ISC2 CISSP Exam Questions
DRAG DROP Match the name of access control model with its associated restriction. Drag each access control model to its appropriate restriction access on the right. 
HOTSPOT In the network design below, where is the MOST secure Local Area Network (LAN) segment to deploy a Wireless Access Point (WAP) that provides contractors access to the Internet and authorized enterprise services? 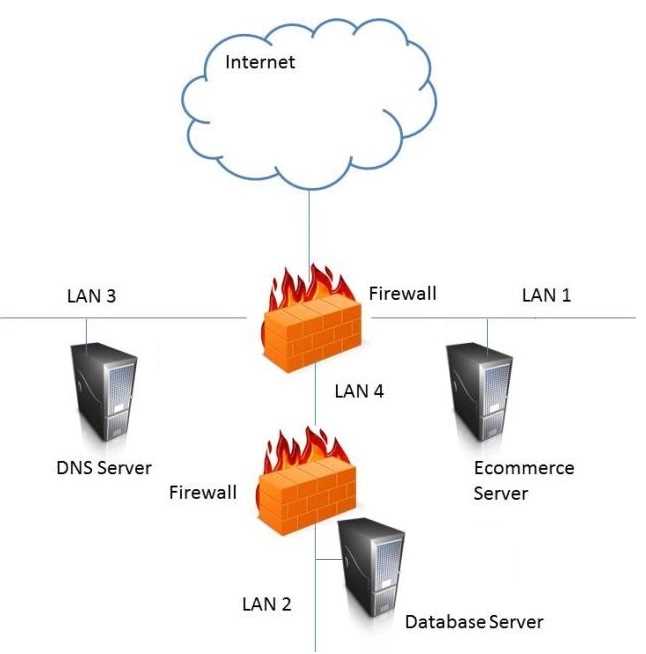
DRAG DROP Rank the Hypertext Transfer protocol (HTTP) authentication types shows below in order of relative strength. Drag the authentication type on the correct positions on the right according to strength from weakest to strongest. 
DRAG DROP Match the name of access control model with its associated restriction. Drag each access control model to its appropriate restriction access on the right. 

