Prepare Better for the MD-102 Exam with Our Free and Reliable MD-102 Exam Questions – Updated for 2025.
At Cert Empire, we are dedicated to offering the most accurate and up-to-date exam questions for students preparing for the Microsoft MD-102 Exam. To support effective preparation, we’ve made parts of our MD-102 exam resources free for everyone. You can practice as much as you want with Free MD-102 Practice Test.
Question 1
Your on-premises network contains an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a domain controller named dc1.contoso.com. You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune Suite. You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources shown in the following table. 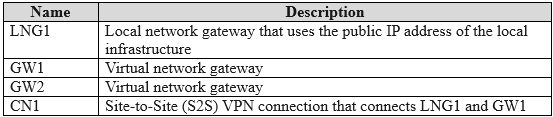 The subscription contains the virtual networks shown in the following table.
The subscription contains the virtual networks shown in the following table. 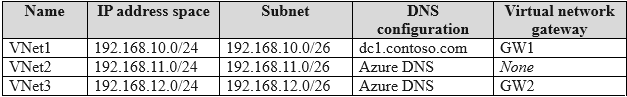 You plan to deploy Windows 365 Enterprise Cloud PC. You need to create an Azure network connection (ANC) that will use Microsoft Entra hybrid join. Which virtual network can you use for the ANC?
You plan to deploy Windows 365 Enterprise Cloud PC. You need to create an Azure network connection (ANC) that will use Microsoft Entra hybrid join. Which virtual network can you use for the ANC?
Show Answer
A
To create an Azure Network Connection (ANC) for Windows 365 that uses Microsoft Entra hybrid join, the selected virtual network (VNet) must have network line-of-sight to an on- premises Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain controller. This connectivity allows the Cloud PCs to join the on-premises domain. An ANC is configured to use a single VNet and a single subnet within that VNet. While any of the three VNets could potentially be configured with the required connectivity (e.g., via a VPN gateway or ExpressRoute), the question asks which single VNet can be used. Without any information indicating that VNet2 or VNet3 have the required connectivity, and given that VNet1 is a valid VNet in a supported region, it stands as a viable candidate for this configuration.
VNet2 only: There is no information provided to indicate that VNet2 has the necessary on- premises connectivity while VNet1 does not. VNet3 only: Similar to VNet2, there is no information confirming that VNet3 has the required connectivity to the on-premises domain controller. VNet1 and VNet2: An Azure Network Connection is configured for a single virtual network. You cannot select multiple VNets for a single ANC. VNet1 and VNet3: This option is incorrect for the same reason; an ANC maps to one specific VNet, not multiple.
Microsoft Documentation - Create an Azure network connection: This document outlines the
requirements for creating an ANC. For Microsoft Entra hybrid join, it explicitly states, "The
virtual network must have connectivity to your on-premises domain controller." It also shows
that the creation process involves selecting a single virtual network.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-365/enterprise/create-azure-networkconnection
Microsoft Documentation - Azure network connection health checks: This document details
the verification checks performed on an ANC, which include "AD domain join" and "Domain
name resolution." These checks would fail if the selected VNet lacks line-of-sight and proper
DNS configuration to reach the on-premises domain controller.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-365/enterprise/health-checks
Question 2
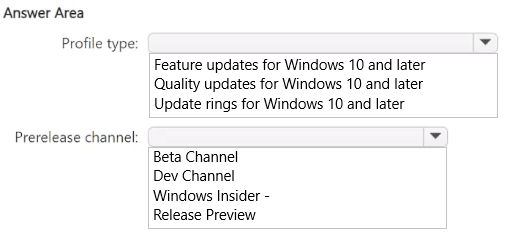
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 subscription. You have 25 Microsoft Surface Hub devices that you plan to manage by using Microsoft Intune. You need to configure the devices to meet the following requirements: Enable Windows Hello for Business. Configure Microsoft Defender SmartScreen to block users from running unverified files. Which profile type template should you use for each requirement? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Show Answer
ENABLE WINDOWS HELLO FOR BUSINESS: IDENTITY PROTECTION CONFIGURE MICROSOFT DEFENDER SMARTSCREEN TO BLOCK USERS FROM RUNNING UNVERIFIED FILES: DEVICE RESTRICTIONS
In Microsoft Intune, specific configuration tasks are mapped to dedicated profile templates for streamlined management. 1. Windows Hello for Business is an identity and credential management feature. The Identity protection profile template is designed exclusively for configuring Windows Hello for Business settings on Windows 10/11 devices, including Surface Hubs. 2. Microsoft Defender SmartScreen settings are part of the broader device security and feature controls. The Device restrictions profile template for Windows 10 and later contains a specific category for "Microsoft Defender SmartScreen," which includes the options to control how it handles unverified files and applications.
1. Microsoft Learn | Manage Windows Hello for Business on devices with Microsoft Intune:
"To manage settings for Windows Hello for Business on Windows 10/11 devices, you'll use
an Identity protection profile as part of a device configuration policy."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/identity-protection-configure
2. Microsoft Learn | Windows 10/11 device settings to allow or restrict features using Intune:
This document details the settings available in the Device restrictions template. Under the
"Microsoft Defender SmartScreen" section, it lists settings such as "Block users from
ignoring SmartScreen warnings" and "Prevent bypassing SmartScreen warnings for files,"
which directly address the requirement.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/configuration/device-restrictionswindows-10
3. Microsoft Learn | Manage Surface Hub with Microsoft Intune: This document confirms
that Surface Hub devices running Windows 10/11 Team edition are managed using
standard Windows device configuration profiles in Intune, including the aforementioned
templates.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/surface-hub/manage-surface-hub-with-intune
Question 3
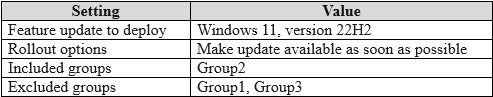
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that contains the security groups shown in the following table. 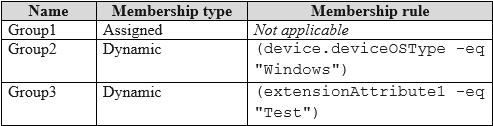

Show Answer
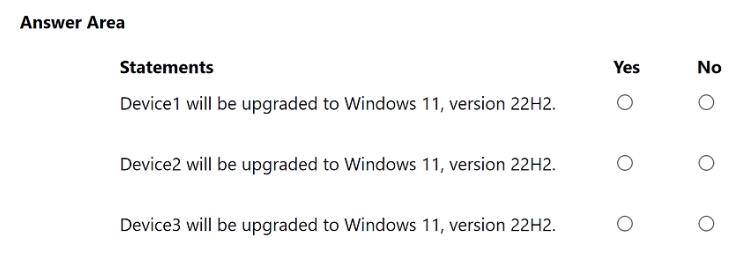
DEVICE1 WILL BE UPGRADED TO WINDOWS 11, VERSION 22H2. NO DEVICE2 WILL BE UPGRADED TO WINDOWS 11, VERSION 22H2. YES DEVICE3 WILL BE UPGRADED TO WINDOWS 11, VERSION 22H2. NO
The deployment profile for the Windows 11, version 22H2 feature update is assigned to Group2 (the included group) but is blocked for devices in Group1 and Group3 (the excluded groups). In Microsoft Intune, an exclusion will always override an inclusion. Device1: This device is a member of the included Group2 because its operating system is "Windows." However, it is also a member of the excluded Group3 because its extensionAttribute1 is set to "Test." Since exclusions take precedence, Device1 will not be upgraded. Device2: This device is a member of the included Group2 as its OS is "Windows." It is not a member of the excluded Group1 (by assignment) or the excluded Group3 (its extensionAttribute1 is not "Test"). Therefore, Device2 will be upgraded. Device3: This device is a member of the included Group2 because its OS is "Windows." It is also an assigned member of the excluded Group1. Because exclusions override inclusions, Device3 will not be upgraded.
Microsoft Intune Documentation - Assign device profiles: This document explicitly states
that assignments to excluded groups override assignments to included groups. "If a device
is in two groups, one group that's assigned to an exclusion and another group that's
assigned for inclusion, the device is excluded and doesn't receive the policy."
Source: Microsoft Learn, "Assign user and device profiles in Microsoft Intune,"
section: Include and exclude groups.
Azure AD Documentation - Dynamic membership rules: This resource explains the syntax
for creating dynamic membership rules for groups, which is used here for Group2 and
Group3.
Source: Microsoft Learn, "Dynamic membership rules for groups in Azure Active
Directory."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/enterprise-users/groups-dynamicmembership
Question 4
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune. You need to ensure that users can only enroll devices that meet the following requirements: Android devices that support the use of work profiles. iOS devices that run iOS 11.0 or later. Which two restrictions should you modify? To answer, select the restrictions in the answer area.
Show Answer
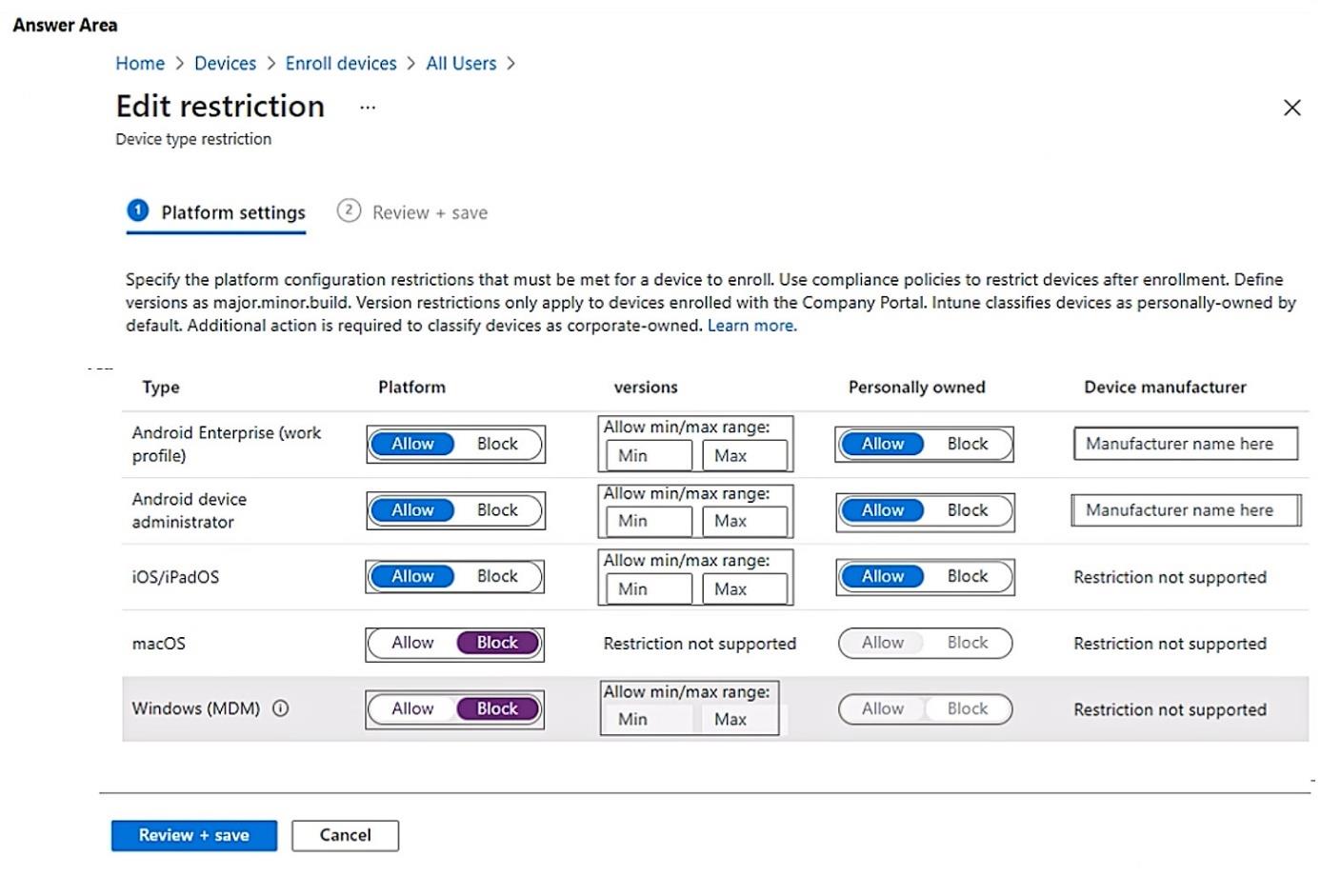
1. ANDROID DEVICE ADMINISTRATOR 2. IOS/IPADOS
Block the Android device administrator platform in the enrollment device type restriction so only Android Enterprise Work Profile-capable devices can enroll. Then edit the iOS/iPadOS restriction to set a minimum OS version of 11.0, ensuring only iPhones/iPads running iOS 11 or later are accepted.
1. Microsoft Intune “ Create a device platform restriction
https://learn.microsoft.com/mem/intune/enrollment/enrollment-restrictions-platform
Blocking Android device administrator forces enrollment through Android Enterprise Work
Profile.
Platform restrictions let you set minimum iOS/iPadOS version (e.g., 11.0).
Question 5
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune Suite. You use Intune to manage Windows 11 devices. You need to implement Windows Local Administrator Password Solution (Windows LAPS). What should you configure?
Show Answer
B
To implement Windows Local Administrator Password Solution (LAPS) in Microsoft Intune, you must create an Account protection policy. This policy type is located within the Endpoint security workload of the Intune admin center. It is the specific, purpose-built profile for configuring all LAPS settings, such as the backup directory (Azure AD or on-premises Active Directory), password age, complexity, and the name of the administrator account to manage.
A. a configuration profile: While configuration profiles are used for many device settings, Intune provides a dedicated Account protection policy specifically for LAPS, making it the most precise and correct tool. C. an app protection policy: These policies manage data security within applications (e.g., preventing copy/paste) and are not used for configuring operating system-level account management features. D. a device compliance policy: A compliance policy evaluates a device's state against a set of rules to determine if it is compliant; it does not actively configure features like LAPS.
Microsoft Learn: "Create a LAPS policy." This official documentation explicitly states: "Use
the following steps to create a policy to manage Windows LAPS... In the Microsoft Intune
admin center, go to Endpoint security > Account protection > select Create Policy."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/windows-laps-configure#createa-laps-policy
Microsoft Learn: "Manage Windows LAPS with Microsoft Intune." This document provides
an overview and confirms that LAPS policies are part of the Account protection policies in
Endpoint security.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/windows-laps-overview
Question 6
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that contains 500 computers that run Windows 11. The computers are Microsoft Entra joined and are enrolled in Microsoft Intune. You plan to manage Microsoft Defender for Endpoint on the computers. You need to prevent users from disabling Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. What should you do?
Show Answer
B
The most direct and precise method to prevent users from disabling Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is to enable Tamper Protection. In Microsoft Intune, Tamper Protection is a specific setting configured within an Endpoint security antivirus policy. This type of policy is purpose- built for managing all aspects of Microsoft Defender Antivirus, including enforcing settings that prevent unauthorized changes by local users or malicious applications. Creating an antivirus policy allows an administrator to granularly control Defender settings without applying a broader, potentially disruptive set of configurations.
A. From the Microsoft Intune admin center, create a security baseline: While a security baseline can enable Tamper Protection, it applies a wide range of pre-configured settings, making it less precise than a targeted antivirus policy for this specific requirement. C. From the Microsoft Entra admin center, create a Conditional Access policy: Conditional Access policies are used to grant or block access to cloud resources based on conditions. They do not configure security settings directly on the endpoint itself. D. From the Microsoft Intune admin center, create a device compliance policy: A compliance policy can check if Defender is enabled and report the device as non-compliant if it's not. However, it is a reactive measure and does not prevent the user from disabling it.
1. Microsoft Learn: "Protect security settings with tamper protection." This document
explicitly states the primary method for configuration: "In the Microsoft Intune admin center,
go to Endpoint security > Antivirus, and then choose + Create Policy. ... For Profile, select
Microsoft Defender Antivirus." This confirms that the antivirus policy is the correct tool.
tamper-protection-for-your-organization-using-microsoft-intune
2. Microsoft Learn: "Antivirus policy for endpoint security in Intune." This document
describes the purpose of antivirus policies: "Use endpoint security Antivirus policies to help
your security admins focus on managing the discrete group of antivirus settings for
managed devices."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/endpoint-security-antiviruspolicy
3. Microsoft Learn: "Use compliance policies to set rules for devices you manage with
Intune." This source clarifies that compliance policies are for evaluating and reporting on
device state, not for enforcing configuration settings.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/device-compliance-get-started
Question 7
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune. You need to deploy a custom app to Android devices. The app uses the APK file format. Which type of app should you select for the deployment?
Show Answer
LINE-OF-BUSINESS (LOB)
In Microsoft Intune, a line-of-business (LOB) app is an application that is added from an app installation file, which is typically developed in-house. For Android devices, this specifically refers to uploading the app installation package file (APK) directly into the Intune admin center for deployment. This method is used for custom apps that are not intended for the public Google Play Store.
built-in: This app type is for a curated list of common applications, such as Microsoft 365 apps, that Intune makes easy to deploy, not for custom APKs. Android store: This option is used to deploy publicly available applications directly from the official Google Play Store. Managed Google Play: This is the enterprise app store for Android Enterprise. While you can publish private apps to it, the direct upload of an APK file into Intune is categorized as a LOB app. web link: This option deploys a shortcut to a web app or website on the device's home screen, not an installable APK file.
Microsoft Learn. (2024). Add an Android line-of-business app to Microsoft Intune. Microsoft
Docs. Retrieved from https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/apps-lob-android
Microsoft Learn. (2024). App types in Microsoft Intune. Microsoft Docs. Retrieved from
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/apps-add#app-types-in-microsoft-intune
Question 8
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. You use Microsoft Intune to manage all devices. You need to prepare a Win32 app named App1.exe for deployment. What should you do first?
Show Answer
CHANGE APP1.EXE TO THE INTUNEWIN FORMAT.
Before a Win32 application can be deployed using Microsoft Intune, it must be prepared and packaged. The required first step is to use the Microsoft Win32 Content Prep Tool to convert the application's setup files (in this case, App1.exe) into a single .intunewin file. This packaging process wraps the installer and any other necessary files into a format that Intune can distribute and manage. This prepared file is then uploaded to Intune when creating the application deployment.
From the Microsoft Intune admin center, create an app configuration policy: App configuration policies are used to supply custom settings to an app after it is installed, not to prepare the app package itself. From the Microsoft 365 Apps admin center, create a deployment configuration: This admin center is specifically for managing Microsoft 365 Apps (Office), not for preparing or deploying general Win32 applications. Upload App1.exe to Azure Blob Storage: You upload the prepared .intunewin file to Intune during the app creation wizard, not the raw .exe file to a separate Azure Blob Storage account.
Microsoft Learn. (2024). Win32 app management in Microsoft Intune. Microsoft Docs.
Retrieved from https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/apps-win32-appmanagement
Microsoft Learn. (2024). Prepare Win32 app content for upload. Microsoft Docs. Retrieved
from https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/apps-win32-prepare (This
document explicitly states, "Before you can add a Win32 app to Microsoft Intune, you must
prepare the app by using the Microsoft Win32 Content Prep Tool.")
Question 9
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune. For macOS devices, you create an update policy named Policy1 that has the following settings: All other updates (OS, built-in apps): Download and install Assignments: Included groups: All Devices Which two types of updates can be downloaded and installed by using Policy1? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
Show Answer
B, E
The Microsoft Intune update policy for macOS devices includes a setting specifically named "All other updates (OS, built-in apps)". The scenario states that Policy1 configures this exact setting to "Download and install". This setting is designed to manage updates for the core operating system (macOS) and the applications that are included with the OS by default (built-in apps). Therefore, Policy1 will download and install both macOS updates and built-in app updates.
configuration file: This is a separate, distinct category within the macOS update policy for managing security data files (e.g., XProtect) and is not governed by the "All other updates" setting. firmware: Firmware updates are managed by their own specific setting within the Intune policy, separate from the "All other updates" category. critical: Critical updates are also a distinct, configurable category within the macOS update policy, allowing them to be managed independently of other OS and app updates.
Microsoft Learn: Manage macOS software update policies in Intune. This official
documentation details the configurable settings for macOS update policies. It explicitly lists
"Critical updates," "Firmware updates," "Configuration file updates," and "All other updates
(OS, built-in apps)" as separate, distinct settings, confirming that the latter only controls OS
and built-in app updates.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/software-updates-macos (Refer
to the "Update policy settings" section).
Question 10
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune. The subscription contains a group named Group1. Group1 contains devices enrolled in Intune. You deploy Remote Help in Intune. You need to configure Remote Help to only allow support administrators to join Remote Help sessions from the devices in Group1. Which type of Microsoft Entra object should you create, and which type of policy should you configure? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Show Answer
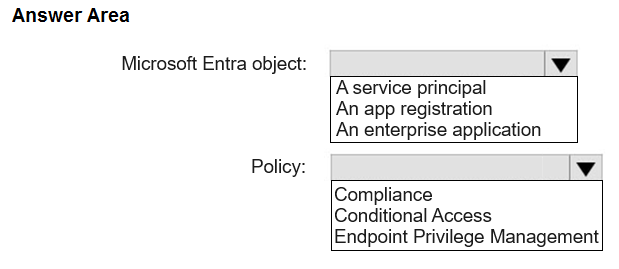
MICROSOFT ENTRA OBJECT: AN ENTERPRISE APPLICATION POLICY: CONDITIONAL ACCESS
To restrict access to a cloud application like Remote Help based on the device a user is signing in from, you must use a Conditional Access policy. This type of policy allows administrators to create "if-then" rules for access control. In this scenario, the rule would be: IF a user in the "support administrators" group tries to access... ...the Remote Help cloud application... THEN they must be using a device that is a member of Group1. The Remote Help service is represented within Microsoft Entra ID as an enterprise application. The Conditional Access policy is configured to target this specific enterprise application. The policy's conditions then use a device filter to ensure the user's device is in the required group (Group1).
Microsoft Intune Documentation | Use Conditional Access with Intune: This document
explains how Conditional Access policies are the primary mechanism for controlling access
to resources. It states, "Conditional Access policies can be used to require devices to be
compliant... With Conditional Access, you can control access to apps and services." This
directly supports using Conditional Access to control access to the Remote Help app.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/conditional-access
Section: "Ways to use Conditional Access with Intune"
Microsoft Entra Documentation | What are enterprise applications in Microsoft Entra ID?:
This source defines an enterprise application as the object you configure and manage
within your tenant. "An enterprise application is an object in Microsoft Entra ID that
represents an application... You can configure properties for the application, such as user
assignment, and create policies like Conditional Access policies." This confirms that the
enterprise application is the correct object type to which policies are applied.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identity/enterprise-apps/what-is-an-enterprise-application
Section: "Overview"
Microsoft Intune Documentation | Configure Conditional Access for Remote Help: This
guide provides a specific example of creating a Conditional Access policy for Remote Help.
The steps clearly show selecting "Remote Help" from the list of cloud apps (which are
enterprise applications) and applying conditions to it. This directly validates both chosen
answers.
Section: "Configure Conditional Access for Remote Help"
Question 11
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune and contains a user named Admin1. Admin1 must use the Microsoft Intune admin center to perform the following tasks: Create and assign apps and policies to users and devices by using Intune. Create, assign, and delete Windows 365 Cloud PC provisioning policies. You need to assign the required roles to Admin1. The solution must meet the following requirements: Follow the principle of least privilege. Minimize administrative effort. What should you do?
Show Answer
ASSIGN ADMIN1 THE CLOUD PC ADMINISTRATOR ROLE.
The built-in Cloud PC Administrator role grants full permissions to manage all Windows 365 features within the Microsoft Intune admin center. This includes the required tasks of creating, assigning, and deleting Cloud PC provisioning policies. Crucially, this role also includes permissions to manage Intune objects that Cloud PCs rely on, such as creating and assigning applications and configuration policies. Assigning this single, pre-defined role satisfies all requirements while minimizing administrative effort, as it avoids the overhead of creating and maintaining a custom role. It also adheres to the principle of least privilege by being more specific than broader roles like Intune Administrator or Global Administrator.
Assign Admin1 the Help Desk Operator role: This role is for remote support tasks and lacks permissions to create or assign apps, policies, or manage Cloud PC provisioning. Assign Admin1 the Cloud PC Reader role: This is a read-only role. It does not permit creating, assigning, or deleting any policies or applications. Create a custom Microsoft Entra role and assign the role to Admin1: Microsoft Entra roles are for managing Entra ID resources. Intune and Windows 365 management are handled through Intune's own RBAC system. Create a custom Intune role and assign the role to Admin1: While this could achieve the principle of least privilege, it fails the "minimize administrative effort" requirement, as a suitable built-in role already exists.
1. Microsoft Intune Documentation - Role-based access control (RBAC) with Microsoft
Intune: This document details the permissions for built-in roles. The "Cloud PC
Administrator" role is listed with permissions to manage Cloud PCs, device configurations,
and managed apps, which directly aligns with the question's requirements.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/fundamentals/role-based-accesscontrol#built-in-roles
2. Windows 365 Documentation - Role-based access control for Windows 365: This source
explicitly states that the "Cloud PC Administrator" is a built-in role for Microsoft Intune that
allows for the management of Cloud PCs. It confirms this role has the necessary
permissions for provisioning policies.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-365/enterprise/role-based-access-control
Question 12
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune. The subscription contains Windows 11 devices enrolled in Intune. The subscription contains three groups named Departement1, Department2, and Department3. You need to deploy Microsoft 365 Apps to the Windows 11 devices. The solution must meet the following requirements: Users in Department1 and Department2 must receive the full Microsoft 365 Apps suite, including Microsoft Project and Visio. Users in Department3 must receive the full Microsoft 365 Apps suite, including Microsoft Project, but without Visio. All other users must receive the full Microsoft 365 Apps suite without Microsoft Project or Visio. What is the minimum number of deployments you should create?
Show Answer
3
In Microsoft Intune, each unique combination of applications within the Microsoft 365 Apps suite constitutes a distinct app configuration that must be created as a separate deployment. The scenario requires three unique software configurations: 1. Microsoft 365 Apps + Project + Visio (for Department1 and Department2). 2. Microsoft 365 Apps + Project (for Department3). 3. Microsoft 365 Apps only (for all other users). Therefore, a minimum of three separate app deployments must be created. Each deployment will be assigned to its respective group, using exclusions for the "all other users" deployment to prevent conflicts with the more specific group assignments.
1: A single deployment cannot deliver three different combinations of applications to different user groups. 2: Two deployments are insufficient as there are three unique software configurations required by the different groups. 4: This is not the minimum number. Department1 and Department2 have identical requirements and can be targeted by a single deployment, making three the minimum.
Microsoft Learn: Add Microsoft 365 apps to Windows 10/11 devices with Microsoft Intune.
This document details the process of creating a Microsoft 365 Apps deployment. The "Step
2: Configure app suite" section shows that the selection of apps (including additional ones
like Project and Visio) is part of a single app configuration. To deploy a different set of apps,
a new app configuration must be created.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/apps-add-office365
Microsoft Learn: Assign apps to groups with Microsoft Intune. This document explains how
to assign apps and use include/exclude assignments. To fulfill the scenario's requirements,
one deployment would be assigned to "All Users" while excluding Department1,
Department2, and Department3 to avoid deployment conflicts.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/apps-assign
Question 13
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune. You configure Intune to send log data to Log Analytics. You need to review events involving devices that fail to enroll in Intune. What should you monitor?
Show Answer
A
To review events involving devices that fail to enroll in Intune, you must monitor the operational logs. When Intune diagnostic settings are configured to send data to a Log Analytics workspace, the IntuneOperationalLogs table is specifically designed to capture information about the success or failure of device enrollments. This log provides the necessary event details to troubleshoot enrollment issues as required by the scenario.
B. audit logs: These logs (IntuneAuditLogs) track administrative actions, such as creating or modifying policies, not device-initiated enrollment events. C. the Intune Device log: This log (IntuneDevices) contains inventory data for devices that have already successfully enrolled, not information on failed attempts. D. device compliance organizational logs: These logs provide aggregated compliance reports and are not used for troubleshooting individual device enrollment failures.
Microsoft. (2023). Send log data to storage, event hubs, or Log Analytics in Intune.
Microsoft Learn. Retrieved from https://learn.microsoft.com/enus/mem/intune/fundamentals/review-logs-using-azure-monitor. This document explicitly
states, "OperationalLogs: Show the success or failure of users and devices that enroll in
Intune..."
Microsoft. (2023). Use Log Analytics to examine the Intune logs. Microsoft Learn. Retrieved
from https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/fundamentals/review-logs-using-azuremonitor-log-analytics. This guide provides examples of using Kusto Query Language (KQL)
on the IntuneOperationalLogs table to find enrollment information.
Question 14
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune. The subscription contains corporate-owned, fully managed Android Enterprise devices. You plan to deploy a configuration profile that will have a device restrictions profile type named Profile1. Profile1 will assign maintenance windows for system updates. What should you configure from the Configuration settings for Profile1?
Show Answer
GENERAL
In Microsoft Intune, when creating a device restrictions profile for corporate-owned, fully managed Android Enterprise devices, the settings for system updates are located under the General category. This section contains the "System update" policy, which can be configured to "Maintenance window". This allows an administrator to specify a start and end time during which the OS updates will be automatically installed on the devices, ensuring updates occur during non-critical hours.
Device experience: This section is used for configuring settings like kiosk mode, lock screen customization, and other user interface elements, not system update schedules. Connectivity: This section is for managing network-related settings, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, NFC, and cellular data controls, not operating system updates. Power Settings: This section controls device power and battery-related behaviors, such as screen-off timeouts and battery charge modes, which are distinct from system update policies.
Microsoft. (2024). Android Enterprise device settings to allow or restrict features on
corporate-owned devices using Intune. Microsoft Learn. Retrieved from
Section: General
Details: This official documentation explicitly lists "System update" as a setting under the
"General" category for Android Enterprise corporate-owned device restrictions. It details the
options, including "Maintenance window," and the ability to set a start and end time.
Question 15
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. You use Microsoft Intune to manage Windows 365 Cloud PC devices. You need to deploy a Windows 365 Security Baseline to the Cloud PC devices. The solution must meet the following requirements: Block data execution prevention. Enable virtualization-based security (VBS) and Secure Boot. What should you configure for the Windows 365 Security Baseline profile? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Show Answer
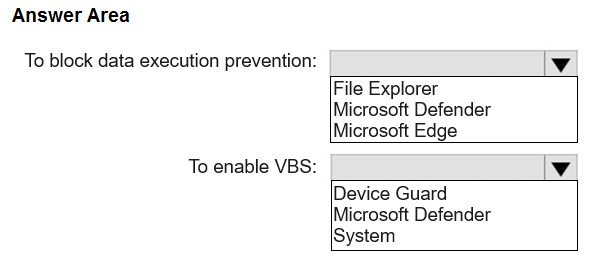
TO BLOCK DATA EXECUTION PREVENTION: MICROSOFT DEFENDER TO ENABLE VBS: DEVICE GUARD
In Microsoft Intune, the Windows 365 Security Baseline provides a template of pre- configured security settings. Data Execution Prevention (DEP) is a system-level security feature that helps prevent damage from viruses and other security threats by monitoring programs to ensure they use system memory safely. These exploit protection settings are managed within the Microsoft Defender configuration group in the security baseline. This category includes settings for Microsoft Defender Antivirus, Attack Surface Reduction, and Exploit Guard, which encompasses DEP. Virtualization-based security (VBS) uses hardware virtualization to create a secure, isolated region of memory. This feature is a core component of what Microsoft collectively terms Device Guard. The Device Guard settings category in Intune profiles is the specific location to configure VBS features, including Secure Boot, Credential Guard, and code integrity policies.
Microsoft Intune Documentation | Security baselines:
Windows security baselines: This document outlines the settings available in Windows
security baselines. The "Microsoft Defender" section details settings for antivirus, exploit
protection, and attack surface reduction.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/security-baselines-windows
Device Guard settings: This documentation confirms that settings to enable virtualization-
based security (VBS) are located under the "Device Guard" profile settings.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/endpoint-protection-windows-10#deviceguard
Microsoft Hardware Dev Center Documentation:
Virtualization-based Security (VBS): This official source explains that VBS is the core
technology for a set of security solutions, including Device Guard.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/design/device-experiences/oem-vbs
Question 16
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune. You create a new Android app protection policy named Policy1 that prevents screen captures in all Microsoft apps. You discover that an unmanaged email client installed on Android devices can still capture screens. You need to ensure that users can only use Microsoft apps to access email. What should you do?
Show Answer
A
The existing App Protection Policy (APP) correctly applies data protection settings to managed Microsoft apps. However, it cannot control unmanaged applications. The core issue is that an unmanaged email client is accessing corporate data. To resolve this, a Conditional Access (CA) policy is required. By creating a CA policy that targets the Exchange Online cloud app and includes the "Require app protection policy" grant control, you can block access from any application that is not managed by an Intune APP. This effectively prevents the unmanaged email client from connecting and forces users to use a managed app like Microsoft Outlook.
B. Create a compliance policy: A compliance policy assesses the health and configuration of the entire device (e.g., OS version, encryption), not which specific applications are used to access corporate data. C. Modify the Data protection settings of Policy1: Modifying the settings within the existing policy will not extend its control to the unmanaged email client, which is the source of the problem. D. Modify the assignments of Policy1: Changing the user or group assignments for the policy does not change which applications the policy targets; it will still not apply to the unmanaged app.
1. Microsoft Learn | App-based Conditional Access with Intune: "You can create Conditional
Access policies that require users to use a policy-protected app to access corporate data...
This restriction ensures that corporate data is only accessed by apps that you can manage
and protect with Intune app protection policies."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/app-based-conditional-accessintune
2. Microsoft Learn | How to use app-based Conditional Access policies to protect access to
Microsoft 365 apps: This guide details the steps for creating the required policy. "Step 2:
Configure an Azure AD Conditional Access policy for Microsoft 365 apps... For Grant, select
Require app protection policy."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/app-based-ca-m365
3. Microsoft Learn | App protection policies overview: This document clarifies the scope of
App Protection Policies, stating they are "rules that ensure an organization's data remains
safe or contained in a managed app." This highlights that they do not affect unmanaged
apps.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/app-protection-policy
Question 17
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. All Windows devices are enrolled in Microsoft Intune. You need to create an app protection policy named Policy1 and apply Policy1 to the devices. What can you protect by using Policy1?
Show Answer
MICROSOFT EDGE
Microsoft Intune app protection policies (APP), also known as Mobile Application Management (MAM), can be created for Windows 11 devices. These policies protect data within an application. According to Microsoft's official documentation, the only application that currently supports app protection policies on the Windows platform is Microsoft Edge. This allows administrators to enforce policies such as restricting cut, copy, and paste operations between Edge and unmanaged applications, thereby protecting organizational data accessed through the browser.
Microsoft Outlook: App protection policies are supported for the Microsoft Outlook mobile app on iOS/iPadOS and Android, but not for the Outlook desktop client on Windows. Microsoft OneDrive: App protection policies are supported for the Microsoft OneDrive mobile app on iOS/iPadOS and Android, but not for the OneDrive sync client on Windows. Microsoft Teams: App protection policies are supported for the Microsoft Teams mobile app on iOS/iPadOS and Android, but not for the Teams desktop client on Windows.
1. Microsoft Learn. (2024). App protection for Windows devices. "You can create MAM
policies for Windows 11 devices. Currently, the only supported app for MAM on Windows is
Microsoft Edge." [URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/app-protectionpolicy-settings-windows]
2. Microsoft Learn. (2024). Microsoft Intune protected apps. This document lists the
applications that support Intune app protection policies, broken down by platform
(iOS/iPadOS, Android). It shows extensive support for apps like Outlook, OneDrive, and
Teams on mobile platforms but not for Windows. [URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/enus/mem/intune/apps/apps-supported-with-mam]
Question 18
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. You use Microsoft Intune to manage all Windows 11 devices. You create an attack surface reduction (ASR) policy named Profile1 based on the Attack Surface Reduction Rules profile and assign Profile1 to all the devices. A user reports that an Adobe Reader plug-in is now blocked. You need to ensure that the plug-in is unblocked. What should you do?
Show Answer
C
The most direct and appropriate solution is to modify the existing Attack Surface Reduction (ASR) policy, Profile1. ASR policies in Microsoft Intune allow for granular exclusions for specific files, folders, or processes that are incorrectly identified as malicious. By configuring an exclusion for the Adobe Reader plug-in within Profile1, the plug-in will be allowed to run while the ASR rule remains active and protects the device from other potential threats. This approach precisely targets the reported issue without weakening the overall security posture.
A. Create an Endpoint Privilege Management policy and assign the policy to all the devices. Endpoint Privilege Management is used to manage elevation requests for standard users, not to create exclusions for ASR rules that block processes. B. Add a scope tag to Profile1. Scope tags are for role-based access control (RBAC) to determine which administrators can manage Intune objects; they do not alter policy behavior on devices. D. Create a device compliance policy and assign the policy to all the devices. Device compliance policies are used to evaluate if a device meets organizational standards, not to configure security settings like ASR rule exclusions.
1. Microsoft Learn | Attack surface reduction rules deployment overview: This document
explains how to operationalize ASR rules, including the process of handling false positives
by creating exclusions. It states, "You can exclude files and folders from being evaluated by
most attack surface reduction rules."
asr-rules
2. Microsoft Learn | Enable attack surface reduction rules: This guide details the
configuration of ASR rules via Microsoft Intune, including how to set exclusions. The section
on Intune configuration explicitly shows the settings for creating exclusions within an ASR
profile.
3. Microsoft Learn | Policy CSP - Defender: The documentation for the Defender
Configuration Service Provider (CSP) details the AttackSurfaceReductionOnlyExclusions
setting, which corresponds to the per-rule exclusion capability configured in the Intune UI.
Question 19
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. All devices are enrolled in Microsoft Intune. You need to ensure that devices that have NOT checked in for 30 days are deleted from Intune. What should you configure from the Microsoft Intune admin center?
Show Answer
C
Device cleanup rules in Microsoft Intune are the specific feature designed to automatically remove device records that are inactive, stale, or have not checked in for a specified number of days. By configuring a device cleanup rule, an administrator can set the inactivity threshold (between 30 and 270 days) to automatically delete these device objects from the Intune portal. This directly fulfills the requirement to delete devices that have not checked in for 30 days, helping to maintain an accurate inventory and manage licenses.
A. a device limit restriction: This setting defines the maximum number of devices a user can enroll in Intune, not for removing inactive devices. B. automatic enrollment: This feature streamlines the process of enrolling new devices into Intune management, not the removal of existing, inactive ones. D. a configuration profile: This is used to deploy settings, policies, and configurations to managed devices, not to manage the lifecycle of the device record in Intune.
Microsoft. (2024). Automatically delete devices with cleanup rules in Microsoft Intune.
Microsoft Learn. Retrieved from https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/remoteactions/devices-wipe#automatically-delete-devices-with-cleanup-rules Microsoft. (2023).
What is a device configuration profile in Microsoft Intune?. Microsoft Learn. Retrieved from
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/configuration/device-profiles Microsoft.
(2024). Set enrollment restrictions. Microsoft Learn. Retrieved from
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/enrollment/enrollment-restrictions-set
Question 20
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. All devices are enrolled in Microsoft Intune. You create a Conditional Access policy named Policy1 that requires multifactor authentication (MFA). You need to ensure that Policy1 only applies to devices marked as noncompliant. Which settings of Policy1 should you configure?
Show Answer
B
The "Filter for devices" setting within the Conditions of a Conditional Access policy allows for granular targeting based on device attributes. To ensure a policy applies only to noncompliant devices, an administrator would configure a rule expression within this filter. The expression would use the isCompliant device property, setting it to target devices where this value is false (e.g., device.isCompliant -eq false). This is the most direct and precise method to scope a policy to devices based on their Intune compliance status.
Device platforms under Conditions: This setting targets devices based on their operating system (e.g., Windows, iOS, Android), not their compliance state. Target resources: This defines the cloud applications, user actions, or authentication contexts that the policy protects, not the characteristics of the device initiating the access request. Grant: This setting defines the access control to be enforced (the action), such as requiring MFA. It does not define the conditions under which the policy applies. Session: This setting is used to configure session-level controls, like sign-in frequency or application-enforced restrictions, which occur after the initial conditions are met.
1. Microsoft Learn: "Filter for devices as a condition in Conditional Access policy." This
document explicitly states, "You can also use the filter for devices condition to target specific
devices based on their compliance state... To target non-compliant devices, you can use the
following expression: (device.isCompliant -eq false)." URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/enus/entra/identity/conditional-access/concept-condition-filters-for-devices
2. Microsoft Learn: "Conditional Access: Conditions." This article provides an overview of
the available conditions, positioning "Filter for devices" as the mechanism for creating
expressions on device properties, distinguishing it from broader conditions like "Device
platforms." URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identity/conditionalaccess/concept-conditional-access-conditions
3. Microsoft Learn: "Conditional Access: Grant." This document details the grant controls,
confirming they are the enforcement actions (like "Require multifactor authentication" or
"Require device to be marked as compliant") taken after conditions are matched. URL:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identity/conditional-access/concept-conditionalaccess-grant
Question 21
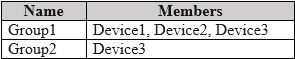
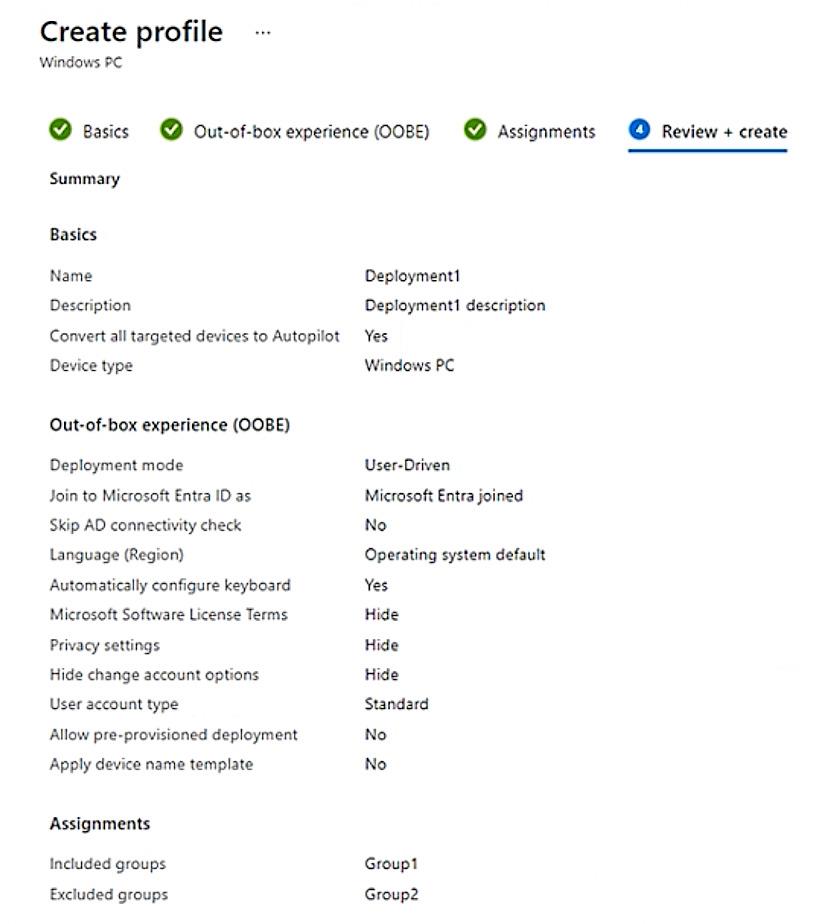
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft Entra tenant that contains the devices shown in the following table. 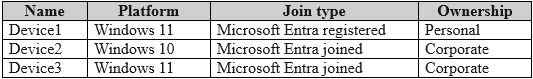
Show Answer
1. THE DEPLOYMENT PROFILE CAN BE ASSIGNED TO GROUP1 – NO 2. THE DEPLOYMENT PROFILE CAN BE ASSIGNED TO GROUP2 – YES 3. THE DEPLOYMENT PROFILE WILL BE APPLIED TO DEVICE2 – NO
Windows Autopilot deployment profiles can be targeted only to Microsoft Entra device groups. User (or Microsoft 365) groups are not valid targets, so Group1 cannot receive the profile. Group2 is a dynamic DEVICE security group and therefore is an eligible assignment target. Device2 is not registered in Windows Autopilot; the dynamic-membership rule for Group2 (device.devicePhysicalIDs -any -contains “[ZTDId]”) selects only devices that are already in the Autopilot service. Because Device2 lacks an Autopilot ID, it is not a member of Group2 and will not receive the profile.
1. Microsoft Learn – “Assign Windows Autopilot deployment profiles to devices”
https://learn.microsoft.com/mem/autopilot/enrollment-autopilot#assign-a-profile
(Only device groups can be selected for profile assignment.)
2. Microsoft Learn – “Create a dynamic group with Autopilot devices”
https://learn.microsoft.com/mem/autopilot/autopilot-device-group#rule-example
(Rule uses device.devicePhysicalIDs and “[ZTDId]”; only already-registered Autopilot
devices satisfy the rule.)
Question 22
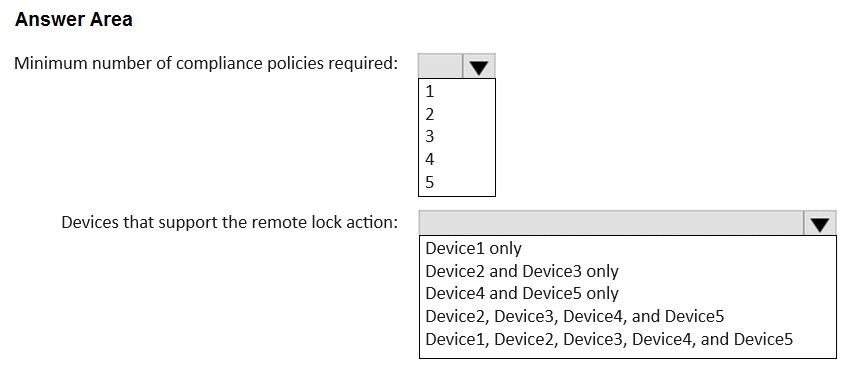
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 tenant that uses Microsoft Intune to manage the devices shown in the following table. 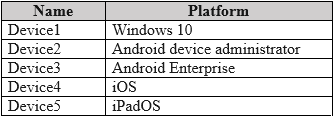
Show Answer
MINIMUM NUMBER OF COMPLIANCE POLICIES REQUIRED: 4 DEVICES THAT SUPPORT THE REMOTE LOCK ACTION: DEVICE2, DEVICE3, DEVICE4, AND DEVICE5
Minimum Number of Compliance Policies In Microsoft Intune, compliance policies are configured based on the device's operating system platform. To determine the minimum number of policies needed, we must identify the unique platforms from the provided list of devices. Windows 10: Requires a "Windows 10 and later" policy. (1 policy) Android device administrator: Requires a dedicated "Android device administrator" policy. (1 policy) Android Enterprise: Requires a separate "Android Enterprise" policy. (1 policy) iOS and iPadOS: These two platforms are managed together under a single "iOS/iPadOS" policy. (1 policy) Therefore, a minimum of four distinct compliance policies are required to cover all the specified device platforms. Remote Lock Support The remote lock action is a device management feature whose availability differs across platforms. Supported: The remote lock action is fully supported for Android device administrator, Android Enterprise, iOS, and iPadOS. Not Supported: The remote lock action is not supported for the Windows platform in Microsoft Intune. While other actions like 'Wipe' or 'Restart' are available for Windows, 'Remote Lock' is not. Thus, only Device2, Device3, Device4, and Device5 support the remote lock action.
Compliance Policy Platforms: According to Microsoft's official documentation, you create
compliance policies by selecting a specific platform. The platforms listed in the question
(Windows 10 and later, Android device administrator, Android Enterprise, and iOS/iPadOS)
are distinct options during policy creation.
Microsoft Learn. (2025). Create a compliance policy in Microsoft Intune. Retrieved from
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/protect/create-compliance-policy (Refer to the
"Create the policy" section).
Remote Lock Action Support: Microsoft's documentation on remote device actions explicitly
lists the platforms that support the "Remote lock" feature. It confirms support for Android,
iOS, and macOS but explicitly states it is not supported for Windows.
Microsoft Learn. (2025). Remotely lock devices with Microsoft Intune. Retrieved from
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/remote-actions/device-remote-lock (Refer to the
"Supported platforms" section).
Question 23
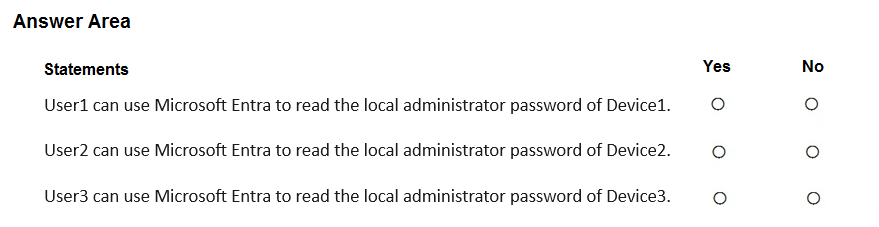
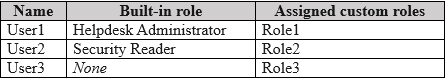
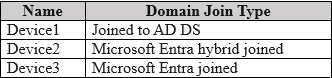
HOTSPOT - Your network contains an on-premises Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain. You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune and syncs with the AD DS domain. Windows Local Administrator Password Solution (Windows LAPS) is enabled in Microsoft Entra ID. The subscription has the custom roles shown in the following table. 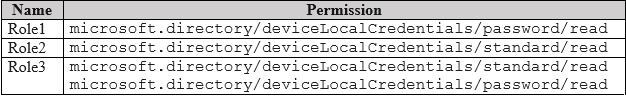
Show Answer
STATEMENT 1: NO STATEMENT 2: NO STATEMENT 3: YES
Device1: A device that is only "Joined to AD DS" is not managed by Microsoft Entra LAPS. Entra LAPS requires devices to be either Microsoft Entra joined or Microsoft Entra hybrid joined. Therefore, the password for Device1 is not stored in Microsoft Entra and cannot be read from it. User2: To read a LAPS password from Microsoft Entra, a user requires the specific delegated permission microsoft.directory/deviceLocalCredentials/password/read. User2's assigned role, Role2, lacks this permission, granting only standard/read access. Thus, User2 cannot retrieve the password for any device. User3: User3 has the necessary microsoft.directory/deviceLocalCredentials/password/read permission through Role3. Device3 is "Microsoft Entra joined," which is a supported scenario for Microsoft Entra LAPS. With the correct permission and a supported device join type, User3 can successfully retrieve the local administrator password.
Microsoft Official Documentation: "Get started with Windows LAPS and Microsoft Entra ID"
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identity/devices/howto-manage-local-admin-passwords
Specific Section: Under the "Prerequisites" section, it states, "The Windows LAPS feature
requires that your Windows devices are either Microsoft Entra joined or Microsoft Entra
hybrid joined." This confirms why Device1 is not applicable.
Microsoft Official Documentation: "Role-based access control for Windows LAPS"
Specific Section: The documentation explicitly lists the two permissions for LAPS:
microsoft.directory/deviceLocalCredentials/password/read (to recover the password) and
microsoft.directory/deviceLocalCredentials/standard/read (to read metadata). This confirms why
User2's permissions are insufficient and User3's are sufficient.
Question 24
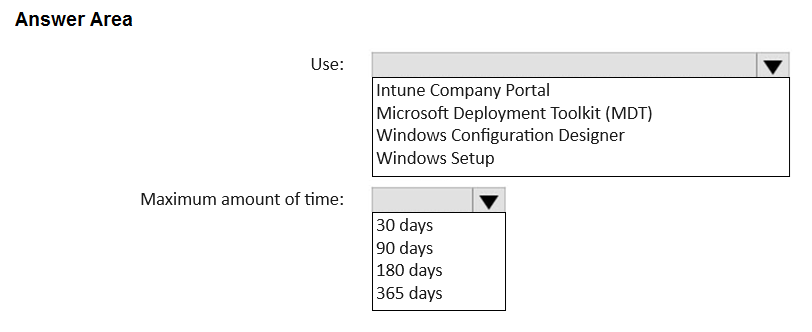
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription and use Microsoft Intune. You purchase 50 Windows devices. You configure automatic enrollment to Intune for Microsoft Entra joined devices. You need to use a provisioning package to join the devices to Microsoft Entra. What should you use to create the provisioning package, and what is the maximum amount of time you can use the package for bulk enrollment? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Show Answer
TO CREATE THE PROVISIONING PACKAGE, YOU SHOULD USE: WINDOWS CONFIGURATION DESIGNER YOU CAN USE THE PACKAGE FOR BULK ENROLLMENT FOR A MAXIMUM OF: 180 DAYS
To create a provisioning package (.ppkg) for enrolling Windows devices into Intune and joining them to Microsoft Entra ID, the correct tool is the Windows Configuration Designer (WCD). WCD is part of the Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (ADK). When creating the package for bulk enrollment, you must acquire a bulk enrollment token from Microsoft Entra ID. This token is embedded within the provisioning package and has a defined expiration period. According to official Microsoft documentation, this token is valid for a maximum of 180 days from the date of creation. After this period, the package will no longer be able to enroll devices.
1. Microsoft Learn: Bulk enrollment for Windows devices. This document explicitly states,
"You can use Windows Configuration Designer (WCD) to create a provisioning package
(.ppkg)..." and "...the token is valid for 180 days."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/enrollment/windows-bulk-enroll
2. Microsoft Learn: Create a provisioning package for Windows 10/11. This guide details the
process and confirms the use of Windows Configuration Designer for creating .ppkg files for
various configurations, including Azure AD join and MDM enrollment.
Question 25
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. You need to configure the automated investigation and response (AIR) remediation level for a device named Device1 to require approval for all folders. What should you create?
Show Answer
B
In Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, device groups are the specific mechanism used to apply targeted configurations to a set of devices. To configure a unique automated investigation and response (AIR) remediation level for a specific device, such as requiring approval for all remediation actions, you must first create a device group. You can then add the device (Device1) to this group and apply the desired remediation level policy directly to that group. This allows for granular control over automation settings on a per-group basis.
A. a security group: While used for assigning permissions and some policies in Azure AD and Intune, security groups are not the primary object used to configure specific Defender for Endpoint settings like AIR remediation levels. C. an administrative unit: Administrative units are Azure AD containers for delegating administrative permissions over a subset of directory objects; they are not used for applying device configuration policies. D. an action group: Action groups are a feature of Azure Monitor used to define a collection of notification pan action group: Action groups are a feature of Azure Monitor used to define a collection of notification preferences and actions to be triggered by an alert, which is unrelated to
device configuration.
1. Microsoft Learn. "Create and manage device groups." This document explicitly states, "In
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, you can create device groups and use them to... Configure
device-specific settings such as automated remediation level."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/security/defender-endpoint/machinegroups
2. Microsoft Learn. "Configure automated investigation and response capabilities in
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint." This guide details the configuration process, stating, "You
can set the automation level for each device group." It outlines the steps which involve
navigating to the device groups settings.
Question 26
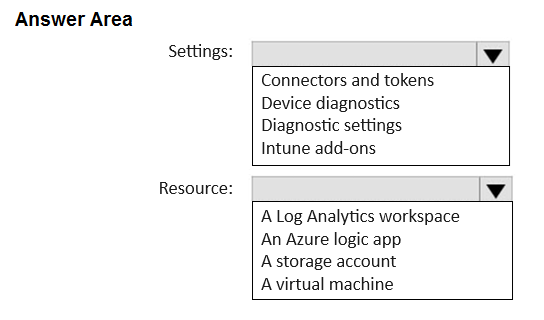
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. You need to route Microsoft Intune logs to an Azure resource that supports the use of visuals, monitoring, and alerting. Which settings should you configure in Intune, and which resource should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Show Answer
INTUNE SETTING TO CONFIGURE: DIAGNOSTIC SETTINGS AZURE RESOURCE TO USE: LOG ANALYTICS WORKSPACE
To route Microsoft Intune platform logs to an external Azure resource, you must configure Diagnostic settings within the Intune admin center. This feature allows you to select specific log categories and send them to a chosen destination. A Log Analytics workspace is the appropriate Azure resource for this requirement because it is the primary data store for Azure Monitor Logs. It is specifically designed to collect, aggregate, and analyze log data, and it natively supports creating complex queries with Kusto Query Language (KQL), building interactive visualizations with Azure Workbooks, and configuring alerts based on log data, thereby fulfilling all the requirements of the question.
1. Microsoft Learn | Send log data to Azure Storage, Azure Event Hubs, or Azure Monitor.
This document explicitly states, "Microsoft Intune has built-in logs... You can use diagnostic
settings to send platform log data to Azure Monitor." It further describes the destinations,
noting that a Log Analytics workspace is "Best for complex queries, alerting, and seeing
data from multiple sources."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/fundamentals/review-logs-using-azuremonitor
2. Microsoft Learn | Overview of Log Analytics in Azure Monitor. This resource details the
capabilities of a Log Analytics workspace, confirming it is the correct choice for analysis and
visualization. It states, "Log Analytics is a tool in the Azure portal that's used to edit and run
log queries against data in the Azure Monitor Logs store... You can also use Log Analytics to
write a query and then use its results to create an alert rule or a workbook."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/logs/log-analytics-overview
Question 27
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune. You need to configure a compliance policy for the iOS/iPadOS platform. The solution must meet the following requirements: • Require jailbroken devices to be marked as noncompliant. • Mark devices without a password lock as noncompliant. Which compliance policy settings should you configure for each requirement? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Show Answer
REQUIRE JAILBROKEN DEVICES TO BE MARKED AS NONCOMPLIANT: DEVICE HEALTH MARK DEVICES WITHOUT A PASSWORD LOCK AS NONCOMPLIANT: SYSTEM SECURITY
In Microsoft Intune, compliance policy settings for iOS/iPadOS are grouped into categories. The Device Health category includes settings to verify the integrity of the operating system, such as the "Jailbroken devices" check. This setting is used to mark devices as noncompliant if they have been jailbroken. The System Security category contains settings related to securing the device at the system level. This includes password requirements, such as "Require a password to unlock mobile devices," which ensures that a device is marked as noncompliant if it does not have a passcode set.
1. Microsoft Learn | iOS/iPadOS compliance settings in Microsoft Intune: This official
documentation details the available compliance settings.
Device Health: The "Jailbroken devices" setting is listed under this section. It states, "When
enabled, evaluate devices for jailbreak status. When a device is jailbroken, it's marked as
not-compliant."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/compliance-policy-createios#device-health
System Security: The "Require a password to unlock mobile devices" setting is listed under
this section. It states, "When set to Require, users must enter a password before they can
access their device."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/compliance-policy-createios#system-security
Question 28
You have a Microsoft Intune subscription. You have devices enrolled in Intune as shown in the following table. 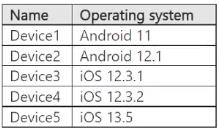
Show Answer
B
In Microsoft Intune, app configuration policies are platform-specific. When creating a policy for managed devices, you must select a target operating system platform. A single policy cannot be applied to both iOS/iPadOS and Android devices simultaneously. The devices in the table belong to two distinct platforms: Android Enterprise: Device1 and Device2. iOS/iPadOS: Device3, Device4, and Device5. Therefore, to manage App1 across all devices, a minimum of two separate app configuration policies are required: one for the Android devices and another for the iOS devices.
A. 1: This is incorrect because app configuration policies in Intune are platform-specific. The policy creation workflow requires you to choose either iOS/iPadOS or Android Enterprise, meaning a single policy cannot target both operating systems. C. 3, D. 4, & E. 5: These options are incorrect because they exceed the minimum number required. A single policy for a specific platform can target multiple devices and OS versions within that same platform family. For example, one iOS policy can cover all three iOS devices, and one Android policy can cover both Android devices.
Source: Microsoft Learn, App configuration policies for Microsoft Intune.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/app-configuration-policies-overview
Reference: In the section Types of app configuration policy, the description for the Managed
devices channel states, "This policy channel relates to the app configuration delivered
through the MDM OS channel. The app configuration policy for managed devices chooses a
platform."
Source: Microsoft Learn, Add app configuration policies for managed iOS/iPadOS devices.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/app-configuration-policies-use-ios
Reference: Under the section Create an app configuration policy for managed iOS/iPadOS
devices, Step 4 explicitly requires the administrator to set the Platform to iOS/iPadOS.
Source: Microsoft Learn, Add app configuration policies for managed Android Enterprise
devices.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/app-configuration-policies-use-android
Reference: Under the section Create an app configuration policy, Step 4 requires the
administrator to set the Platform to Android Enterprise. This confirms that a separate policy
must be created specifically for the Android platform.
Question 29
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. All devices are enrolled in Microsoft Intune. You have a device group named Group1 that contains five Windows 11 devices. You need to ensure that the devices in Group1 automatically receive new Windows 11 builds before the builds are released to the public. What should you configure in Intune? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Show Answer
CREATE AN “UPDATE RINGS FOR WINDOWS 10 AND LATER” POLICY AND ASSIGN IT TO GROUP1.
WITHIN THAT RING SET SERVICING CHANNEL TO “WINDOWS INSIDER – RELEASE PREVIEW CHANNEL”.
Intune delivers pre-release Windows builds through Windows Update for Business update- ring policies. Selecting the Windows Insider Release Preview channel in an Update ring enrolls the targeted devices in Windows Insider for Business and automatically distributes Windows 11 builds ahead of general (public) availability, meeting the requirement.
1. Microsoft Learn – “Manage Windows 10 and Windows 11 software updates in Intune” →
Create an update ring; Servicing channel options include “Windows Insider – Release
Preview Channel”.
https://learn.microsoft.com/mem/intune/protect/windows-update-for-business-configure
2. Microsoft Learn – “ Windows Insider Program for Business: choose your channel”
(Release Preview gets builds before they are generally available).
https://learn.microsoft.com/windows-insider/program-windows-insider#choose-your-channel
Question 30
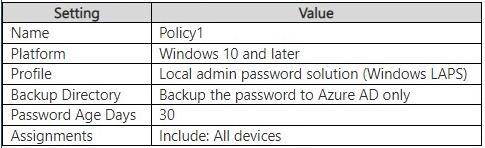
 You have an Endpoint security policy that is configured as shown in the following table.
You have an Endpoint security policy that is configured as shown in the following table.
 For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select
No.
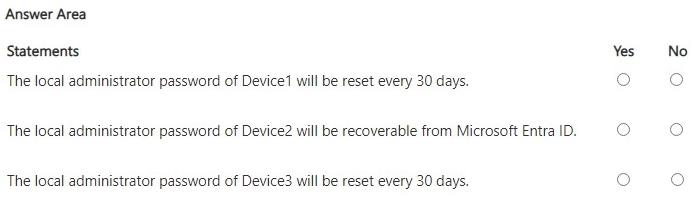
Show Answer
1. Microsoft Learn Manage Windows LAPS with Microsoft Intune, Prerequisites > Supported
device join types (Azure AD joined, Hybrid Azure AD joined) and Backup directory behavior.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/windows-laps-intune
2. Microsoft Learn Windows LAPS overview, section Supported management solutions and
Azure AD scenarios. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windowsserver/identity/laps/windows/laps-overview
Question 31
You have a Microsot Entra tenant named contoso.com. You have a workgroup computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 11. You need to add Computer1 to contoso.com. What should you use?
Show Answer
THE SETTINGS APP
To join a Windows 11 device to a Microsoft Entra tenant, the standard and recommended method is through the graphical user interface provided by the Settings app. An administrator or user would navigate to Settings > Accounts > Access work or school and select Connect. From there, the option "Join this device to Microsoft Entra ID" initiates the process, prompting for Entra credentials to complete the join operation. This is the primary procedure for enrolling a single, existing Windows device into Entra management.
Computer Management: This tool is used for local system administration and joining computers to a traditional Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain, not a Microsoft Entra tenant. netdom.exe: This is a command-line utility specifically designed for joining computers to a traditional Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain. It does not support joining to Microsoft Entra ID.
Microsoft Entra. (2024). Join a new Windows device to Microsoft Entra ID during the first-
run experience. Microsoft Learn. Retrieved from https://learn.microsoft.com/enus/entra/identity/devices/join-procedure (This document explicitly details the procedure
using the Settings app for an existing device).
Microsoft. (2023). Netdom join. Microsoft Learn. Retrieved from
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-server-2012-r2and-2012/cc772217(v=ws.11)) (This documentation confirms netdom.exe is for joining an
Active Directory domain).
Question 32
HOTSPOT - You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune. From the Microsoft Intune admin center, you add the apps shown in the following table. 
Show Answer
APP1: A REQUIRED ASSIGNMENT TO A USER GROUP APP2: AN AVAILABLE ASSIGNMENT TO A USER GROUP
App1: The requirement is for the application to be installed automatically for all users in the marketing department on any of their enrolled devices. A 'Required' assignment ensures the app is pushed and installed without user interaction. Assigning it to a user group ensures the policy follows the user, so the app is installed on any new or existing Windows device they enroll in Intune. App2: The requirement is for the app to be 'available for download' on personal, unenrolled Android devices for HR department users. An 'Available' assignment makes the app optional for users to install from the Company Portal. For devices that are not enrolled in Intune (common in Bring-Your-Own-Device scenarios), app assignments are targeted at user groups to allow access via the Company Portal without forcing device management.
Microsoft Intune Documentation - Add apps to Microsoft Intune: This document explains the
different assignment types.
Required: "The app is installed on devices in the selected groups." This forces the
installation.
Available for enrolled devices: "Users install the app from the Company Portal app or
Company Portal website." This makes the installation optional for users on managed
devices.
Available with or without enrollment: "Assign this app to groups of users with devices that
are not enrolled with Intune." This is the specific scenario for App2.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/apps-add#assign-an-app
Microsoft Intune Documentation - Assign apps to groups: This source clarifies the distinction
between user and device groups.
"If you assign the app to a user group, the app is available to that user on every device they
enroll in Intune... For unenrolled devices (BYOD), apps can be made available to users
through the Intune Company Portal." This directly supports the reasoning for both App1 and
App2 being assigned to user groups.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/apps-assign#assign-an-app-to-groups
Question 33
You have a Microsoft 365 Business Standard subscription and 100 Windows 10 Pro devices that are joined to Microsoft Entra. You purchase Microsoft 365 E5 licenses for all users. You need to upgrade the Windows 10 Pro devices to Windows 10 Enterprise. The solution must minimize administrative effort. Which upgrade method should you use?
Show Answer
SUBSCRIPTION ACTIVATION
Windows 10 Subscription Activation automatically steps a Windows 10 Pro installation up to Windows 10 Enterprise when an Azure AD-joined device is signed in by a user who has an Enterprise E3/E5 license. No re-imaging, media, or additional deployment tools are required, so administrative effort is minimal.
• Microsoft Deployment Toolkit lite-touch deployment – Requires creating deployment shares, images, and manual task-sequence execution; unnecessary effort compared with automatic license step-up. • In-place upgrade using Windows installation media – Needs media creation, scripting, user interaction, and device reboots; overkill when license assignment alone suffices. • Windows Autopilot – Simplifies new-device provisioning but still demands profile creation and device registration; not intended solely for edition upgrade of already-deployed PCs.
1. Microsoft Learn “ Windows 10/11 Subscription Activation
https://learn.microsoft.com/windows/deployment/windows-10-subscription-activation
(See section Azure AD-joined devices running Windows Pro.)
2. Microsoft Learn “ Deploy Windows Enterprise licenses
https://learn.microsoft.com/microsoft-365/commerce/subscriptions/windows-10-enterprisee3-overview
(Explains automatic upgrade from Pro to Enterprise when E3/E5 license is assigned.)
Question 34
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription. You have 10 computers that run Windows 10 and are enrolled in Microsoft Intune. You need to deploy the Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise suite to all the computers. What should you do?
Show Answer
A
The correct method to deploy software applications, including the Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise suite, to devices managed by Microsoft Intune is by using the app management features within the Intune admin center. An administrator would navigate to the "Apps" section, select to add a new app, and choose the "Microsoft 365 Apps for Windows 10 and later" app type. This allows for the configuration and assignment of the Office suite to the targeted computers.
B. From the Microsoft Intune admin center, create a Windows 10 and later device profile: Device configuration profiles are used to manage and configure settings, features, and security policies on devices, not to deploy application installers. C. From the Microsoft Entra admin center, add an enterprise application: Enterprise applications in Microsoft Entra ID are used to manage identity, user access, and single sign- on (SSO) for cloud applications, not for deploying client software to endpoints. D. From the Microsoft Entra admin center, add an app registration: App registrations are for developers to integrate their custom applications with the Microsoft identity platform for authentication and authorization purposes, not for software deployment.
Microsoft Learn: "Add Microsoft 365 apps to Windows 10/11 devices with Microsoft Intune".
This official documentation outlines the exact procedure: "You can create an app
deployment for Microsoft 365 Apps for Windows 10 and later devices from the Microsoft
Intune admin center. Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center. Select Apps > All apps >
Add."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/apps-add-office365
Microsoft Learn: "What is Microsoft Intune app management?". This document clarifies that
Intune's app management capabilities are used to "assign and install apps to devices and
users."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/app-management
Microsoft Learn: "Assign device profiles in Microsoft Intune". This source explains that
profiles are for "settings and features on your devices," differentiating them from app
deployment.
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/configuration/device-profile-assign
Question 35
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription. You have a Windows device named Device1 that is enrolled in Microsoft Intune. On January 1,2024, you assign an app named App1 to Device1 as a required app. The install of App1 fails. What is the next date that Intune will attempt to install App1?
Show Answer
A
For required applications that fail to install on a Windows device, the Microsoft Intune service will re-evaluate and attempt the installation again. The Intune Management Extension agent, which handles Win32 app deployments, checks for new assignments and retries failed installations approximately every 24 hours. Therefore, if the installation of App1 failed on January 1, 2024, the next attempt would occur on the following day, January 2, 2024.
B. January 5, 2024: This suggests a 4-day retry cycle, which is not the standard interval for failed required app installations in Intune. C. January 8, 2024: This suggests a 7-day retry cycle. While Intune has 7-day cycles for re- evaluating uninstalled required apps, the retry for a failed installation is 24 hours. D. January 31, 2024: This suggests a 30-day retry cycle, which is an incorrect interval for Intune app installation retries.
1. Microsoft Learn. "Troubleshoot app installation issues in Microsoft Intune." Under the
"App installation fails" section, it states, "For required apps, the agent checks for new apps
or retries app installations every 24 hours."
URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/troubleshoot-app-install#appinstallation-fails
2. Microsoft Learn. "Microsoft Intune management extension." This document details the
agent's functionality, including its check-in frequency. It confirms the agent checks with the
Intune service on an hourly basis for notifications and retries failed Win32 app installations
every 24 hours.