH, CISA): Analysts, Pen Testers, Risk Specialists often move into the $100K–$120K range. These certs prove you can execute specialized work.
- Advanced Roles (CISSP, CISM): Security Architects, Senior Consultants, or Managers average $130K–$160K. These are the certifications that move you from technician → leader.
- Principal / Partner Level (CISSP + CCSP / CISM + specialization): Consultants, CISOs, and Directors regularly see $170K–$200K+, often with bonuses and equity.
📌 Regional Variations:
- San Francisco, New York, and London markets tend to pay 15–25% higher.
- Remote consulting often allows you to bill $100–$200/hour, especially with CISSP or CCSP.
Final Verdict – Choosing the Right Cybersecurity Certification in 2025
The certification landscape in 2025 can feel overwhelming. With dozens of acronyms – CISSP, CISM, CEH, CCSP, CySA+, how do you choose the right one?
The answer: map your certifications to your career goals.
- If you’re a beginner, start with Security+.
- If you’re aiming for defense work, pursue CySA+ → CISSP.
- If you’re drawn to ethical hacking, build CEH → OSCP.
- If you want to lead or manage, go CISM + CISSP.
- If you love cloud or consulting, CCSP is your best bet.
Certifications aren’t just about passing exams, they’re about building trust with employers and clients. They prove you’re committed, current, and capable of handling evolving threats.
By 2025, organizations need consultants who combine technical depth, compliance knowledge, and leadership skills. If you follow a structured roadmap, earning Security+, leveling up with CySA+/CEH, and finally adding CISSP or CISM – you’ll not only secure a high-paying, future-proof career, but also position yourself as a trusted advisor in a field that’s exploding with demand.
👉 Many professionals preparing for Security+, CEH, or CISSP rely on Cert Empire’s updated exam dumps to study smarter and align with the latest exam objectives. Practicing with updated questions gives you the confidence to pass on your first attempt and move one step closer to your career goals.
Cybersecurity consulting isn’t just about defending systems; it’s about shaping the future of digital trust. If you start now, you can be one of the professionals leading that change.
Last Updated on by Team CE