Microsoft MS-102
HOTSPOT
Overview
Litware, Inc. is a consulting company that has a main office in Montreal and a branch office in Seattle.
Litware collaborates with a third-party company named A. Datum Corporation.
Environment
On-Premises Environment
The network of Litware contains an Active Directory domain named litware.com. The domain contains three organizational units (OUs) named LitwareAdmins, Montreal Users, and Seattle Users and the users shown in the following table.

The domain contains 2,000 Windows 10 Pro devices and 100 servers that run Windows Server 2019.
Cloud Environment
Litware has a pilot Microsoft 365 subscription that includes Microsoft Office 365 Enterprise E3 licenses and Azure AD Premium P2 licenses.
The subscription contains a verified DNS domain named litware.com.
Azure AD Connect is installed and has the following configurations:
• Password hash synchronization is enabled.
• Synchronization is enabled for the LitwareAdmins OU only.
Users are assigned the roles shown in the following table.

Self-service password reset (SSPR) is enabled.
The Azure AD tenant has Security defaults enabled.
Problem Statements
Litware identifies the following issues:
• Admin1 cannot create conditional access policies.
• Admin4 receives an error when attempting to use SSPR.
• Users access new Office 365 service and feature updates before the updates are reviewed by Admin2.
Requirements
Planned Changes
Litware plans to implement the following changes:
• Implement Microsoft Intune.
• Implement Microsoft Teams.
• Implement Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
• Ensure that users can install Office 365 apps on their device.
• Convert all the Windows 10 Pro devices to Windows 10 Enterprise ES.
• Configure Azure AD Connect to sync the Montreal Users OU and the Seattle Users OU.
Technical Requirements
Litware identifies the following technical requirements:
• Administrators must be able to specify which version of an Office 365 desktop app will be available to users and to roll back to previous versions.
• Only Admin2 must have access to new Office 365 service and feature updates before they are released to the company.
• Litware users must be able to invite A. Datum users to participate in the following activities:
• Join Microsoft Teams channels.
• Join Microsoft Teams chats.
• Access shared files.
• Just in time access to critical administrative roles must be required.
• Microsoft 365 incidents and advisories must be reviewed monthly.
• Office 365 service status notifications must be sent to Admin2.
• The principle of least privilege must be used.
You are evaluating the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

HOTSPOT You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that uses Microsoft Defender for Office 365. You need to automate Attack simulation training for users when a phishing campaign is detected in real-time. Which type of automation should you use. and which condition should you configure for the Attack simulation training? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. 
HOTSPOT You have three devices enrolled in Microsoft Endpoint Manager as shown in the following table. 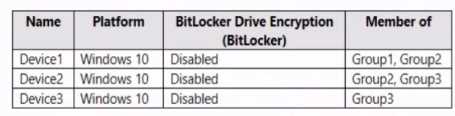 The device compliance policies in Endpoint Manager are configured as shown in the following table.
The device compliance policies in Endpoint Manager are configured as shown in the following table. 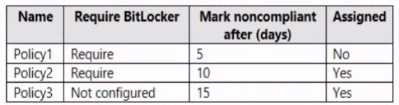 The device compliance policies have the assignments shown in the following table.
The device compliance policies have the assignments shown in the following table. 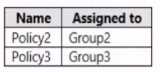 For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement Is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement Is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. 
HOTSPOT You need to meet the technical requirements and planned changes for Intune. What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. 
Case Study
Your organization is deploying Microsoft Intune to manage mobile devices and ensure corporate data security. The company wants to automatically enroll all Windows, iOS, and Android devices used by specific users into Intune as soon as they sign in with their Microsoft 365 credentials.
The IT department has already created Azure AD user groups and device groups to organize users and assets. According to the technical requirements, only selected users from a specific Azure AD group should be targeted for automatic enrollment in Intune. Other users should remain unaffected until the next phase of rollout.
To achieve this, you must configure the correct Intune setting that controls automatic enrollment behavior and then assign it to the appropriate Azure AD group.
HOTSPOT You need to configure automatic enrollment in Intune. The solution must meet the technical requirements. What should you configure, and to which group should you assign the configurations? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. 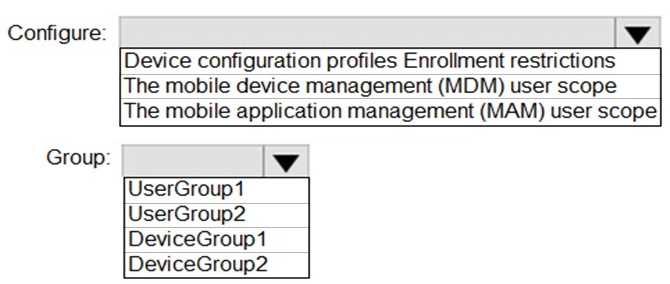
HOTSPOT As of March, how long will the computers in each office remain supported by Microsoft? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. 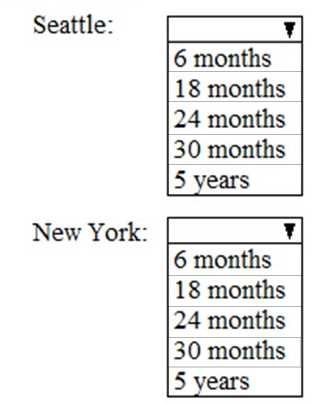
HOTSPOT You have a Microsoft 365 tenant that contains devices enrolled in Microsoft Intune. The devices are configured as shown in the following table. 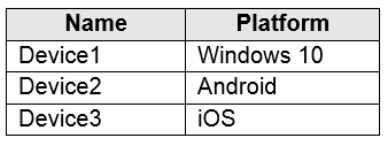 You plan to perform the following device management tasks in Microsoft Endpoint Manager: Deploy a VPN connection by using a VPN device configuration profile. Configure security settings by using an Endpoint Protection device configuration profile. You support the management tasks. What should you identify? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
You plan to perform the following device management tasks in Microsoft Endpoint Manager: Deploy a VPN connection by using a VPN device configuration profile. Configure security settings by using an Endpoint Protection device configuration profile. You support the management tasks. What should you identify? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. 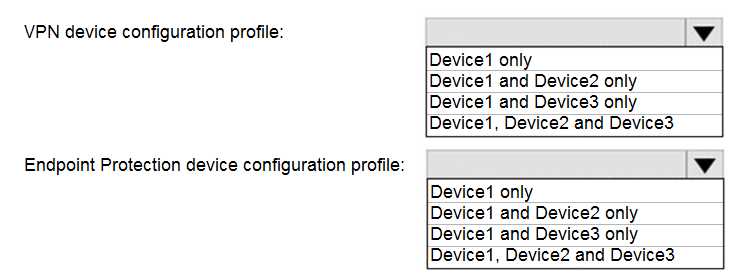
HOTSPOT You have an Azure subscription and an on-premises Active Directory domain. The domain contains 50 computers that run Windows 10. You need to centrally monitor System log events from the computers. What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. 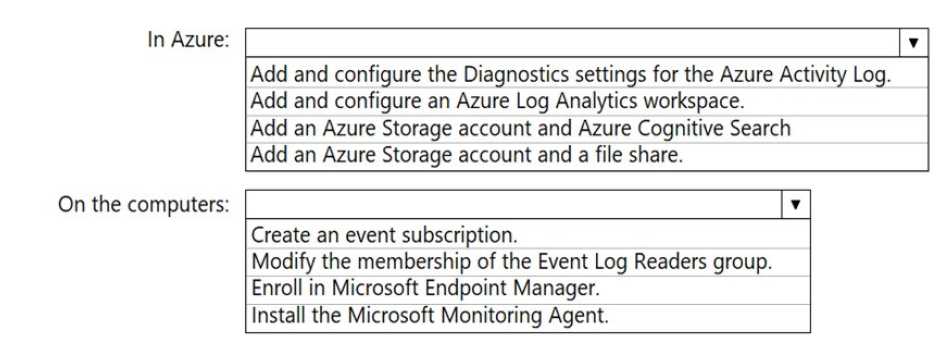
HOTSPOT You have three devices enrolled in Microsoft Endpoint Manager as shown in the following table. 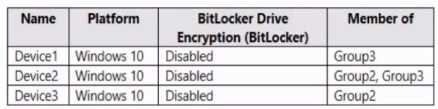 The device compliance policies in Endpoint Manager are configured as shown in the following table.
The device compliance policies in Endpoint Manager are configured as shown in the following table. 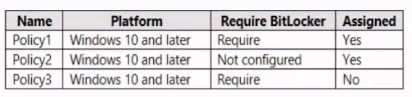 The device compliance policies have the assignments shown in the following table.
The device compliance policies have the assignments shown in the following table. 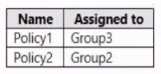 For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. 
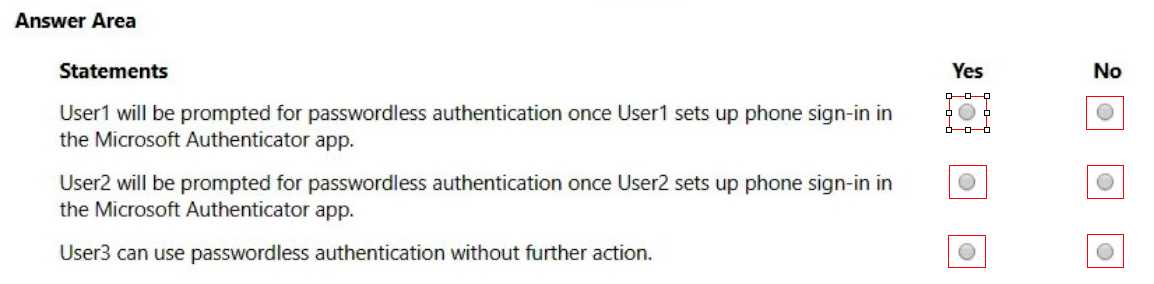
HOTSPOT You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that contains the users shown in the following table. 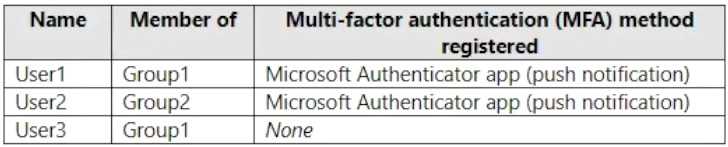 You configure the Microsoft Authenticator authentication method policy to enable passwordless authentication as shown in the following exhibit. Both User1 and User2 report that they are NOT prompted for passwordless sign-in in the Microsoft Authenticator app. For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
You configure the Microsoft Authenticator authentication method policy to enable passwordless authentication as shown in the following exhibit. Both User1 and User2 report that they are NOT prompted for passwordless sign-in in the Microsoft Authenticator app. For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.