If you’re stuck between CISM and CISSP, it’s one of those choices in cybersecurity that sounds simple but keeps looping in your head the more you think about it. Both certs have crazy weight in the industry. Both can change your career track fast.
But they are built for different types of security pros and figuring out which one matches your skills, your mindset, and your goals in 2026 could save you months (or even years) of going in circles. So let’s break it down properly, without the marketing noise, and get you some real answers.
Comparison
| Aspect | CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) | CISM Exam (Certified Information Security Manager) |
| Offered By | (ISC)² (International Information System Security Certification Consortium) | ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) |
| Focus Area | Technical and managerial aspects of cybersecurity | Governance, risk management, and information security management |
| Ideal For | Security practitioners, engineers, consultants, and managers | IT managers, security managers, and governance professionals |
| Experience Requirement | 5 years in 2 or more of the 8 CISSP domains | 5 years in information security management, with 3 years in management roles |
| Domains Covered | 8 domains (e.g., Security & Risk Management, Security Architecture, etc.) | 4 domains (e.g., Information Security Governance, Risk Management, etc.) |
| Exam Format | Computer Adaptive Test (CAT); 100–150 questions; 3 hours | 150 multiple-choice questions; 4 hours |
| Passing Score | 700 out of 1000 | 450 out of 800 |
| Renewal Requirements | Earn 120 CPE credits over 3 years and pay annual maintenance fees | Earn 120 CPE credits over 3 years and pay annual maintenance fees |
| Average Salary | Higher globally; around $120,000+ (varies by location) | Also high; around $110,000+ (varies by location) |
| Difficulty Level | Considered more technical and broader in scope | More management and governance-focused |
The Evolving Demand for CISSP Certification for Cybersecurity Professionals
Cyber threats today aren’t jokes. Data leaks, ransomware takeovers, cloud breaches. They’re hitting hospitals, banks, startups, even city governments. Companies aren’t playing around anymore. They want pros who can handle chaos and ensure data security by setting up bulletproof systems before the chaos even starts.
CISSP professionals are getting pulled into more types of projects than ever:
- Cloud migrations that need security from Day 1
- Third-party vendor risk assessments
- Incident response teams cleaning up after a breach
- Policy overhauls to meet international data laws
Companies used to treat security like a “tech thing.” Now it’s a business priority. Boards of Directors are actually asking questions about cybersecurity budgets. That’s where having a CISSP in the room makes all the difference. It’s like being the translator between hardcore tech teams and executive decision-makers, especially when discussing cism and cissp certifications .
By 2026, the demand is so hot that CISSP-certified folks aren’t just getting job offers, they’re getting counteroffers. If you’re planning to take the exam soon, this Ultimate CISSP Exam Guide for 2026 walks you through everything from domains to study timelines and first-time pass strategies. Companies don’t want to lose people who have that cert stamped on their profiles.
In plain words:
If you’ve got job roles like CISSP under your belt, you’re holding a golden ticket in cybersecurity hiring today.
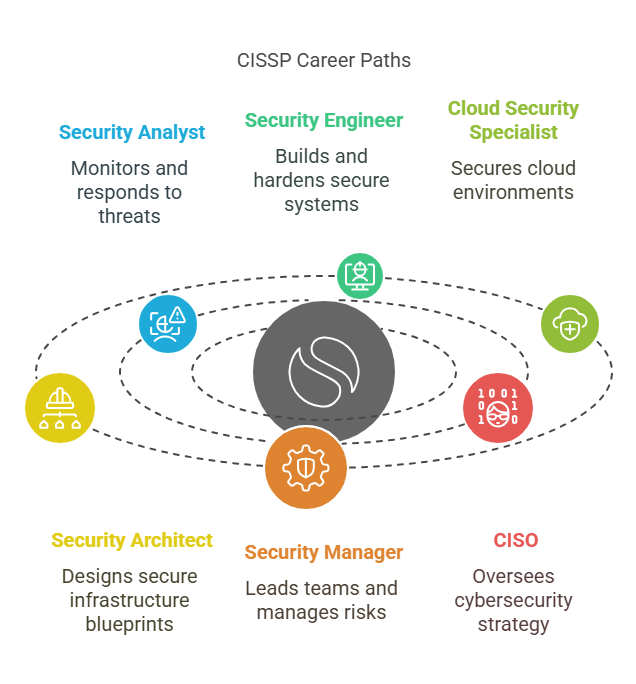
Roles and Responsibilities You Can Expect After CISSP
CISSP doesn’t lock you into one boring job title. It actually opens a lot of doors depending on what you’re into.
Common Roles for CISSP Holders often involve security assessment tasks.
- Security Analyst — monitoring, investigating, responding to threats
- Security Engineer — building secure systems, hardening networks
- Cloud Security Specialist — securing AWS, Azure, GCP environments
- Security Architect — designing the entire blueprint of secure infrastructures
- Security Manager — leading teams, setting security policies, managing risks
- CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) — the ultimate boss of cybersecurity at a company
Typical Responsibilities:
- Setting up security frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST, etc.
- Handling compliance reports for audits and certifications
- Running vulnerability scans and penetration testing exercises
- Responding to incidents like breaches, ransomware attacks, phishing takeovers
- Designing access control, encryption protocols, secure software development processes
Industries Actively Hiring CISSP-Certified Experts
The days when only banks and defense firms cared about security are long gone. Now, almost every industry is desperate for good cybersecurity folks to help build a robust information security program .
Industries Hiring CISSP Pros Like Crazy in 2026:
Finance and Banking:
Always the goldmine for CISSP jobs. Banks, credit unions, trading platforms. They’re all battling hackers daily. Finance firms want people who can secure customer data, transaction systems, and regulatory compliance without blinking.
Healthcare and Biotech:
Patient data is one of the hottest black market commodities. HIPAA violations can tank hospitals overnight. That’s why healthcare chains are investing serious cash into software development security programs and security operations run by CISSP-certified experts.
Tech Companies:
From small SaaS startups to cloud giants, if it has servers or apps, it needs cybersecurity brains. CISSP pros here get to work on cool stuff, like securing AI models, network security, cloud-native apps, crypto systems, and next-gen tech.
Government and Defense Contractors:
You wanna talk steady work and big clearances? This is the sector. Defense contractors practically require CISSP for higher security roles. Plus, with global politics heating up, cyber defense is becoming top-priority spending.
Retail and E-commerce:
Big brands are scared of breaches leaking customer info. Add to that new privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA, others coming in 2026), and retailers are scrambling to lock down digital transactions and loyalty databases.
Insurance and Legal:
Insurance firms are now building dedicated cybersecurity teams. Why? Because cyber insurance payouts are massive, and they need experts to assess risks better.
Same goes for big law firms protecting client confidentiality.
Education and Universities:
Cyberattacks on schools? Yep, huge spike. Universities hold valuable research data, personal records, financial info. They’re hiring CISSP folks for risk management and secure IT frameworks.
The CISM Certification Advantage: Management, Strategy, and Leadership
If CISSP is about building strong security systems, then CISM is about making sure those systems actually support the business and survive board meetings.
CISM isn’t the cert you get because you want to fix routers or tune firewalls; instead, it focuses more on identity and access management . You go for CISM because you want to lead security programs, shape policies, manage risks, and talk big business language without getting lost.
For a broader perspective, you can also explore our CISSP vs CISA Comparison 2026 to see how CISSP stacks up against audit-focused career paths
By 2026, companies aren’t just asking, “Can you stop hackers?” They’re asking, “Can you explain to investors how secure we are?”
That’s where CISM-certified pros fit in beautifully.
Biggest CISM advantage? It highlights the key differences and turns you into a translator between tech teams and business leadership. And trust me, companies are desperate for that translator right now.
People with CISM certs get invited to meetings that tech guys don’t even know are happening. They’re the ones helping CIOs and CFOs sign off on multi-million dollar security budgets. They’re the ones setting up entire risk frameworks, not just patching software.
Why CISM Certification is a Favorite for Aspiring Security Managers
There’s a reason CISM is climbing the charts for security managers and risk consultants.
CISM focuses on four key areas:
- Information security governance
- Risk management
- Program development and management
- Incident management
Instead of asking, “How do I fix this firewall?” CISM asks, “Is our entire network protected based on risk prioritization? If not, why?”
It shifts your thinking from fixing stuff to controlling environments.
Aspiring security managers love CISM because:
- It’s management-focused without drowning you in hardcore tech stuff
- It teaches you how to build long-term security programs, not just one-off fixes
- It gives you a framework to handle incidents, audits, and compliance headaches professionally
Also, companies hiring CISOs, Security Managers, or Risk Leaders are practically scanning resumes for the word “CISM” now.
Key Skills That CISM Certification Focuses On
If you’re gonna survive and thrive with CISM, you gotta build a different skill set compared to your technical security buddies. Here’s what CISM drills into you:
1. Risk Assessment
You’ll learn to spot where companies are weak — and not just technical weaknesses, but process weaknesses too. Missing policies, bad vendor contracts, weak user training — it all counts as risk.
2. Business Alignment:
CISM teaches you that security isn’t about building the biggest digital castle. It’s about building enough security to protect business objectives without wasting money or slowing growth.
3. Information Security Program Development:
You’ll figure out how to build security strategies from scratch. What policies are needed? What training? What monitoring? How do you phase things in over 1, 3, 5 years?
4. Incident Handling:
When a breach happens (and it will), you’ll know how to assess it, contain it, recover from it, and legally report it. Fast, clean, and compliant.
These are boardroom-level skills, not just server room skills. That’s what makes CISM stand out compared to technical-only certs.
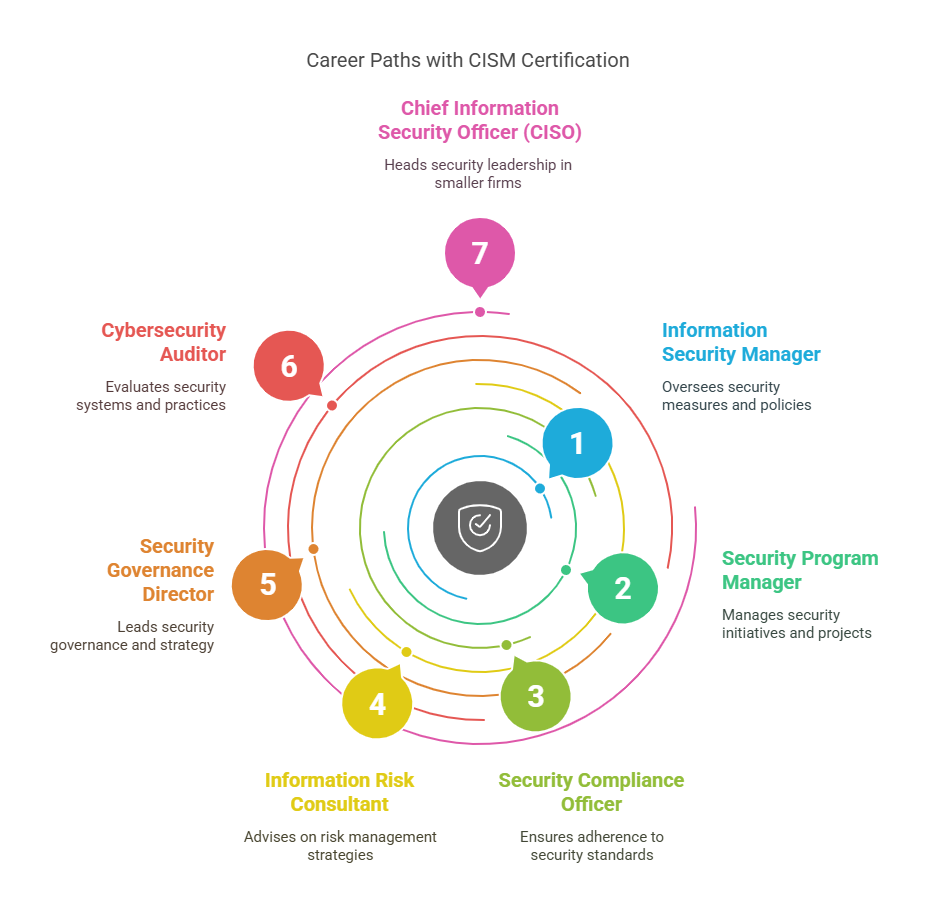
Career Directions After Earning Your CISM Credential
Once you bag your CISM, you’re not stuck in one boring path either. This cert is flexible.
It plants your flag in the leadership world of cybersecurity.
Common job titles after getting CISM:
- Information Security Manager
- Security Program Manager
- Security Compliance Officer
- Information Risk Consultant
- Security Governance Director
- Cybersecurity Auditor
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) (especially for smaller to mid-sized firms)
CISM vs CISSP Exam Comparison: What Really Sets Them Apart?
Eligibility Requirements: Not as Simple as Signing Up
CISSP:
You need 5 years of paid, full-time work experience in at least two of the eight CISSP domains.
(Stuff like Security and Risk Management, Asset Security, Security Engineering, etc.)
CISM:
You need 5 years of work experience too but here’s the twist, it must be specifically tied to information security management. Not just working in IT; understanding the exam details is crucial too . You gotta have been involved in managing, designing, overseeing security programs.
Short version:
- CISSP likes hands-on security people.
- CISM likes people who managed security as a business process.
Pro tip:
There are waivers for both exams. Like if you have a degree or other certs, you can shave off 1 year of experience sometimes. But don’t rely on that to save you. Better to just have the real-world scars to back it up.
Exam Structure and Domains: Very Different Brain Games
CISSP:
- 125–175 questions
- 3 hours
- Computerized Adaptive Testing (CAT) format
- Covers 8 huge domains (everything from access control to security operations)
Adaptive testing means:
- Answer questions right, they get harder.
- Mess up a few, it gets easier but kills your score.
- You can’t skip questions or come back later.
It’s intense. It’s strategic. You have to think on your feet.
CISM:
- 150 questions
- 4 hours
- Fixed multiple-choice test
- Covers 4 main areas (risk management, governance, program development, incident response)
CISM questions look innocent but are sneaky, adding to the overall exam difficulty . They give you 4 right-sounding answers. Your job? Pick the one that aligns most with ISACA’s preferred risk management thinking.
If you’re still weighing your options, don’t miss our CISSP vs CCSP Certification Comparison 2026, which dives into how CISSP compares with the cloud-focused CCSP path.
Preparation Time and Study Load
CISSP:
If you don’t have hardcore cyber experience, plan for 4-6 months of prep minimum. Daily study. Flashcards. Mock exams. Mind maps.
The CBK (Common Body of Knowledge) guide alone is 1200+ pages. Many successful candidates also reinforce learning with focused practice using CISSP exam dumps to get a realistic sense of exam question styles and difficulty. To preview how these scenario-based items actually look, try a free CISSP practice question and benchmark your readiness.
CISM:
CISM feels easier to digest if you already work in security management. Prep time varies, some people pass after 2 months of study, others grind for 5+ months. It depends on how much you’re already used to business-aligned thinking. If you’re aiming to pass on the first try, reviewing updated CISM exam dumps can help solidify your understanding of risk-focused questions and ISACA’s logic. You can also test your exam-day thinking with a free CISM practice question designed to mirror ISACA’s risk-driven style.
To streamline your study process, explore resources available at Cert Empire, where professionals prepare smarter, not harder.
Reality check:
CISSP requires mastering mountains of material.
While CISSP requires mastering mountains of material, CISM requires mastering frameworks and thinking critically, not just memorizing, making you a systems security professional cissp.
Pass Rates: No Walk in the Park
Official pass rates aren’t public for either exam. But based on community estimates:
- CISSP first-time pass rates: around 50%-60%
- CISM first-time pass rates: around 60%-70%
Meaning:
Half the people who sit for CISSP walk out needing to retake it.
CISM is statistically a bit less brutal, but don’t mistake “easier” for “easy.” Both exams hurt if you don’t prep right.
How Long Do You Wait for Results?
CISSP:
You get a provisional pass/fail right after the exam. Official email confirmation comes about 2–5 business days later.
CISM:
No instant feedback. You gotta wait 4–8 weeks to get your results from ISACA.
It’s a slow, painful wait.
CISSP or CISM? It Comes Down to Where You Want Your Career to Go
By now you’re probably thinking, “Alright, they’re different but which one actually fits me better?”
That’s the real question, honestly. And it’s gotta be personal.
If you pick a cert based on which one sounds cooler to other people, you’ll hate your job two years later.
CISSP and CISM pull your career into very different zones.
Technical vs Strategic: Two Totally Different Mindsets
CISSP is for the security professional who loves being deep inside the system.
- Designing networks
- Setting encryption policies
- Implementing IAM setups
- Building disaster recovery plans
You live and breathe configurations, alerts, architectures. You enjoy fixing things. Solving technical puzzles. Making stuff ironclad.
CISM is for the cybersecurity leader who wants to steer the ship instead of plugging every hole themselves.
- Building security programs
- Managing third-party risk
- Creating board reports about cybersecurity posture
- Handling vendor assessments and legal compliance
You want to know the tech (sure) but you don’t want to spend all day inside SIEM dashboards.
You’d rather be talking budgets, priorities, strategies.
Which Certification Employers Prefer for Security Leadership Roles
In 2026, companies are smarter about hiring security leaders.
They don’t just want the most certified person anymore. They want the person whose mindset matches the job’s needs.
For technical leadership (ex: Security Architects, Senior Security Engineers):
- CISSP wins hands down.
- Recruiters basically assume if you’re architecting security solutions at enterprise scale, you better have CISSP on your resume.
For governance leadership (ex: Security Managers, CISOs, Risk Directors):
- CISM usually edges out.
- Companies want leaders who can show alignment between business goals and security controls — not just leaders who know how to block ports.
Thinking Long-Term: Future-Proofing Your Cybersecurity Career
You don’t wanna chase short-term hype. You wanna build a career that stays strong even when tech fads shift.
CISSP future-proofs you if:
- You’re planning to stay hands-on with security tech.
You want flexibility to shift between architecture, engineering, auditing, and consulting. - You love diving into technical challenges and learning new systems.
CISM future-proofs you if:
- You’re eyeing Director-level or C-suite roles.
- You’re good at long-term planning, politics, risk appetite discussions.
- You’re fine letting the SOC analysts handle the alerts while you plan the 3-year roadmap.
How Salaries Differ for CISSP vs CISM Certified Professionals
CISSP salaries in 2026 are holding strong. On average, CISSP holders in the US are pulling between $145,000 and $165,000 a year.
CISM salaries?
They’re even a little higher in many cases, usually falling between $150,000 and $175,000 a year.
Quick takeaway:
- If you’re technical and stay technical (security engineer, security architect), CISSP pays beautifully.
- If you move into governance, program management, and leadership, CISM nudges ahead.
Geographic Salary Variations and Market Demand
Where you live can absolutely jack up or water down your paycheck.
Top-paying states for CISSP and CISM folks right now:
- California (especially Silicon Valley)
- New York
- Virginia and D.C. metro area (lots of government cyber jobs)
- Texas (booming tech hubs in Austin and Dallas)
- Washington (Seattle’s cloud tech sector is huge)
In these places, don’t be surprised if salaries break $180k with 7–10 years of experience.
On the flip side, smaller cities or areas without big enterprise presence usually offer around $120k–$135k for similar roles.
Job Titles and Compensation Packages Tied to Each Certification
Typical roles for CISSP holders and their salaries in 2026:
- Security Engineer – $135k–$155k
- Security Architect – $150k–$170k
- SOC Manager – $140k–$165k
- Penetration Tester (Senior Level) – $145k–$160k
Typical roles for CISM holders and their salaries in 2026:
- Information Security Manager – $150k–$175k
- Risk and Compliance Officer – $145k–$165k
- Security Program Director – $160k–$180k
- CISO (Small to Mid-sized Companies) – $175k–$220k
Also, the higher you climb, the more bonuses and perks kick in — think stock options, retention bonuses, training stipends.
In big companies, CISOs and Program Directors with CISM certs are getting bonuses of 15–25% of base salary.
Wrapping It Up: CISSP or CISM: Choose the One That Moves You Forward
At the end of the day, nobody’s gonna climb into your career and live it for you. If CISSP fires you up because you love building security from the ground up, go that way. If CISM feels right because you want to lead security programs and talk strategy with execs, chase it. Both certs are solid.
Both open doors. Just don’t let hype, peer pressure, or job ads make your decision for you. Pick the path that actually fits where you want to be two, five, ten years from now. That’s how you’ll get the career wins that actually feel worth it.