SC-100.pdf
Q: 1
A customer is deploying Docker images to 10 Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) resources across four
Azure subscriptions. You are evaluating the security posture of the customer.
You discover that the AKS resources are excluded from the secure score recommendations. You need
to produce accurate recommendations and update the secure score.
Which two actions should you recommend in Microsoft Defender for Cloud? Each correct answer
presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Options
Q: 2
You have an Azure subscription that contains multiple network security groups (NSGs), multiple
virtual machines, and an Azure Bastion host named bastion1.
Several NSGs contain rules that allow direct RDP access to the virtual machines by bypassing bastion!
You need to ensure that the virtual machines can be accessed only by using bastion! The solution
must prevent the use of NSG rules to bypass bastion1.
What should you include in the solution?
Options
Q: 3
Your company plans to provision blob storage by using an Azure Storage account The blob storage
will be accessible from 20 application sewers on the internet. You need to recommend a solution to
ensure that only the application servers can access the storage account. What should you
recommend using to secure the blob storage?
Options
Q: 4
Your company has on-premises Microsoft SQL Server databases.
The company plans to move the databases to Azure.
You need to recommend a secure architecture for the databases that will minimize operational
requirements for patching and protect sensitive data by using dynamic data masking. The solution
must minimize costs.
What should you include in the recommendation?
Options
Q: 5
You are designing security for an Azure landing zone. Your company identifies the following
compliance and privacy requirements:
• Encrypt cardholder data by using encryption keys managed by the company.
• Encrypt insurance claim files by using encryption keys hosted on-premises.
Which two configurations meet the compliance and privacy requirements? Each correct answer
presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Options
Q: 6
You receive a security alert in Microsoft Defender for Cloud as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit tab.) 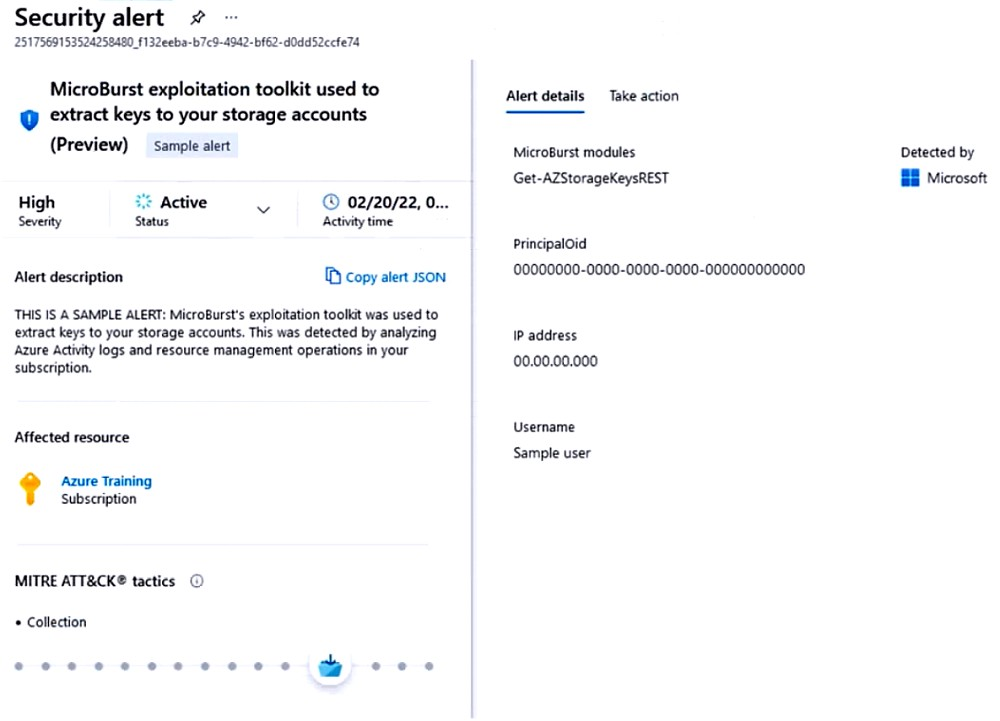 After remediating the threat which policy definition should you assign to prevent the threat from reoccurring?
After remediating the threat which policy definition should you assign to prevent the threat from reoccurring?
Options
Q: 7
Your company is developing a new Azure App Service web app. You are providing design assistance
to verify the security of the web app.
You need to recommend a solution to test the web app for vulnerabilities such as insecure server
configurations, cross-site scripting (XSS), and SQL injection. What should you include in the
recommendation?
Options
Q: 8
You have an Azure subscription.
You plan to deploy Azure App Services apps by using Azure DevOps.
You need to recommend a solution to ensure that deployed apps maintain compliance with
Microsoft cloud security benchmark (MCSB) recommendations.
What should you include in the recommendation?
Options
Q: 9
Your company plans to deploy several Azure App Service web apps. The web apps will be deployed to
the West Europe Azure region. The web apps will be accessed only by customers in Europe and the
United States.
You need to recommend a solution to prevent malicious bots from scanning the web apps for
vulnerabilities. The solution must minimize the attach surface.
What should you include in the recommendation?
Options
Q: 10
You have a multicloud environment that contains an Azure subscription, an Amazon Web Services
(AWS) subscription, and a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) subscription.
You plan to assess data security and compliance.
You need to design a Compliance Manager solution that meets the following requirements:
• Provides recommended improvement actions that include detailed implementation guidance
• Automatically monitors regulatory compliance
• Minimizes administrative effort
What should you include in the solution?
Options
Question 1 of 10

