
What is Microsoft AZ-204?
The Microsoft AZ-204 exam, also known as Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure, is designed for developers who want to prove their skills in building, testing, and maintaining applications on the Azure platform. It validates your ability to work with cloud services, integrate security, and develop scalable solutions using Azure tools and services.
Who should take this exam
This Microsoft Azure Developer Associate (AZ-204) exam is ideal for:
- Developers with 1–2 years of professional experience in cloud and Microsoft Azure.
- Software engineers who design, build, and maintain cloud applications.
- Professionals who want to specialize in Azure application development.
If you are aiming for a career in cloud development, this is one of the most relevant certifications.
If you want a complete AZ-204 certification guide that explains all domains, prerequisites, and preparation strategies, check out this resource: AZ-204 Certification: Azure Developer Exam Guide.
Prerequisites and recommendations
While there are no official prerequisites, Microsoft recommends that candidates have:
- Some hands-on experience with Azure SDKs, APIs, PowerShell, CLI, and data connections.
- Strong knowledge of at least one programming language (C#, Java, JavaScript, or Python).
- Basic understanding of Azure services, data storage options, and security concepts.
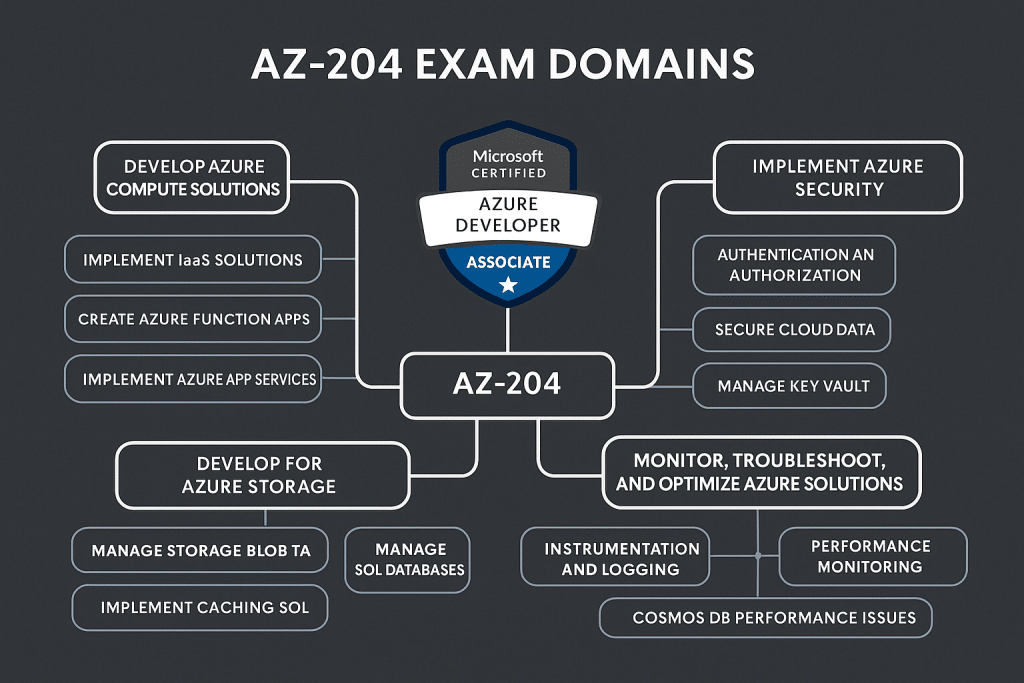
Exam objectives and domains
The AZ-204 exam measures your ability to develop and maintain solutions on Azure. The domains include:
- Develop Azure compute solutions
- Develop for Azure storage
- Implement Azure security
- Monitor, troubleshoot, and optimize solutions
- Connect to and consume Azure services and third-party services
Preparing for AZ-204 can seem challenging, but following effective strategies makes a huge difference. Learn how to pass AZ-204 exam with proven tips and techniques here: How to Pass AZ-204 Exam Tips & Techniques.
Objective details by domain
1. Develop Azure Compute Solutions (25–30%)
This domain focuses on building and running applications in the cloud. You need to know how to deploy, manage, and optimize compute resources. Key areas include:
- Azure App Services: Build and deploy web apps, mobile backends, and APIs. Configure deployment slots, scaling, and authentication.
- Azure Functions: Implement serverless code for event-driven solutions. Learn triggers, bindings, and function scaling.
- Containers: Use Azure Container Instances or Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) to run containerized applications.
- Background Jobs: Implement Azure WebJobs or Logic Apps for background tasks.
- Practical Tip: Focus on hands-on labs for App Services and Functions, as many exam scenarios require deployment or troubleshooting tasks.
2. Develop for Azure Storage (10–15%)
Cloud applications need efficient data storage solutions. This domain tests your ability to select and implement the right storage type for your application. Key areas include:
- Blob Storage: Store unstructured data such as images, videos, and logs. Learn access tiers and secure access.
- Cosmos DB: Work with globally distributed NoSQL databases for low-latency applications. Understand partitioning, consistency levels, and scaling.
- Azure SQL Database: Implement relational storage with security, performance tuning, and backup options.
- Queue Storage & Table Storage: Use queues for asynchronous processing and tables for NoSQL storage.
- Practical Tip: Practice creating, reading, updating, and deleting data in all storage types to strengthen your hands-on skills.
3. Implement Azure Security (15–20%)
Security is critical for cloud solutions. This domain ensures that you can protect applications and data in Azure. Key areas include:
- Authentication & Authorization: Implement Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) authentication, manage users, groups, and roles.
- RBAC (Role-Based Access Control): Control permissions for users and applications effectively.
- Secrets Management: Use Azure Key Vault to store and access keys, secrets, and certificates securely.
- API Security: Protect APIs using OAuth 2.0, Managed Identities, or certificates.
- Practical Tip: Focus on implementing secure access and understanding RBAC scenarios, as they are frequently tested.
4. Monitor, Troubleshoot, and Optimize Solutions (10–15%)
Applications must run efficiently and reliably. This domain tests your ability to track performance, identify issues, and optimize solutions. Key areas include:
- Monitoring: Use Application Insights, Log Analytics, and Azure Monitor to track application performance.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnose issues in code, storage, or services and resolve them.
- Optimization: Scale resources, tune performance, and manage costs effectively.
- Practical Tip: Practice setting up alerts, dashboards, and logs to simulate real-world monitoring scenarios.
5. Connect to and Consume Azure Services and Third-Party Services (25–30%)
Modern applications often interact with multiple services. This domain evaluates your ability to integrate Azure services and external APIs. Key areas include:
- Practical Tip: Build a small project integrating multiple services to understand connections, triggers, and data flows.
- REST APIs & SDKs: Consume Azure and third-party APIs programmatically.
- Event-Driven Solutions: Work with Event Grid, Event Hubs, and Service Bus for asynchronous messaging.
- Logic Apps & Azure Functions Integration: Automate workflows and connect services seamlessly.
What changed in this version
Microsoft updates the exam regularly to reflect new Azure services and best practices. In the latest version, more focus has been placed on:
- Identity and access management with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD)
- Containerization and Kubernetes
- Event-driven architectures
Registration and scheduling
You can register for the exam directly through the Microsoft Certification website. The exam is available as:
- Online proctored – take from home or office.
- Test center – Pearson VUE testing locations worldwide.
Pricing and vouchers
- Standard exam cost: $165 USD (may vary by region).
- Microsoft often provides discount vouchers through training programs, student offers, and company partnerships.
Policies you should know
- You must show a valid government ID on exam day.
- Rescheduling or cancellation is allowed up to 24 hours before the exam.
- Microsoft has a retake policy, if you fail, you can retake after 24 hours, and subsequent retakes require a longer wait.
Scoring and results
- The exam is scored on a scale of 100–1000.
- Passing score: 700.
- Results are displayed immediately after completing the exam, and a detailed score report is available in your certification dashboard.
Exam day and test experience
Expect around 40–60 questions in different formats: multiple choice, case studies, drag-and-drop, and hands-on labs.
Time allowed: 120 minutes.
Make sure you:
- Stay calm and manage your time across all questions.
- Have a quiet space (if taking online).
- Test your computer and internet connection in advance.
Study plan and resources
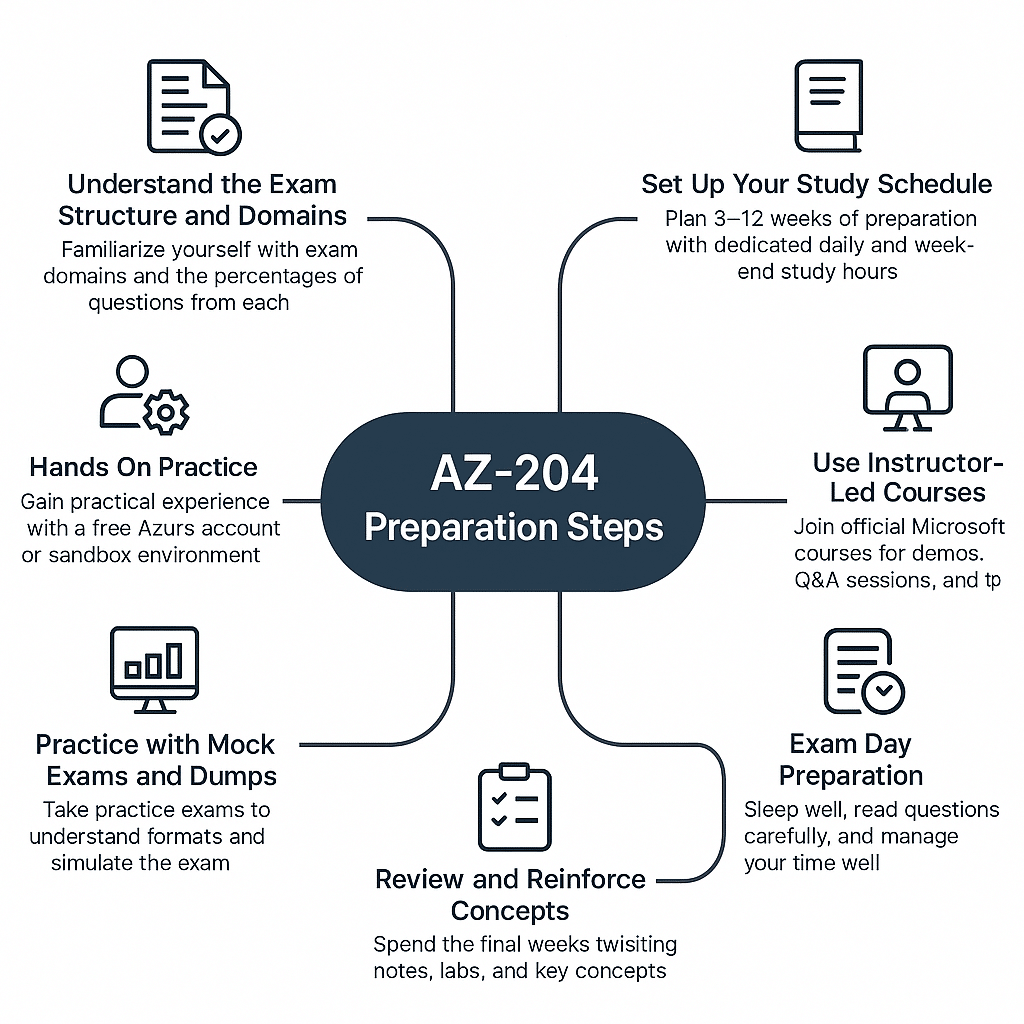
Step 1: Understand the Exam Structure and Domains
Before starting, familiarize yourself with the exam domains and the percentage of questions from each.
Knowing this helps you prioritize your study time according to the weight of each domain.
Step 2: Set Up Your Study Schedule
- Plan 8–12 weeks of preparation depending on your experience.
- Dedicate 1–2 hours daily on weekdays and 3–4 hours on weekends.
- Break study sessions into reading, hands-on practice, and review.
- Use a calendar or planner to track progress and ensure all domains are covered.
Step 3: Learn with Microsoft Learn
Microsoft offers free, structured learning paths for AZ-204. Recommended modules:
- Developing Azure compute solutions (App Services, Functions, WebJobs)
- Working with Azure storage (Blob, Cosmos DB, SQL)
- Implementing security (Microsoft Entra ID, Key Vault, RBAC)
- Monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimizing solutions
- Integrating Azure services and third-party APIs
Tip: Take notes while going through these modules to create a personal study guide.
Step 4: Hands-On Practice
Practical experience is essential for AZ-204. Steps to practice:
- Create a free Azure account or use a sandbox environment.
- Build small projects using Azure Functions, App Services, and Logic Apps.
- Work with Blob storage, Cosmos DB, and Azure SQL Database.
- Implement authentication, RBAC, and Key Vault in sample applications.
- Test event-driven solutions using Event Grid, Event Hubs, or Service Bus.
Tip: Hands-on practice helps you understand real-world scenarios and boosts confidence for lab-based exam questions.
Step 5: Use Instructor-Led Courses (Optional but Helpful)
If you prefer guided learning:
- Join official Microsoft courses for AZ-204, often offered online.
- Focus on practical demos, Q&A sessions, and instructor tips.
- These courses are especially helpful for complex topics like security, containerization, and integration.
Step 6: Practice with Mock Exams and Dumps
- Take practice exams to get familiar with question formats and time management.
- Use resources like Cert Empire for practice questions and detailed explanations.
- Review wrong answers carefully to understand your weak areas.
- Simulate the exam experience by taking full-length tests under timed conditions.
Step 7: Review and Reinforce Concepts
- Spend the last 1–2 weeks before the exam reviewing:
- Azure compute solutions (Functions, App Services, Containers)
- Storage solutions and security implementations
- Event-driven integration and API connections
- Monitoring, logging, and troubleshooting techniques
- Revisit notes and practice labs repeatedly until confident.
Step 8: Exam Day Preparation
- Ensure your exam environment is ready (for online proctored exams).
- Sleep well the night before and avoid last-minute cramming.
- Read each question carefully during the exam and manage your time efficiently.
Certification validity and renewal
The certification is valid for one year.
Renewal is free and can be done online by passing a short renewal assessment on Microsoft Learn.
Career outcomes
Earning the AZ-204 certification can help you secure roles such as:
- Azure Developer
- Cloud Developer
- Cloud Solutions Engineer
- Software Engineer (Cloud-focused)
| Job Role | Average Salary (USD/year) |
|---|---|
| Azure Developer | $95,000 – $120,000 |
| Cloud Application Developer | $90,000 – $115,000 |
| Software Engineer (Azure-focused) | $85,000 – $110,000 |
| Cloud Solutions Developer | $100,000 – $125,000 |
| DevOps Engineer (with Azure expertise) | $105,000 – $130,000 |
| Full-Stack Developer (Azure projects) | $90,000 – $115,000 |
| Cloud Consultant (Azure Development) | $110,000 – $135,000 |
Note:
- Salaries can differ a lot depending on region. For example, in the U.S. and Western Europe, the salaries are at the higher end, while in Asia and Eastern Europe, they may be lower.
- Professionals with more hands-on Azure experience (3+ years) or multiple certifications (like AZ-204 + AZ-400) usually earn on the higher side.
It also increases your chances of higher salary and better career opportunities in the cloud development field.
Earning your AZ-204 opens doors to many roles like Azure Developer, Cloud Solutions Engineer, and Software Engineer (Cloud). Explore job roles and career trends for AZ-204 certified professionals here: Job Roles & Career Trends for AZ-204 Certified.
Related or next-step certifications
After AZ-204, many professionals move to:
- DP-203: Data Engineer Associate
- AZ-400: DevOps Engineer Expert
- AZ-305: Azure Solutions Architect Expert
How this exam compares to similar certifications
- AZ-900 – beginner-friendly, focuses on fundamentals (not coding-heavy).
- AZ-104 – for administrators, not developers.
- AZ-204 – for developers, focuses on coding and building applications.
- AWS Developer Associate – similar exam but for Amazon Web Services instead of Azure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How difficult is the AZ-204 exam?
The AZ-204 exam is moderately challenging. It tests both your theoretical knowledge and practical skills in developing Azure solutions. Hands-on experience with Azure services and coding practice will make it much easier to pass.
Do I need prior Azure experience to take AZ-204?
While not mandatory, having practical experience with Azure is highly recommended. Familiarity with Azure Functions, App Services, storage solutions, and APIs will make preparation smoother and increase your chances of success.
How many hours of study are required to prepare?
Most candidates spend 2–3 months preparing for the AZ-204 exam. A balanced approach of hands-on practice, Microsoft Learn modules, instructor-led courses, and practice exams is most effective.
Is coding required for AZ-204?
Yes. You should be comfortable with at least one programming language such as C#, Java, Python, or JavaScript, as the exam focuses on building, deploying, and managing cloud applications.
What types of questions are on the exam?
The exam includes 40–60 questions in formats such as multiple choice, drag-and-drop, case studies, and hands-on labs. You will have 120 minutes to complete the exam.
What is the passing score for AZ-204?
The exam is scored on a scale from 100 to 1000, with a passing score of 700. After completing the exam, you will immediately see your score and a detailed breakdown of your performance by domain.
Can I retake the exam if I fail?
Yes. If you fail, you can retake the exam after 24 hours for the first retake. Subsequent retakes require longer waiting periods according to Microsoft’s policy.
How long is the certification valid?
The AZ-204 certification is valid for one year. Renewal is free and can be done online by completing a short assessment on Microsoft Learn before the certification expires.
Should I take AZ-900 or AZ-104 before AZ-204?
It’s optional. AZ-900 (Azure Fundamentals) is helpful for beginners to understand cloud basics. AZ-104 (Azure Administrator) focuses on administrative tasks, which can be beneficial but is not required for developers.
What career opportunities does AZ-204 open?
AZ-204 prepares you for roles like Azure Developer, Cloud Developer, Cloud Solutions Engineer, and Software Engineer (Cloud). It also improves your chances for higher salary and career growth in cloud development.


