Cisco CCNA 200-301
Q: 1
DRAG DROP Drag and drop the attack-mitigation techniques from the left onto the Types of attack that they mitigate on the right. 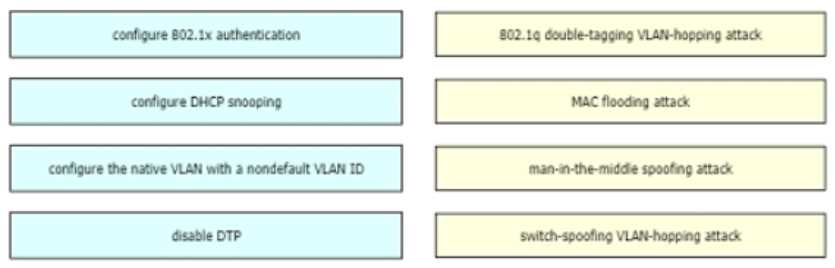
Drag & Drop
Q: 2
Refer to the exhibit. 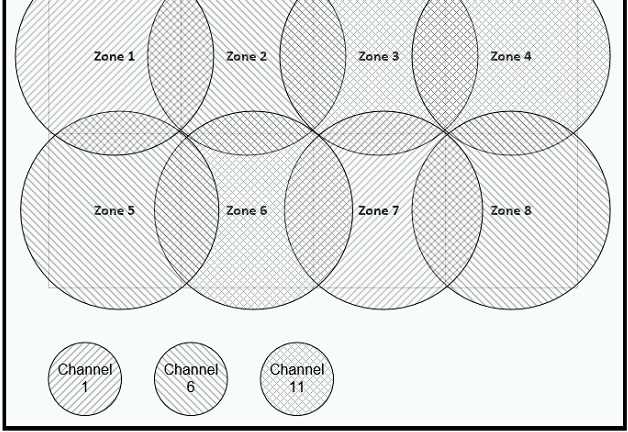 Between which zones do wireless users expect to experience intermittent connectivity?
Between which zones do wireless users expect to experience intermittent connectivity?
Options
Q: 3
Refer to the exhibit.
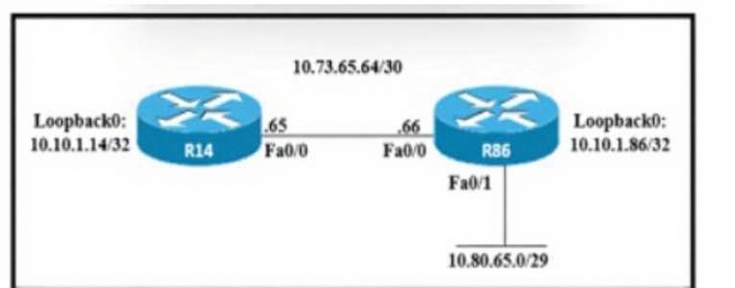
An engineer must configure a floating static route on an external EIGRP network. The destination subnet is the /29 on the LAN Interface of R86. Which command must be executed on R14?
Options
Q: 4
Which protocol must be implemented to support separate authorization and authentication
solutions for wireless APs?
Options
Q: 5
What is a function of the Cisco DNA Center Overall Health Dashboard?
Options
Q: 6
Which command entered on a switch configured with Rapid PVST* listens and learns for a specific
time period?
Options
Q: 7
It work security team noticed that an increasing number of employees are becoming victims of
phishing attacks. Which security program should be implemented to mitigate the problem?
Options
Q: 8
DRAG DROP Drag and drop the IPv6 address type characteristics from the left to the right. 
Drag & Drop
Q: 9
DRAG DROP Drag and drop the AAA terms from the left onto the description on the right. 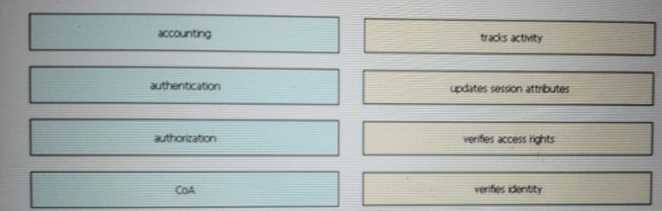
Drag & Drop
Q: 10
DRAG DROP Drag and drop the SNMP components from the left onto the descriptions on the right. 
Drag & Drop
Question 1 of 10

