Network+ N10-009.pdf
Q: 1
A small business is deploying new phones, and some of the phones have full HD videoconferencing
features. The Chief Information Officer (CIO) is concerned that the network might not be able to
handle the traffic if it reaches a certain threshold. Which of the following can the network engineer
configure to help ease these concerns?
Options
Q: 2
Early in the morning, an administrator installs a new DHCP server. In the afternoon, some users
report they are experiencing network outages. Which of the following is the most likely issue?
Options
Q: 3
Which of the following troubleshooting steps would provide a change advisory board with the
information needed to make a decision?
Options
Q: 4
A network administrator needs to fail over services to an off-site environment. This process will take
four weeks to become fully operational. Which of the following DR (Disaster Recovery) concepts
does this describe?
Options
Q: 5
Which of the following is the best way to reduce the likelihood of electrostatic discharge?
Options
Q: 6
SIMULATION
After a recent power outage, users are reporting performance issues accessing the application
servers. Wireless users are also reporting intermittent Internet issues.
INSTRUCTIONS
Click on each tab at the top of the screen. Select a widget to view information, then
use the drop-down menus to answer the associated questions. If at any time you would like to bring
back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.
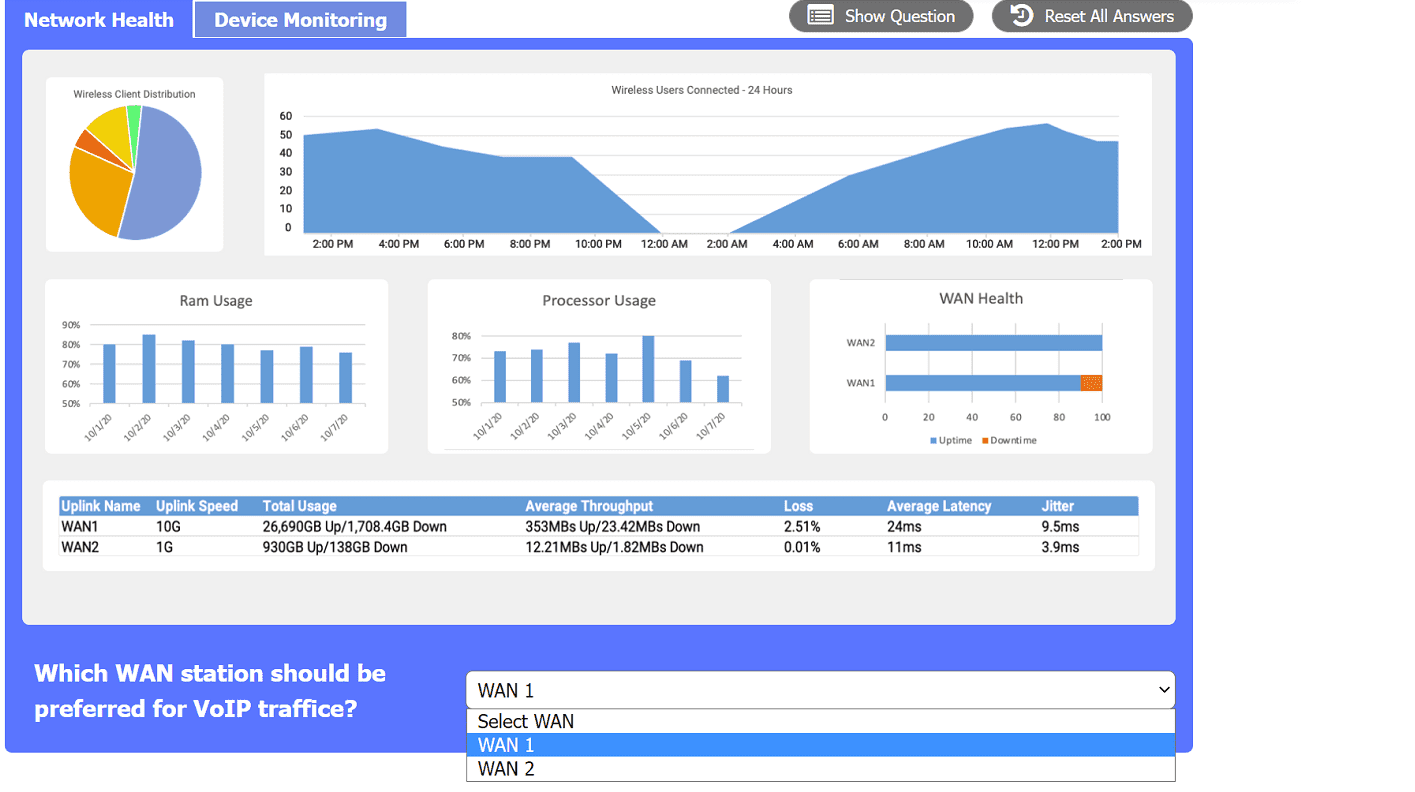
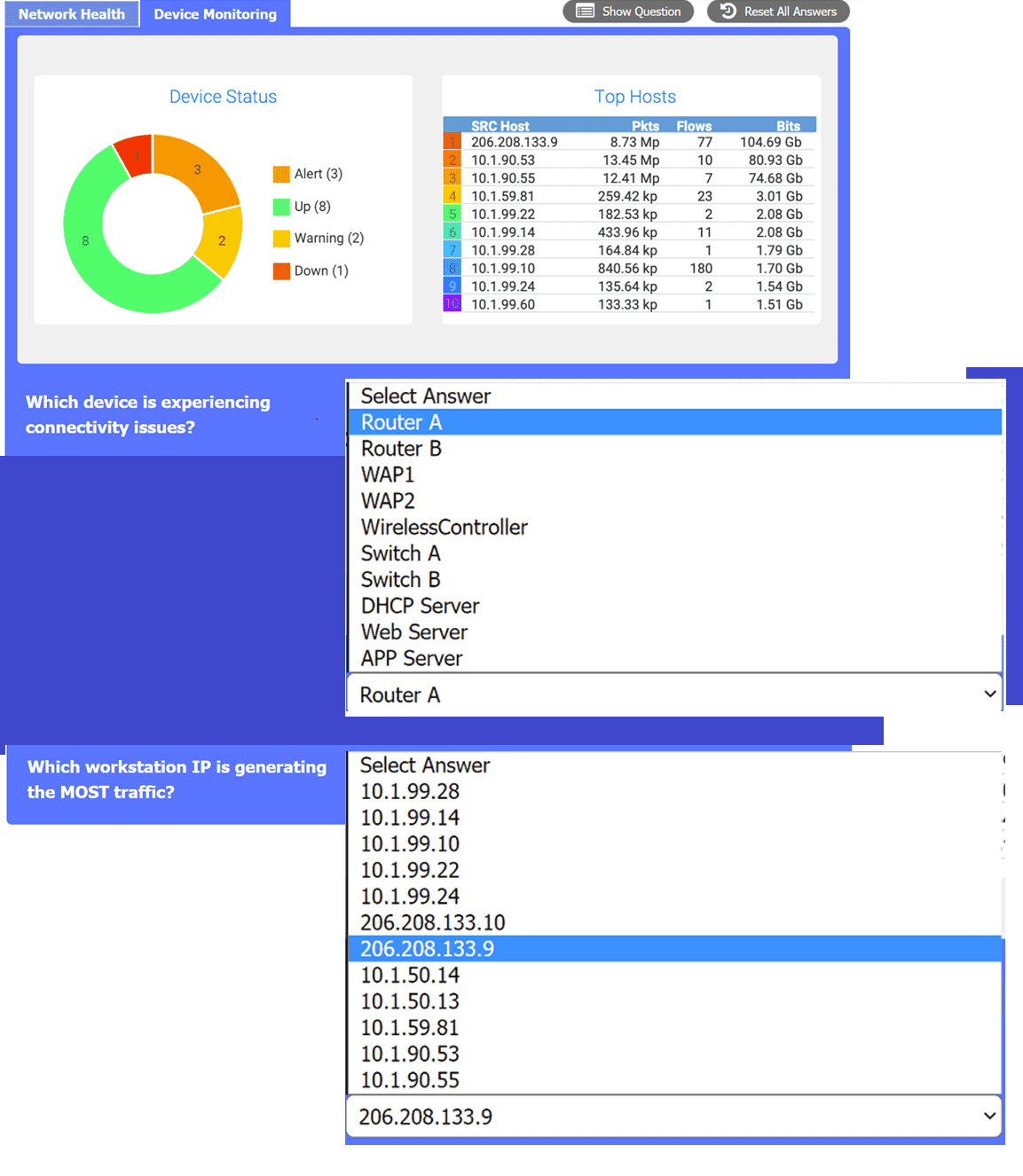


Your Answer
Q: 7
Users are reporting issues with mobile phone connectivity after a cellular repeater was recently
installed. Users also note that the phones are rapidly losing battery charge. Which of the following
should the technician check first to troubleshoot the issue?
Options
Q: 8
After a security incident, a technician reveals that company data was stolen. During the investigation,
it is discovered that a host disguised itself as a switch. Which of the following best describes the
attack that occurred?
Options
Q: 9
A junior network administrator gets a text message from a number posing as the domain registrar of
the firm. The administrator is tricked into providing global administrator credentials. Which of the
following attacks is taking place?
Options
Q: 10
Which of the following should a company implement in order to share a single IP address among all
the employees in the office?
Options
Question 1 of 10

